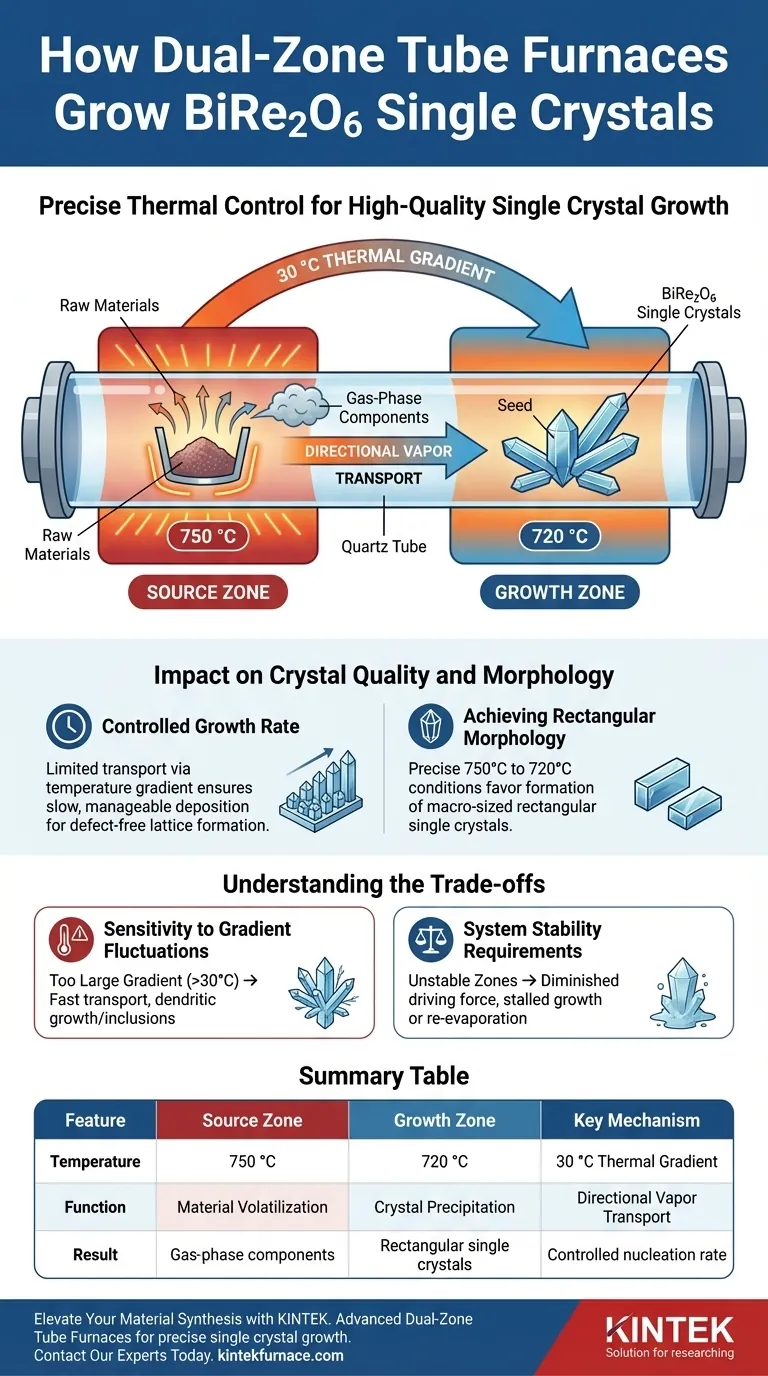
Dual-zone tube furnaces allow for the growth of BiRe2O6 single crystals by establishing a precise, stable temperature gradient between the raw material source and the crystallization area. Specifically, by maintaining the source zone at 750 °C and the growth zone at 720 °C, the furnace creates the thermodynamic conditions necessary to transport gas-phase components from the hot end to the cold end.
The core mechanism relies on a stable temperature differential to drive directional vapor transport. This specific gradient ensures that BiRe2O6 precipitates slowly at the lower temperature, resulting in high-quality, macro-sized rectangular single crystals rather than rapid, disordered solidification.

The Mechanics of Thermal Control
Establishing Independent Zones
The defining feature of a dual-zone furnace is the ability to control two distinct heating areas within the same quartz tube.
For BiRe2O6, the source zone is heated to 750 °C. This higher temperature causes the raw materials to volatilize or react, entering the gas phase.
