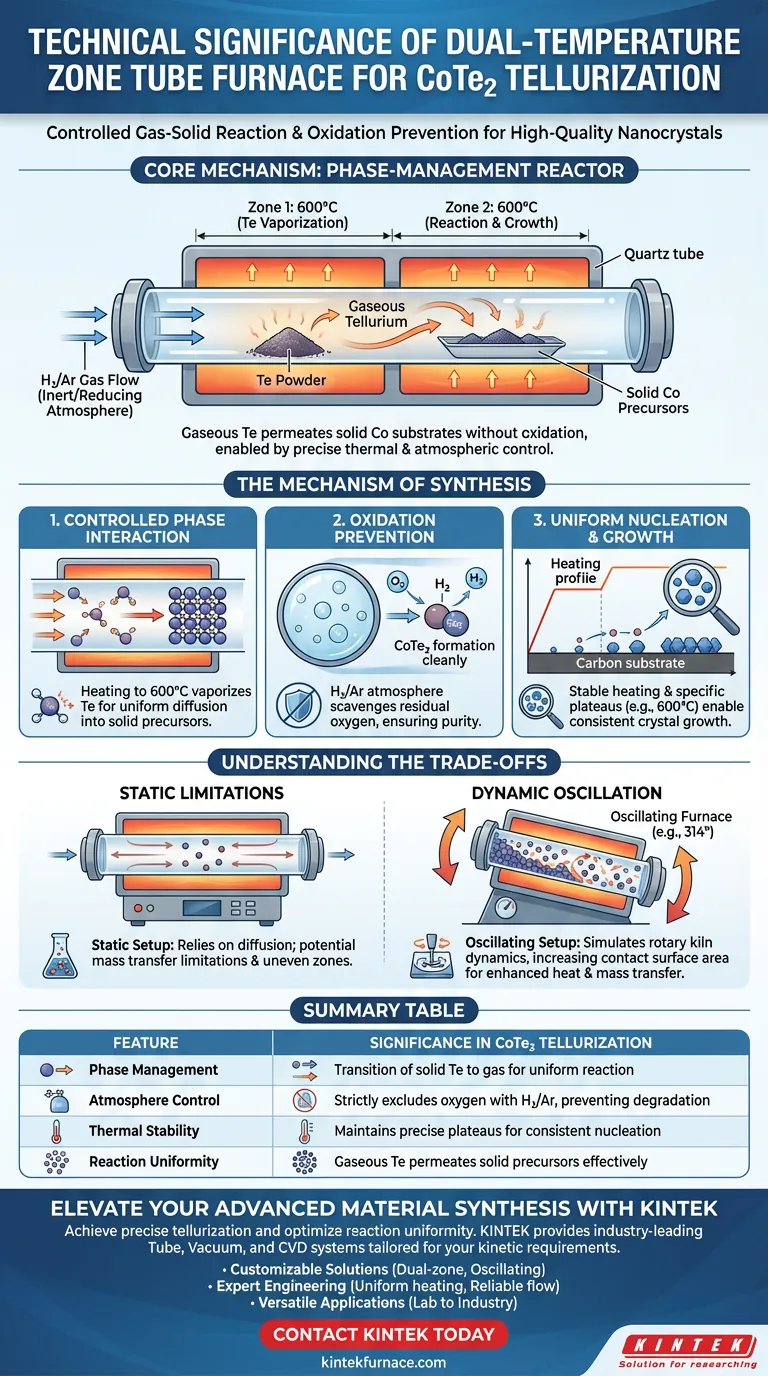
The technical significance of using a tube furnace for CoTe2 tellurization lies in its ability to facilitate a controlled gas-solid reaction while strictly excluding oxygen. By maintaining a reducing atmosphere and precise thermal conditions, the furnace enables the vaporization of tellurium to react uniformly with solid-phase metal precursors.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace functions as a phase-management reactor, allowing gaseous tellurium to permeate and react with solid cobalt substrates without oxidation. This precise control over atmosphere and temperature is the critical factor in achieving the uniform nucleation and growth required for high-quality CoTe2 nanocrystals.

The Mechanism of Synthesis
Controlled Phase Interaction
The primary challenge in CoTe2 synthesis is ensuring thorough contact between reactants that exist in different states.
The tube furnace addresses this by heating the environment to reaction temperatures (e.g., 600 °C).
