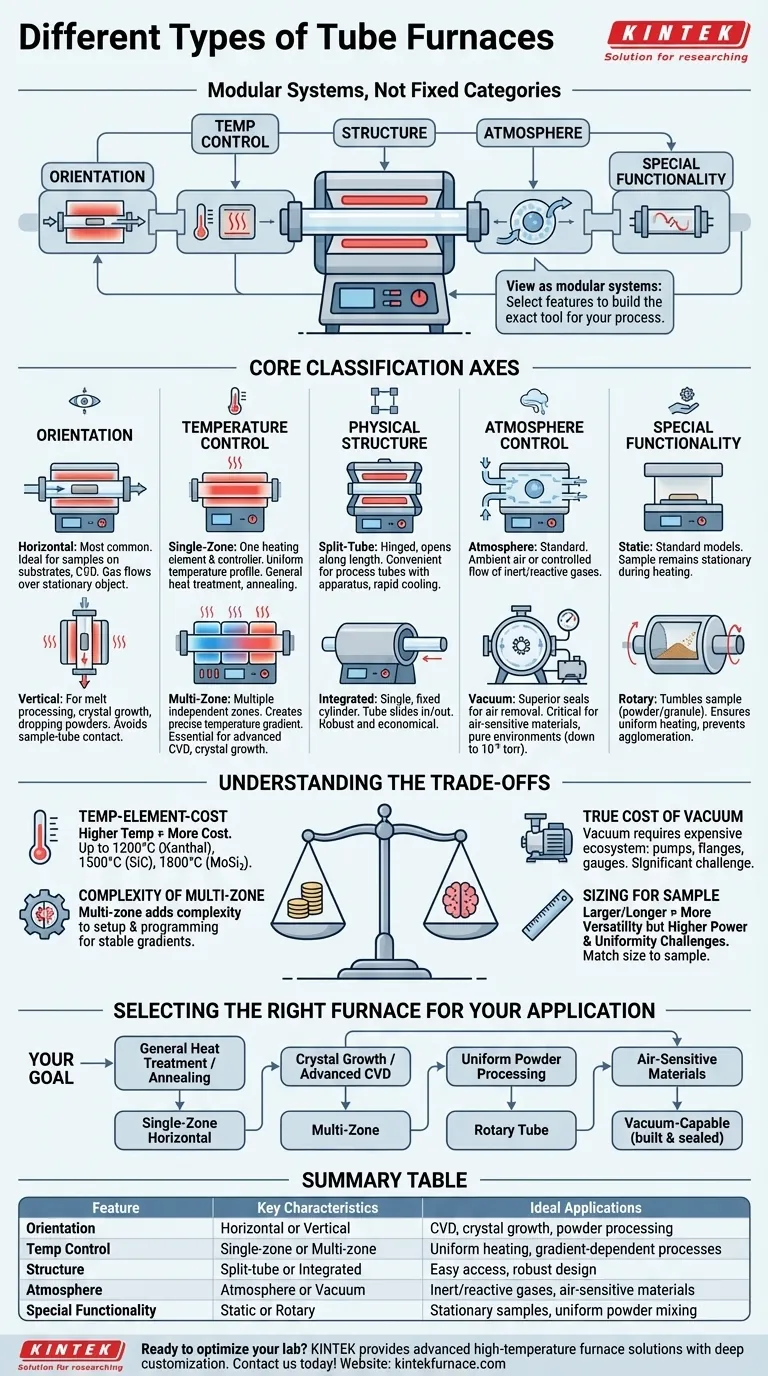
At its core, a tube furnace is not defined by a single "type" but by a combination of independent design features. The primary classifications are based on physical orientation (horizontal/vertical), structure (split/integrated), temperature control (single/multi-zone), and atmospheric capability (atmosphere/vacuum).
The key to understanding tube furnaces is to stop thinking in terms of rigid categories. Instead, view them as modular systems where you select features—like orientation, temperature zones, and vacuum capability—to build the exact tool required for your specific process.
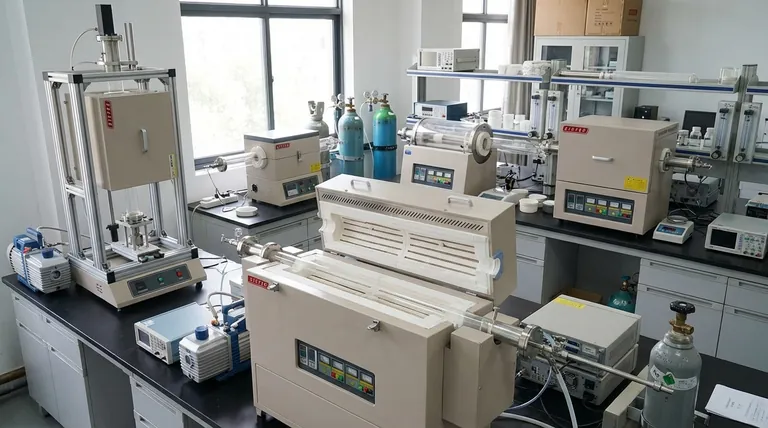

Understanding the Core Classification Axes
A single furnace is often described by several of these characteristics simultaneously. For example, you might use a "three-zone vertical split-tube vacuum furnace." Each term describes a critical feature that dictates its function.