Creating the Growth Environment
Simultaneously, the growth zone is strictly maintained at 720 °C.
This created "cold end" serves as the deposition site. The stability of this temperature is critical; if it fluctuates, the nucleation process can become erratic, leading to polycrystals rather than single crystals.
Driving Gas-Phase Transport
The 30 °C temperature difference acts as the physical driving force.
Thermodynamics dictates that gas-phase components move from the high-temperature zone to the low-temperature zone. This directional transport ensures a continuous supply of material to the crystallization front without mechanical intervention.
Impact on Crystal Quality and Morphology
Controlled Growth Rate
The primary reference emphasizes that BiRe2O6 must grow slowly.
A dual-zone furnace facilitates this by limiting the rate of transport via the temperature gradient. By keeping the differential at roughly 30 °C, the material is not dumped rapidly onto the seed; instead, it arrives at a manageable rate that allows the crystal lattice to form without defects.
Achieving Rectangular Morphology
The specific thermal environment of this setup yields a distinct crystal shape.
Under these precise conditions ($750^\circ\text{C} \to 720^\circ\text{C}$), BiRe2O6 organizes into macro-sized rectangular single crystals. This morphology is a direct indicator of a stable, unperturbed growth environment facilitated by the dual-zone configuration.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Gradient Fluctuations
While effective, this method is highly sensitive to the magnitude of the temperature gradient.
If the difference between zones is too large (e.g., significantly greater than 30 °C), the transport rate may become too fast, leading to dendritic growth or inclusions. Conversely, a gradient that is too shallow may result in no transport at all.
System Stability Requirements
The "dual-zone" capability implies complexity in control.
Both zones must remain stable relative to each other. If the source zone drifts lower or the growth zone drifts higher, the driving force diminishes, potentially stalling growth or causing re-evaporation of the grown crystal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a dual-zone tube furnace for this specific material, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is crystal size: Prioritize the long-term stability of the 750 °C / 720 °C setpoints to allow for extended growth periods without thermal fluctuation.
- If your primary focus is crystal purity: Ensure the temperature gradient is not exceeded, as aggressive transport rates often trap impurities or solvent agents within the crystal lattice.
Success in growing BiRe2O6 lies not just in heating the material, but in the precision of the thermal gap that drives its migration.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Source Zone | Growth Zone | Key Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 750 °C | 720 °C | 30 °C Thermal Gradient |
| Function | Material Volatilization | Crystal Precipitation | Directional Vapor Transport |
| Result | Gas-phase components | Rectangular single crystals | Controlled nucleation rate |
| Critical Factor | Thermal Stability | Precise Setpoint | Gradient consistency |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise crystal growth demands uncompromising thermal stability. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance heating solutions designed for the most rigorous laboratory standards.
Our Expertise Includes:
- Advanced Dual-Zone Tube Furnaces: Achieve the perfect temperature gradient for vapor transport and single crystal growth.
- Customizable Systems: From Muffle and Rotary to Vacuum and CVD systems, our equipment is tailored to your unique R&D requirements.
- Expert Manufacturing: Backed by industry-leading R&D to ensure long-term stability and precise control.
Whether you are growing BiRe2O6 or developing new semiconductor materials, KINTEK provides the reliability your research deserves.
Contact Our Experts Today to find the perfect furnace for your application.
Visual Guide
References
- Premakumar Yanda, Claudia Felser. Direct Evidence of Topological Dirac Fermions in a Low Carrier Density Correlated 5d Oxide. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202512899
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes a vertical tube furnace efficient and energy-saving? Unlock Superior Thermal Control & Cost Savings
- What is the specific role of a Tube Furnace in phosphate/graphene annealing? Unlock High-Performance Electrode Synthesis
- What are the different types of tube furnaces? Find Your Perfect High-Temp Solution
- What advanced features can be found in more elaborate tube furnaces? Unlock Precision and Versatility for Demanding Applications
- What are the safety and usability features of tube furnaces? Essential for Precise Material Processing
- What are the technical requirements for an industrial tube furnace for selective chlorination? Reach 1873 K with Precision
- How does the temperature control program of a tube furnace affect NiSSe nanocrystal formation? Optimize Your Synthesis
- What precautions should be taken when using a 70mm tube furnace? Ensure Safety and Precision in High-Temp Experiments



















