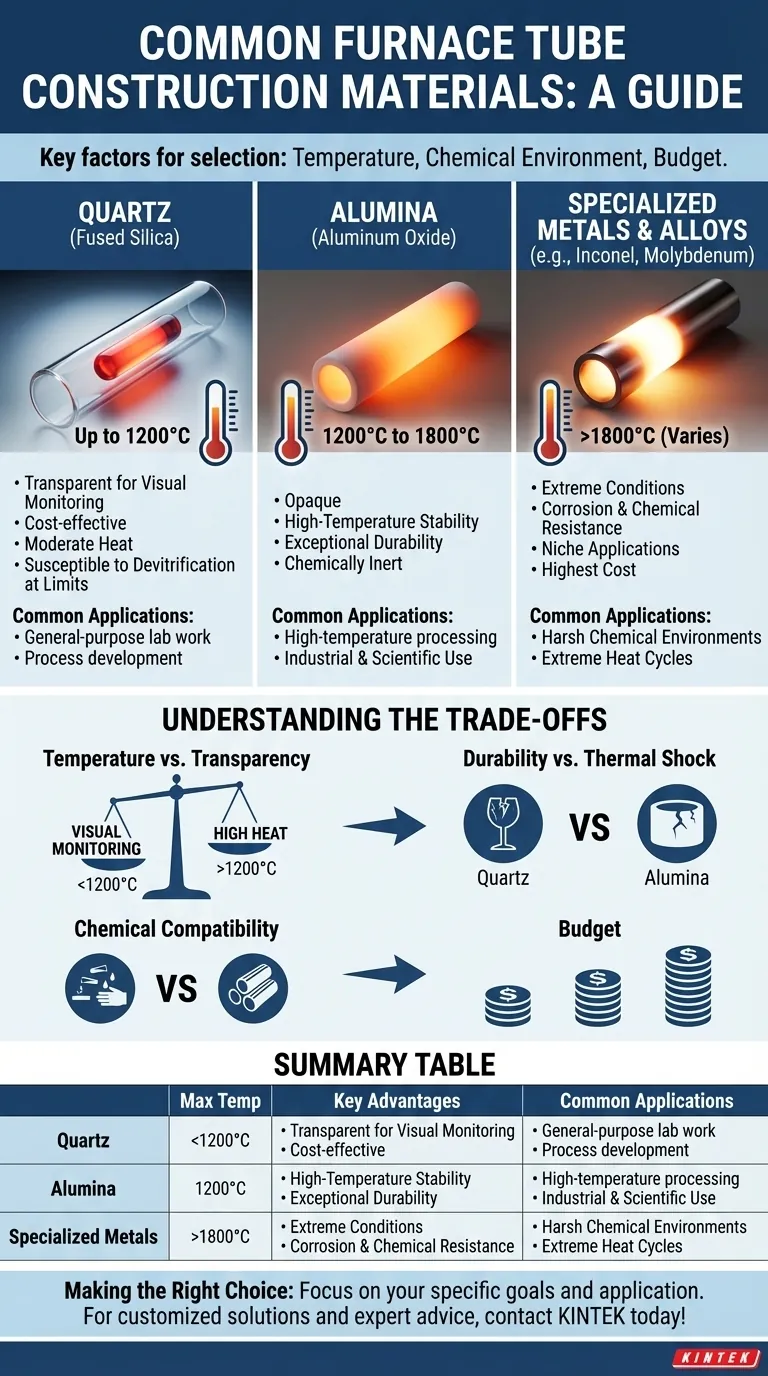
For furnace tubes, the most common materials are quartz and alumina. The selection is driven by the required operating temperature, the chemical environment of the process, and budget. These materials offer an excellent balance of high-temperature stability, chemical inertness, and the ability to withstand thermal stress, ensuring both efficient performance and operational safety.
The choice of a furnace tube material is a critical engineering decision that balances three factors: the maximum operating temperature, the need for chemical resistance, and the material's physical durability against thermal shock. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for a specific application.