Orientation: Vertical vs. Horizontal
Horizontal furnaces are the most common configuration. They are ideal for processing samples on substrates, in boats, or for applications like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) where gas flows over a stationary object.
Vertical furnaces are used for specialized applications. They are excellent for processes where you want to avoid contact between your sample and the tube wall, such as processing melts, growing crystals, or dropping powdered samples through the hot zone.
Temperature Control: Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone
Single-zone furnaces have one set of heating elements and one controller. They are designed to create a single, uniform temperature profile across the center of the heated length and are perfect for general-purpose heat treatment or annealing.
Multi-zone furnaces (e.g., two-zone, three-zone) have multiple, independently controlled heating areas. This allows you to create a precise temperature gradient along the tube length. This capability is essential for advanced processes like CVD or crystal growth, where different temperature stages are required.
Physical Structure: Split-Tube vs. Integrated
Split-tube furnaces are hinged and can be opened along their length. This design is incredibly convenient for placing or removing a process tube that already has end flanges or other apparatus attached, or for rapid cooling.
Integrated furnaces (also called solid-tube) are a single, fixed cylinder. The process tube must be slid in and out from the ends. They are often more robust and can be more economical.
Atmosphere Control: Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
Atmosphere furnaces are the standard. They can operate in ambient air or be sealed with end caps to allow for a controlled flow of inert or reactive gases.
Vacuum furnaces are specifically designed with superior seals and flanges to allow the removal of atmospheric gases. They are critical for processing air-sensitive materials or for applications requiring a pure environment. These systems can achieve various vacuum levels, with high-end models reaching down to 10⁻⁵ torr.
Special Functionality: Static vs. Rotary
Static furnaces are the standard models discussed above, where the sample remains stationary during heating.
Rotary tube furnaces are designed to tumble the sample, typically a powder or granule, during the heating process. The constant mixing ensures every particle is heated uniformly, prevents agglomeration, and improves gas-solid reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing features is a matter of balancing performance, complexity, and cost. Each decision has direct implications for your work.
The Temperature-Element-Cost Relationship
Higher maximum temperatures demand more advanced and expensive heating elements.
- Up to 1200°C: Typically uses Kanthal (FeCrAl) elements.
- Up to 1500°C: Requires Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements.
- Up to 1800°C: Necessitates **Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) ** elements.
Choosing a furnace with a much higher temperature range than you need will result in unnecessary expense.
The Complexity of Multi-Zone Control
While powerful, multi-zone furnaces add complexity to your process setup and programming. Achieving a stable, precise temperature gradient requires more expertise than simply setting a single uniform temperature.
The True Cost of Vacuum
A vacuum-capable furnace is more than just the furnace itself. It requires an ecosystem of expensive components, including vacuum pumps, specialized flanges, and pressure gauges. Achieving and maintaining high vacuum is a significant technical challenge that should not be underestimated.
Sizing the Furnace for Your Sample
A larger tube diameter or a longer hot zone provides more versatility. However, it also leads to higher power consumption and can make achieving perfect temperature uniformity across the entire zone more challenging. It is most efficient to match the furnace size to your typical sample dimensions.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your ultimate goal dictates the necessary combination of features.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment or annealing: A single-zone horizontal furnace is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is crystal growth or advanced CVD: A multi-zone furnace is non-negotiable for creating the required temperature gradients.
- If your primary focus is uniform processing of powders: A rotary tube furnace is specifically designed to solve the challenges of clumping and uneven heating.
- If your primary focus is working with air-sensitive materials: You must select a furnace built and sealed for vacuum operation from the ground up.
By understanding these fundamental design choices, you can specify a tube furnace not as a simple product, but as a precise instrument tailored to your specific scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Key Characteristics | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation | Horizontal or Vertical | CVD, crystal growth, powder processing |
| Temperature Control | Single-zone or Multi-zone | Uniform heating, gradient-dependent processes |
| Physical Structure | Split-tube or Integrated | Easy access, robust design |
| Atmosphere Control | Atmosphere or Vacuum | Inert/reactive gases, air-sensitive materials |
| Special Functionality | Static or Rotary | Stationary samples, uniform powder mixing |
Ready to optimize your lab with a custom tube furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes with tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of individually temperature-controlled zones in multi-zone furnaces? Unlock Precision Thermal Gradients
- What steps are involved in the installation of a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Precision and Safety for Your Lab
- How do multi zone tube furnaces improve laboratory efficiency? Boost Throughput with Parallel Processing
- What are the benefits of integrating multiple heating zones in a tube furnace? Unlock Precise Thermal Control
- What safety precautions should be followed when operating a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Lab Operations



















