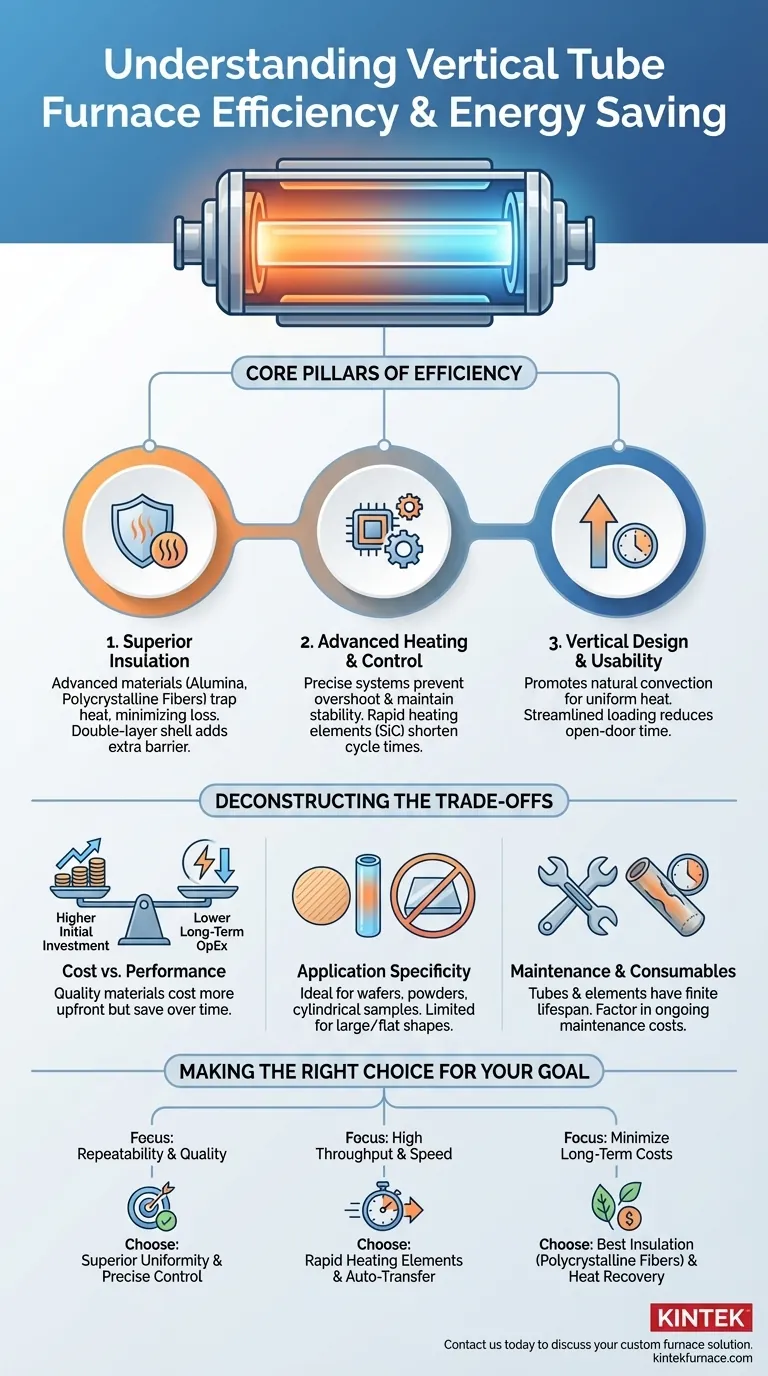
In short, a vertical tube furnace achieves its efficiency through three core pillars. These are superior thermal insulation that traps heat, advanced heating elements and control systems that apply energy precisely, and a design that ensures rapid, uniform heating to minimize wasted energy and time.
The central challenge in any high-temperature process is minimizing heat loss. A vertical tube furnace is not just a heating device; it's a meticulously designed system engineered to contain and control thermal energy with maximum efficiency, directly translating to lower operational costs and more reliable results.

