Vertical tube furnaces ensure operational safety and process reliability through a combination of automated electronic safeguards and high-integrity material construction. Key safety features include integrated overheating and disconnection protection systems that automatically cut power during abnormal conditions. Reliability is anchored in the use of high-quality furnace tubes made from materials like quartz or ceramic, which resist extreme temperatures and chemical corrosion for long-term, stable performance.
The core principle behind a vertical tube furnace's safety and reliability is not just a single feature, but its entire design philosophy. The vertical orientation, automated controls, and robust materials work in concert to provide a stable, uniform heating environment that protects both the operator and the integrity of the process.
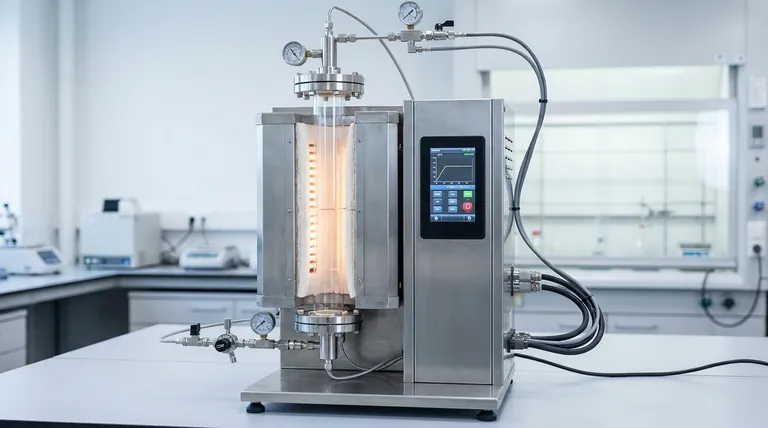

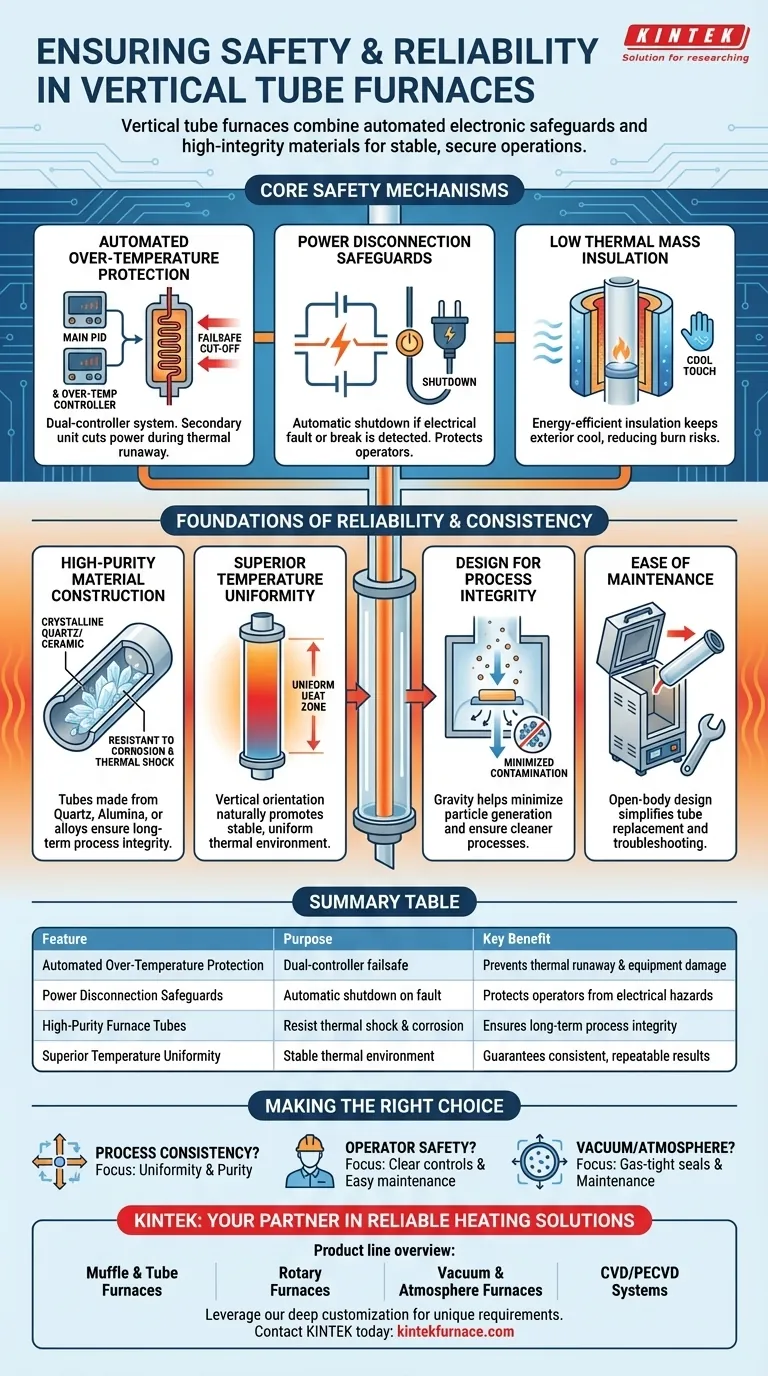
Core Safety Mechanisms
A well-designed vertical tube furnace prioritizes preventing failures before they occur. This is achieved through redundant and automated control systems that monitor the furnace's state at all times.
