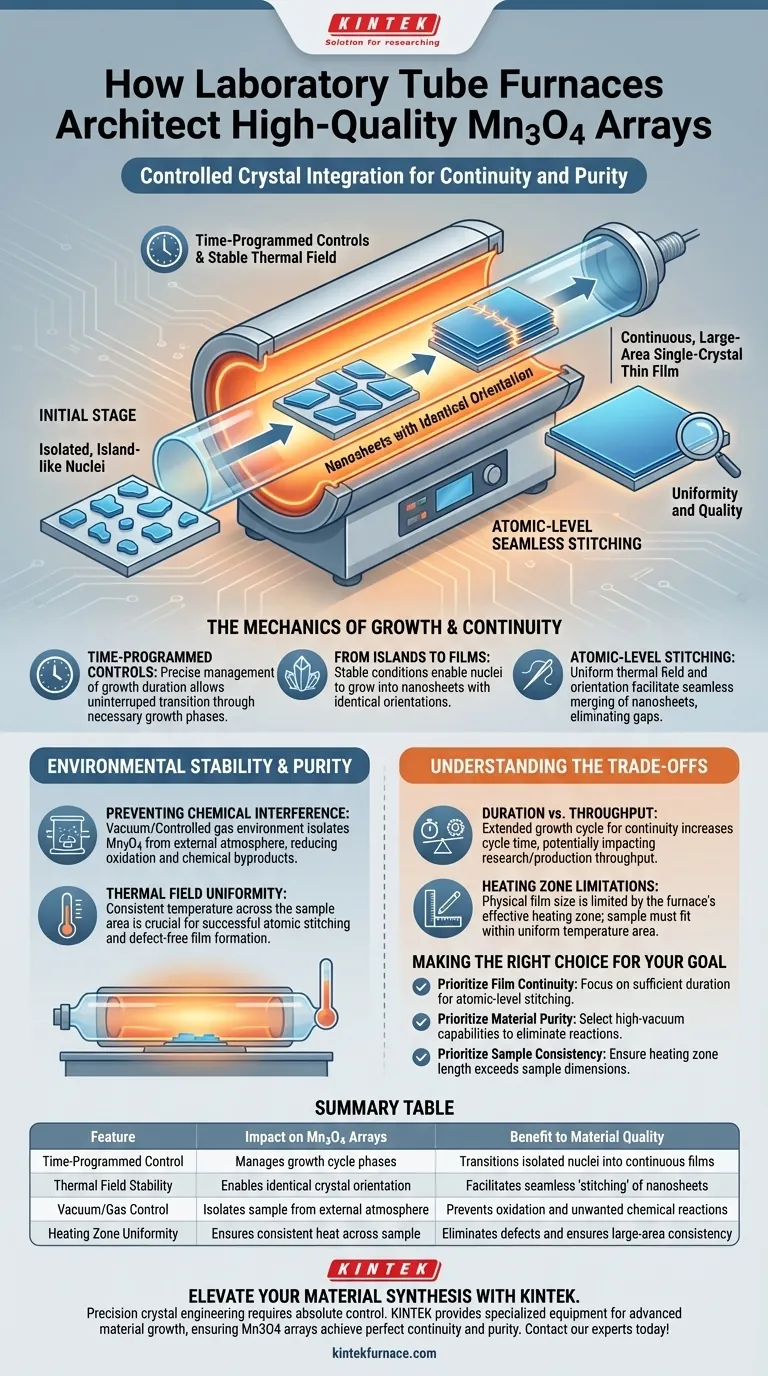
The laboratory tube furnace acts as the critical architect for controlled crystal integration. By utilizing precise time-programmed controls within a highly stable thermal field, it enables Mn3O4 structures to evolve from isolated, island-like nuclei into a continuous film. This controlled environment facilitates "atomic-level seamless stitching," where nanosheets with identical orientations merge to form uniform, large-area single-crystal thin films.
Quality and continuity in Mn3O4 arrays are not instantaneous; they are the result of a managed growth cycle where stable heat allows independent nanosheets to align and physically "sew" themselves together at the atomic level.

The Mechanics of Growth and Continuity
To understand how high-quality arrays are formed, we must look beyond simple heating and examine the specific mechanisms of crystal evolution.
The Role of Time-Programmed Controls
The formation of a continuous Mn3O4 film is strictly a function of time.
The tube furnace allows for precise management of the growth cycle duration. This temporal control is what permits the material to transition through its necessary growth phases without interruption.
From Islands to Films
Initially, the material exists as isolated, island-like nuclei.