At this temperature, the tellurium powder transitions into a gaseous phase. This vapor is then able to diffuse effectively into the solid-phase metal precursors, creating a complete and uniform reaction interface.
Oxidation Prevention
Both cobalt and tellurium are susceptible to oxidation at high temperatures, which would degrade the purity of the final material.
The tube furnace provides a sealed environment for a strictly controlled inert or reducing atmosphere, typically a mixture of Hydrogen and Argon (H2/Ar).
This atmosphere scavenges residual oxygen, ensuring that the CoTe2 formation proceeds without the inclusion of unwanted oxides.
Uniform Nucleation and Growth
The quality of the final nanocrystals depends heavily on the stability of the reaction environment.
By strictly managing the heating rate and holding the reaction at a specific plateau (such as 600 °C for 2 hours), the furnace ensures consistent kinetic energy for the reaction.
This thermal stability facilitates uniform nucleation, allowing CoTe2 nanocrystals to grow evenly within the carbon substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Static vs. Dynamic Limitations
While a standard laboratory tube furnace offers excellent atmosphere control, a static setup relies primarily on gas diffusion for mixing.
In static configurations, mass transfer limitations can occur, potentially leading to uneven reaction zones if the gas flow is not perfectly optimized.
The Role of Mechanical Mixing
As noted in advanced configurations, an oscillating tube furnace can mitigate these static limitations.
By employing large-angle reciprocating movements (e.g., 314 degrees), an oscillating furnace simulates the dynamics of an industrial rotary kiln.
This movement significantly increases the contact surface area between powders and reactive gases, enhancing heat transfer efficiency beyond what a static dual-zone or single-zone furnace can achieve alone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your synthesis, align your furnace configuration with your specific technical requirements:
- If your primary focus is material purity: Prioritize a setup with precise H2/Ar atmosphere controls to strictly prevent oxidation during the high-temperature gas-solid reaction.
- If your primary focus is reaction uniformity: Ensure the heating profile allows sufficient time (e.g., 2 hours) for the gaseous tellurium to fully permeate the solid precursor structure.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Consider an oscillating furnace configuration to enhance the mixing kinetics and heat transfer between the solid and gaseous phases.
The success of CoTe2 tellurization ultimately depends on the precise management of the phase transition between solid precursors and gaseous tellurium.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Significance in CoTe2 Tellurization |
|---|---|
| Phase Management | Enables transition of solid Te to gas for uniform reaction with cobalt |
| Atmosphere Control | Uses H2/Ar mixtures to strictly exclude oxygen and prevent degradation |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains precise plateaus (e.g., 600°C) for consistent nucleation and growth |
| Reaction Uniformity | Allows gaseous tellurium to permeate solid precursors effectively |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise tellurization requires the perfect balance of atmosphere control and thermal stability. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of CoTe2 synthesis and other advanced chemical vapor deposition processes.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Customizable Solutions: From dual-zone setups to oscillating tube furnaces, we tailor equipment to your specific kinetic requirements.
- Expert Engineering: Our R&D-backed manufacturing ensures uniform heating and reliable gas-flow management.
- Versatile Applications: Ideal for lab-scale research and industrial material production.
Ready to optimize your reaction uniformity and material purity? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique laboratory needs with our technical experts.
Visual Guide
References
- Qinghua Li, Shaoming Huang. Efficient Polytelluride Anchoring for Ultralong-Life Potassium Storage: Combined Physical Barrier and Chemisorption in Nanogrid-in-Nanofiber. DOI: 10.1007/s40820-023-01318-9
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory tube furnace contribute to the continuity and quality of Mn3O4 arrays? Master Atomic Stitching
- How do researchers utilize the heating elements in tubular furnaces? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials Research
- What is the function of a linear actuated tube furnace system? Simulating Fire Dynamics for Precise Emission Studies
- What are the objectives of using a tube furnace for dual-layer nanocomposite heat treatment? Maximize Coating Stability
- How does a horizontal tube furnace facilitate the single-step annealing of BZSM nanophosphors? Expert Thermal Control
- How do high-temperature laboratory tube furnaces ensure environmental stability? Precision Thermal Reduction Tips
- What is the role of a laboratory tube annealing furnace in LiMn2O4 coatings? Expert Post-Treatment Insights
- What additional features might a split tube furnace have? Boost Your Lab's Precision and Control



