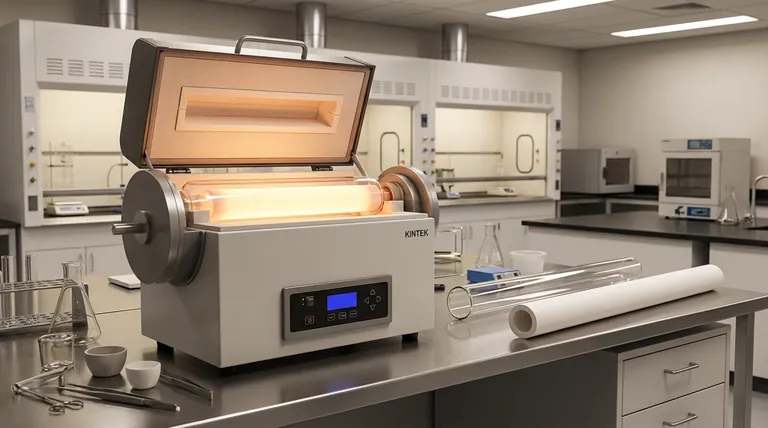

A Breakdown of Primary Tube Materials
The material of your furnace tube directly dictates the operational limits and longevity of your setup. The two most dominant choices, quartz and alumina, serve distinct temperature ranges and use cases.
Quartz: The Standard for Moderate Temperatures
Quartz is a form of high-purity fused silica, valued for its optical clarity and excellent thermal properties at moderate temperatures. It is often the default choice for general-purpose applications.
The primary advantage of quartz is its transparency, allowing for direct visual observation of the process inside the furnace. This is invaluable for research and process development.
It is a cost-effective option suitable for temperatures up to approximately 1200°C. However, it is more susceptible to devitrification (becoming brittle and opaque) with prolonged use at its upper temperature limits.
Alumina: The Workhorse for High Temperatures
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃) is a high-performance ceramic known for its exceptional durability and stability at extreme temperatures.
It is the standard for applications requiring temperatures from 1200°C up to 1800°C. Its robust structure ensures a long service life even with repeated heating and cooling cycles.
Unlike quartz, alumina is opaque. Its primary strengths are superior high-temperature performance and excellent chemical inertness, making it reliable for demanding industrial and scientific processes.
Specialized Metals & Alloys: For Extreme Conditions
In certain highly specific scenarios, specialized metals or superalloys are required. These are custom solutions for processes that exceed the capabilities of ceramics.
Materials like Inconel (a nickel-chromium superalloy), molybdenum, or tungsten are used for their unique properties. They may be chosen for extreme temperature resistance or for their ability to withstand highly corrosive or reactive chemical environments where even alumina would fail.
These materials are significantly more expensive and are reserved for niche applications where their specific performance characteristics are non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace tube is not just about picking the one that can handle the most heat. It involves a series of critical trade-offs that impact cost, usability, and the lifespan of the component.
Temperature vs. Transparency
This is the most fundamental trade-off. If you need to visually monitor your process, you are limited to a quartz tube and its corresponding temperature ceiling of ~1200°C. For any process above this temperature, you must use an opaque material like alumina.
Durability vs. Thermal Shock
Alumina is significantly more durable and resistant to the stress of repeated heat cycles. Quartz, while strong, is more prone to cracking if subjected to rapid temperature changes (thermal shock), especially after extended use.
Chemical Compatibility
While both quartz and alumina are highly inert, they are not universally immune. Highly alkaline or corrosive environments, particularly at high temperatures, may require the use of specialized and costly metal tubes like molybdenum to prevent the tube from being etched or compromised.
Budget
Cost is always a factor. Quartz represents the most economical option for a wide range of applications. Alumina is a moderate investment that provides a significant leap in performance and durability. Superalloys and refractory metals are a major expense, justified only by extreme process requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your application's specific goals should guide your material selection.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work under 1200°C: Choose quartz for its cost-effectiveness and invaluable transparency.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing (1200°C to 1800°C): Alumina is the necessary choice for its superior thermal stability and long-term durability.
- If your primary focus is working with highly corrosive materials or extreme heat cycles: You must investigate a specialized metal or superalloy tube designed for your specific chemical and thermal load.
Ultimately, understanding these material properties empowers you to select a furnace tube that ensures both the success and safety of your work.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Advantages | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Up to 1200°C | Transparent, cost-effective, good thermal properties | General-purpose lab work, processes requiring visual observation |
| Alumina | 1200°C to 1800°C | High-temperature stability, durable, chemically inert | High-temperature processing, industrial and scientific applications |
| Specialized Metals (e.g., Inconel, Molybdenum) | Varies, often >1800°C | Extreme temperature and corrosion resistance | Niche applications with harsh chemical environments or extreme heat |
Struggling to select the perfect furnace tube for your unique lab requirements? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're working with quartz, alumina, or specialized metals, we can help you achieve precise temperature control, chemical inertness, and durability for efficient and safe operations. Contact us today to discuss how our customized furnace tubes can enhance your laboratory's performance and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?



