As the process continues under controlled conditions, these nuclei grow into nanosheets. The furnace's stability ensures that these nanosheets maintain identical crystal orientations, which is a prerequisite for the final stage of growth.
Atomic-Level Seamless Stitching
This is the defining contribution of the tube furnace to material quality.
Because the thermal field is stable and the orientation is uniform, the separate nanosheets undergo a process described as atomic-level "sewing." They merge seamlessly at their boundaries, eliminating gaps and resulting in a single, cohesive thin film rather than a collection of disjointed particles.
Environmental Stability and Purity
While the primary reference highlights the growth mechanism, the environment provided by the furnace is equally critical for material success.
Preventing Chemical Interference
A high-quality tube furnace, particularly one with vacuum capabilities, isolates the Mn3O4 from the external atmosphere.
By operating in a vacuum or controlled gas environment, the furnace prevents the sample from reacting with surrounding gases. This drastically reduces the risks of oxidation, corrosion, or unwanted chemical byproducts that could disrupt the crystal lattice.
Thermal Field Uniformity
The "sewing" process requires a consistent temperature across the entire sample area.
Resistive heating elements surrounding the tube generate a thermal field that must be uniform. If the temperature fluctuates or varies across the sample, the atomic stitching will fail, leading to defects or incomplete film formation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving the perfect Mn3O4 array involves balancing specific operational constraints.
The Duration vs. Throughput Conflict
The "sewing" process required for high continuity cannot be rushed.
Extending the growth duration is necessary to transition from nanosheets to a continuous film. However, this increases the cycle time for each batch, potentially creating a bottleneck in research or production throughput.
Heating Zone Limitations
The physical size of your high-quality film is limited by the furnace's effective heating zone.
You must ensure the "appropriate length" of the heating zone matches your sample size. If the sample extends beyond the zone of uniform temperature, the edges of the array will fail to stitch correctly, resulting in uneven quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring your equipment for Mn3O4 synthesis, prioritize your settings based on your specific end-goal requirements.
- If your primary focus is Film Continuity: Prioritize the duration of the growth cycle to ensure sufficient time for the atomic-level stitching of nanosheets to complete.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Select a furnace with high-vacuum capabilities to eliminate oxidation and prevent reactions with environmental gases.
- If your primary focus is Sample Consistency: Ensure the heating zone length of the furnace exceeds the physical dimensions of your sample to guarantee thermal uniformity.
By mastering the variables of time and thermal stability, you transform the tube furnace from a simple heater into a precision tool for crystal engineering.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on Mn3O4 Arrays | Benefit to Material Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Time-Programmed Control | Manages growth cycle phases | Transitions isolated nuclei into continuous films |
| Thermal Field Stability | Enables identical crystal orientation | Facilitates seamless 'stitching' of nanosheets |
| Vacuum/Gas Control | Isolates sample from external atmosphere | Prevents oxidation and unwanted chemical reactions |
| Heating Zone Uniformity | Ensures consistent heat across sample | Eliminates defects and ensures large-area consistency |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision crystal engineering requires absolute control over every thermal variable. KINTEK provides the specialized equipment needed for advanced material growth, ensuring your Mn3O4 arrays achieve perfect continuity and purity.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Our high-temperature lab furnaces are fully customizable to meet the unique demands of your research, from atomic-level stitching to large-scale thin film production.
Ready to optimize your lab's performance? Contact our experts today to find your custom heating solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Jiashuai Yuan, Wei Liu. Controllable synthesis of nonlayered high-κ Mn3O4 single-crystal thin films for 2D electronics. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56386-9
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- How are tube furnaces utilized in environmental testing? Key Applications for Analysis and Remediation
- How are horizontal furnaces used in materials science? Unlock Precision in Heat Treatment
- How does a laboratory high-temperature tube resistance furnace contribute to the aging treatment of Ni-W-Co-Ta alloys?
- Why are high-precision laboratory tube furnaces used for the chemical activation of oxygen reduction electrocatalysts?
- Why is a vacuum pump used to treat the tube reactor before CVD of g-C3N4? Ensure High-Purity Thin Film Growth
- What are the methods for treating exhaust gas using a tube furnace? Safely Neutralize Hazards in Your Lab
- What is the significance of a multi-zone configuration in a horizontal tube furnace? Master FC-CVD Synthesis Control
- What are the functions of a quartz tube fixed-bed reactor? Ensure Precision in Catalyst Evaluation



















