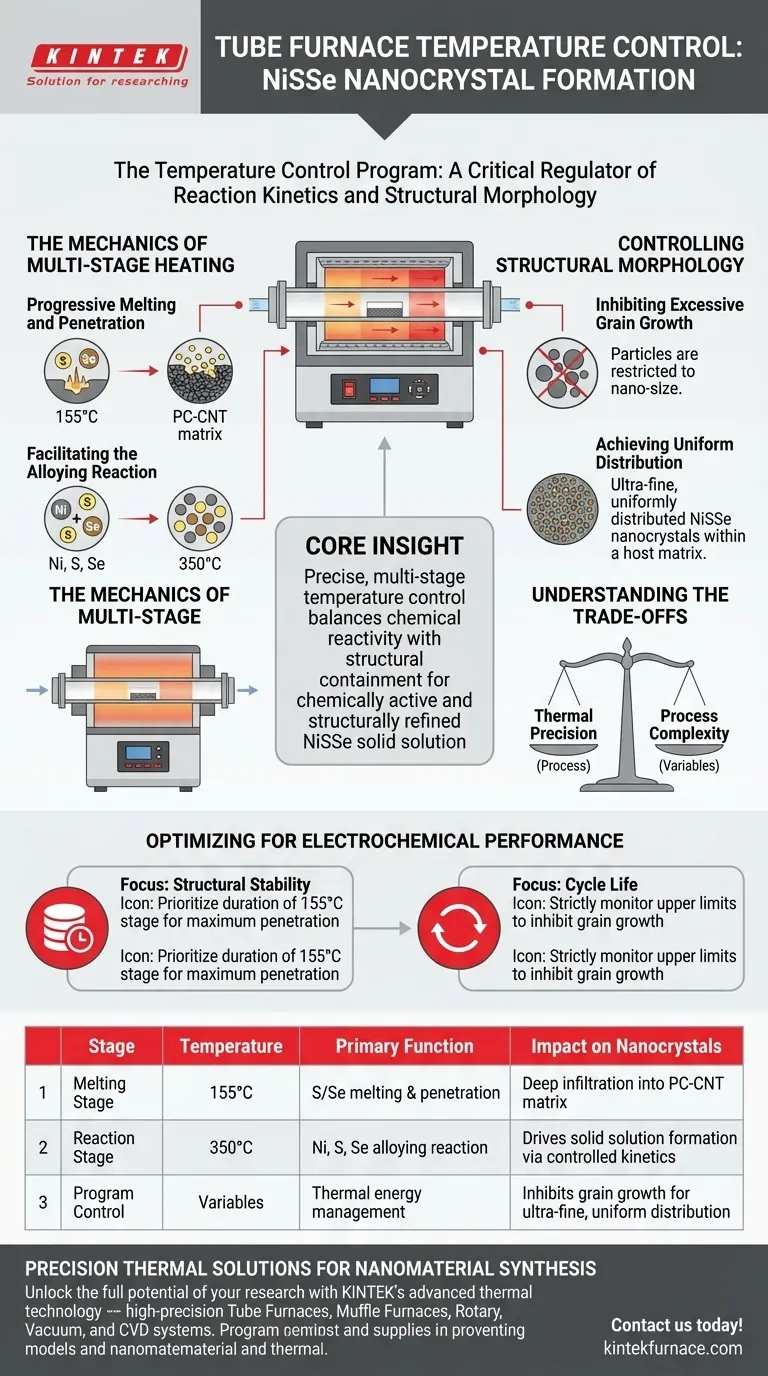
The temperature control program acts as a critical regulator of reaction kinetics and structural morphology. By implementing a multi-stage heating profile—specifically targeting plateaus such as 155 °C and 350 °C—the tube furnace ensures the progressive melting and penetration of sulfur and selenium powders. This staged approach allows for a complete alloying reaction with nickel while simultaneously preventing the nanocrystals from growing too large.
Core Insight: Precise, multi-stage temperature control is the mechanism that balances chemical reactivity with structural containment. It enables the formation of a NiSSe solid solution that is both chemically active and structurally refined, which is essential for surviving the physical stress of electrochemical cycling.

The Mechanics of Multi-Stage Heating
Progressive Melting and Penetration
A standard, single-step heating process often leads to uneven reaction rates. By utilizing a multi-stage program, the furnace allows sulfur and selenium to melt gradually.