Automated Over-Temperature Protection
The primary safety system is a dual-controller setup. A main microprocessor PID controller manages the target temperature, while a separate over-temperature controller acts as a failsafe. If the main controller fails or a thermal runaway event begins, this secondary controller will automatically cut power to the heating elements, preventing catastrophic damage to the equipment and the sample.
Power Disconnection Safeguards
The furnace is equipped with disconnection protection. This function immediately shuts down the power supply if an electrical fault or a break in the connection is detected. This crucial feature protects operators from electrical hazards and prevents further damage to the furnace's electronics.
Low Thermal Mass Insulation
These furnaces utilize energy-efficient, low thermal mass insulation. While its main purpose is to enable rapid heating and cooling cycles, it also serves as a safety feature. This insulation keeps the external surface of the furnace cooler during operation, reducing the risk of accidental burns for personnel working nearby.
Foundations of Reliability and Consistency
Reliability in a furnace is defined by its ability to produce the same result time and time again over a long operational life. This consistency is built into the vertical furnace's physical design and the materials used to construct it.
High-Purity Material Construction
The furnace tube is the heart of the system, and its material is critical. Tubes made from high-purity quartz, alumina ceramic, or specialized metal alloys provide excellent resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. This material integrity prevents the tube from degrading and contaminating the sample, ensuring the long-term reliability of experimental results.
Superior Temperature Uniformity
The vertical orientation naturally promotes excellent temperature uniformity along the heated length of the tube. Gravity-driven convection is more symmetrical in a vertical column, resulting in a stable and consistent thermal environment. This uniformity is essential for reliable outcomes, especially in sensitive processes like crystal growth or thin-film deposition.
Design for Process Integrity
Compared to horizontal models, vertical furnaces are less prone to issues like particle generation and non-uniform film thicknesses. The vertical setup uses gravity to its advantage, minimizing the chances of contaminants settling on sample surfaces and ensuring a cleaner processing environment.
Ease of Maintenance
Many vertical furnaces feature an open-type body design, which allows for the straightforward replacement of the furnace tube. The relative simplicity of a single-zone furnace also makes it easier to troubleshoot and maintain. This focus on serviceability is key to ensuring long-term operational reliability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the design of a vertical tube furnace involves specific considerations that are important to understand for any application.
Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone Simplicity
Most standard models are single-zone furnaces, which provide a single, highly uniform heated area. This design is simple, cost-effective, and reliable. However, it lacks the ability to create complex temperature gradients, which requires a more advanced and expensive multi-zone furnace.
Atmosphere Control Requires Precision
Achieving a controlled atmosphere or vacuum requires optional gas-tight end seals and flanges. While these accessories enable advanced processing, they add complexity. The reliability of the seal is dependent on proper installation and regular maintenance to prevent leaks, which could compromise the process.
Sample Loading and Positioning
The vertical design simplifies batch loading and unloading for many sample types, like crucibles or wafer boats. However, for irregularly shaped samples or processes that require precise horizontal positioning, securing the sample inside the vertical tube can be more complex than simply placing it in a horizontal furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate furnace configuration depends entirely on the demands of your specific process.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and repeatability: Prioritize a model with documented temperature uniformity and a high-purity tube material (like quartz) suitable for your application.
- If your primary focus is operator safety and ease of use: Look for models with clear, independent over-temperature controllers and a design that simplifies maintenance, such as an open-type body for easy tube access.
- If your primary focus is working under a vacuum or controlled atmosphere: Ensure you select the correct gas-tight flange system and understand the maintenance required to guarantee a perfect seal for reliable, leak-free operation.
Ultimately, understanding how these safety and reliability features are integrated allows you to choose a furnace that will perform as a dependable and safe tool for your work.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Over-Temperature Protection | Dual-controller failsafe | Prevents thermal runaway and equipment damage |
| Power Disconnection Safeguards | Automatic shutdown on fault | Protects operators from electrical hazards |
| High-Purity Furnace Tubes (Quartz, Alumina) | Resist thermal shock & corrosion | Ensures long-term process integrity and sample purity |
| Superior Temperature Uniformity | Stable thermal environment from vertical design | Guarantees consistent, repeatable experimental results |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution that prioritizes both safety and unwavering reliability?
At KINTEK, we combine exceptional R&D with in-house manufacturing to deliver advanced, reliable furnace solutions. Our vertical tube furnaces are engineered with the robust safety features and high-integrity construction detailed above, ensuring long-term, stable performance for your most critical processes.
Our capabilities extend to a full range of laboratory furnaces, including:
- Muffle & Tube Furnaces
- Rotary Furnaces
- Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces
- CVD/PECVD Systems
Leverage our strong deep customization capability to tailor a furnace that precisely meets your unique experimental and safety requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our reliable heating solutions can enhance your lab's safety and productivity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