Deconstructing Furnace Efficiency
A furnace's efficiency isn't the result of a single component but rather the synergy between its design, materials, and control systems. Understanding how these elements work together is key to appreciating its energy-saving capabilities.
The Foundation: Superior Insulation
Insulation is the first line of defense against energy waste. The goal is to keep the immense heat generated inside the furnace from escaping into the surrounding environment.
High-quality furnaces use advanced materials like alumina polycrystalline fibers or polycrystalline mullite fiber. These materials are lightweight, resist thermal shock, and have exceptional insulation properties. This dramatically reduces heat loss, allowing the furnace to maintain high temperatures with less continuous energy input.
Some designs also feature a double-layer furnace shell. This creates an air gap between the inner and outer walls, which acts as an additional layer of insulation, further minimizing thermal leakage.
The Engine: Advanced Heating & Control
How a furnace generates and manages heat is critical to its efficiency. It's not just about getting hot, but about getting hot smartly.
The vertical orientation of the furnace naturally promotes excellent temperature uniformity through convection. This even heat distribution ensures that the entire sample is processed consistently, shortening the required heating time and preventing energy from being wasted on "cold spots."
High-quality heating elements, such as those made from silicon carbide, enable very rapid heating rates. Reaching the target temperature quickly means the furnace runs for a shorter duration, directly cutting down on energy consumption for each cycle.
Finally, precise temperature control systems act as the furnace's brain. They prevent overshooting the target temperature and maintain stability with minimal fluctuation, ensuring that exactly the right amount of energy is used—no more, no less.
The Workflow: Design and Usability
The physical design of the furnace also plays an often-overlooked role in its overall efficiency.
The vertical orientation simplifies the loading and unloading of samples, making batch processing faster and more convenient. This streamlined workflow reduces the time the furnace door needs to be open, minimizing heat loss between cycles.
Furthermore, a compact footprint not only saves valuable lab space but also means there is less external surface area from which heat can escape, contributing subtly but surely to its thermal efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, vertical tube furnaces are not a universal solution. It's important to recognize their context and limitations.
Cost vs. Performance
The high-performance materials and advanced control systems that make these furnaces efficient also contribute to a higher initial purchase price. Cheaper furnaces often cut corners on insulation and element quality, leading to higher long-term operational costs that can quickly eclipse the initial savings.
Application Specificity
The tube design, while excellent for uniformity and atmosphere control, limits the size and shape of the samples that can be processed. It is ideal for wafers, powders, and cylindrical components but is unsuitable for large, flat, or irregularly shaped objects that would be better served by a box or muffle furnace.
Maintenance and Consumables
The furnace tube itself is often a consumable, especially when used at extreme temperatures or with reactive materials. Likewise, heating elements have a finite lifespan. These ongoing maintenance costs must be factored into the total cost of ownership.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace means aligning its features with your primary laboratory or production objective.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and quality: The superior temperature uniformity and precise control of a vertical tube furnace will deliver the most consistent and reliable results.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and speed: Look for a model with high-quality heating elements for rapid heating cycles and consider features like automatic transfer systems to streamline batch processing.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operational costs: Prioritize models with the best insulation materials (like polycrystalline fibers) and efficient heat recovery systems to ensure maximum energy savings.
Ultimately, investing in a well-engineered vertical tube furnace is an investment in efficiency, control, and long-term value.
Summary Table:
| Key Efficiency Pillar | How It Saves Energy |
|---|---|
| Superior Insulation | Advanced materials like alumina fibers minimize heat loss, reducing energy input needed to maintain temperature. |
| Advanced Heating & Control | Precise temperature control and uniform heating prevent energy waste on overshooting or 'cold spots'. |
| Vertical Design | Promotes natural convection for even heating and a compact footprint to minimize heat loss surface area. |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and reduce energy costs?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our vertical tube furnaces are engineered with superior insulation and precise control systems to deliver maximum energy savings and reliable performance for your specific applications.
Contact us today to discuss how our deep customization capabilities can create a furnace solution that precisely meets your unique experimental requirements and boosts your productivity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