This controlled melting ensures that these reactants can thoroughly penetrate the porous carbon nanotube (PC-CNT) matrix before the primary reaction begins. This deep infiltration is necessary for uniform material synthesis.
Facilitating the Alloying Reaction
Once the reactants are properly dispersed, the temperature is elevated to the reaction stage (e.g., 350 °C).
This higher temperature tier drives the alloying reaction between the nickel, sulfur, and selenium. Because the reactants were pre-distributed during the lower temperature stage, the resulting reaction is consistent throughout the material.
Controlling Structural Morphology
Inhibiting Excessive Grain Growth
One of the most significant risks in nanocrystal synthesis is the tendency for particles to aggregate and grow too large.
The precise temperature program restricts this behavior. By controlling the thermal energy input, the process inhibits excessive grain growth, ensuring the particles remain in the "nano" regime.
Achieving Uniform Distribution
The outcome of this controlled process is the formation of ultra-fine NiSSe nanocrystals.
These crystals are not only small but are also uniformly distributed within the host matrix. This uniformity is a direct result of the exact temperature management preventing hot spots or uneven reaction zones.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Precision vs. Process Complexity
While a multi-stage program yields superior results, it introduces variables that must be strictly managed.
If the dwell time at the melting stage (155 °C) is too short, penetration into the PC-CNT matrix will be incomplete, leading to surface agglomeration. Conversely, if the ramp rate to the alloying stage (350 °C) is uncontrolled, you risk overriding the grain growth inhibition mechanisms.
The Cost of Thermal Instability
Without precise control, the "solid solution" phase may separate or form irregular clusters.
This lack of uniformity degrades the material's ability to accommodate volume expansion later. The "ultra-fine" structure created by the program is what provides the mechanical buffer during electrochemical charge and discharge cycles.
Optimizing for Electrochemical Performance
To leverage this temperature control for specific outcomes, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability: Prioritize the duration of the lower-temperature stage (155 °C) to ensure maximum penetration into the porous matrix before reaction.
- If your primary focus is Cycle Life: strictly monitor the upper-temperature limits to inhibit grain growth, as smaller nanocrystals better withstand the volume expansion of charging cycles.
The effectiveness of your NiSSe material is determined not just by the ingredients, but by the thermal architecture used to assemble them.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Temperature | Primary Function | Impact on Nanocrystals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melting Stage | 155 °C | Sulfur/Selenium melting & penetration | Ensures deep infiltration into the PC-CNT matrix |
| Reaction Stage | 350 °C | Ni, S, Se alloying reaction | Drives solid solution formation via controlled kinetics |
| Program Control | Variables | Thermal energy management | Inhibits grain growth for ultra-fine, uniform distribution |
Precision Thermal Solutions for Nanomaterial Synthesis
Unlock the full potential of your research with KINTEK’s advanced thermal technology. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-precision Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific multi-stage heating requirements.
Whether you are synthesizing NiSSe nanocrystals or developing next-generation electrochemical materials, our systems provide the thermal stability and ramp-rate accuracy needed to prevent grain growth and ensure material uniformity.
Ready to elevate your material performance? Contact us today to discuss your unique needs with our technical specialists!
Visual Guide
References
- Hyo Yeong Seo, Gi Dae Park. Engineering Porous Carbon Nanotube Microspheres with Nickel Sulfoselenide Nanocrystals for High‐Performance Potassium‐Ion Batteries: Electrochemical Mechanisms and Cycling Stability. DOI: 10.1002/sstr.202500222
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What metallurgical processes benefit from tube furnaces? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment and Material Control
- What materials are commonly used for furnace tube construction and why? Choose the Right Tube for Your Lab's Needs
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Material Processing
- How does the design of tube furnaces ensure uniform heating? Master Precision with Multi-Zone Control
- What applications is a Split Tube Furnace (Single Zone) suitable for? Ideal for Uniform Heating and Easy Access
- Why is a nitrogen atmosphere required in a high-temperature tube furnace during the preparation of Co-HCC nanoparticles?
- What is the basic function of a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Precision Thermal Processing for Material Synthesis
- How does a dual-temperature zone tube furnace contribute to the carbonization of biomass? Precise Material Engineering



















