The most common methods for treating exhaust gas from a tube furnace are combustion via an afterburner and chemical/physical adsorption using a scrubber or trap. The choice between them depends entirely on the chemical composition, concentration, and temperature of the waste gas your process generates.
The core challenge is not simply venting gas, but neutralizing specific chemical hazards before they enter the workspace or environment. Therefore, selecting an exhaust treatment method begins with a clear understanding of the byproducts your specific furnace process creates.

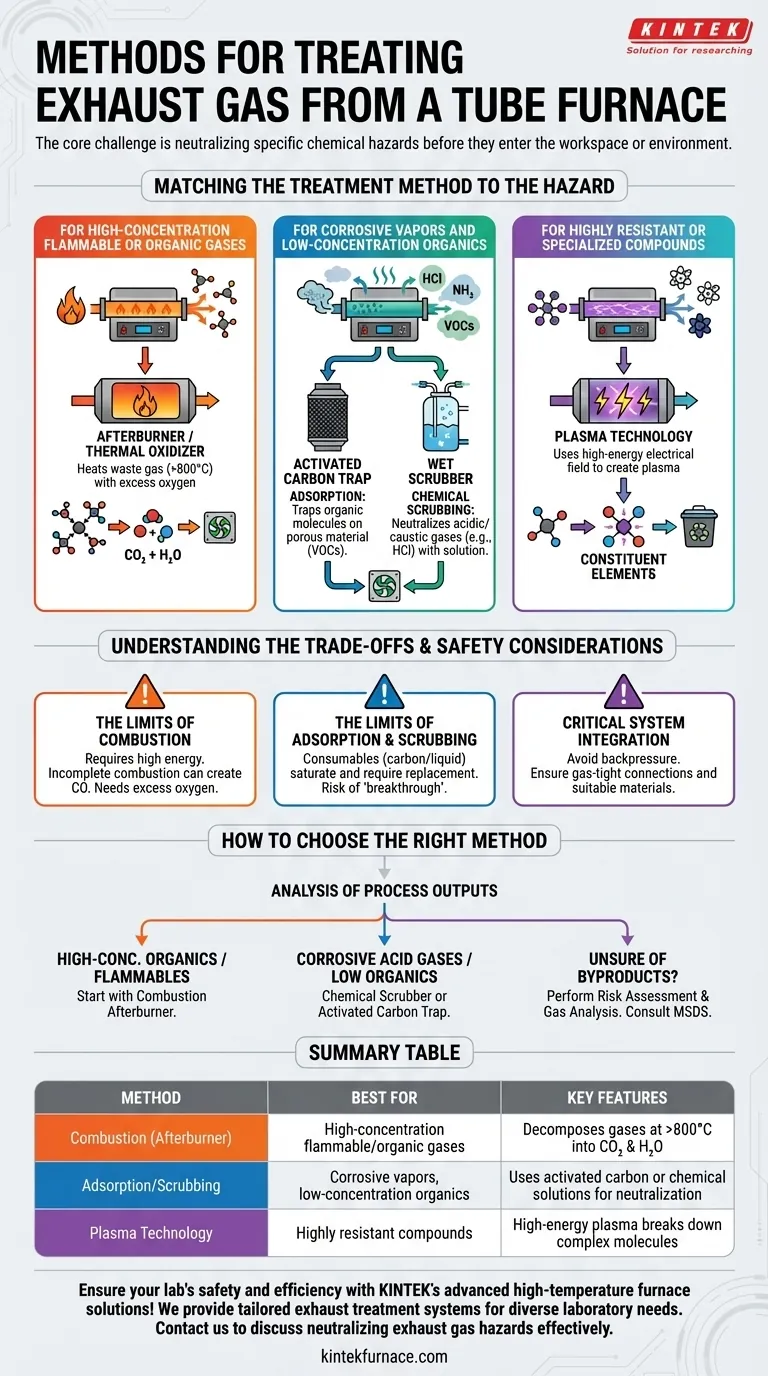
Matching the Treatment Method to the Hazard
Your tube furnace process—whether it's annealing, pyrolysis, or chemical vapor deposition—dictates the type of exhaust you must manage. Each treatment method is designed to neutralize a different class of hazardous material.
For High-Concentration Flammable or Organic Gases
The most effective method is combustion treatment, often implemented as an afterburner or thermal oxidizer.
An afterburner is a secondary heated chamber attached to the furnace exhaust. It heats the waste gas to extremely high temperatures (often >800°C) with an excess of oxygen, causing harmful organic compounds and flammable gases (like hydrogen) to decompose into simpler, safer substances like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O).
For Corrosive Vapors and Low-Concentration Organics
For these applications, adsorption and chemical scrubbing are the standard approach. This involves passing the exhaust gas through a specialized trap or a "wet scrubber" before venting.
Adsorption uses a porous material, most commonly activated carbon, which traps organic molecules on its vast surface area. This is highly effective for removing low concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Chemical scrubbing is used for acidic or caustic gases (e.g., HCl, NH₃). The gas is bubbled through a liquid solution that chemically neutralizes it. For example, an acid gas can be passed through a sodium hydroxide solution.
For Highly Resistant or Specialized Compounds
In some advanced research applications, more complex methods may be required for compounds that are difficult to break down through simple heating or scrubbing.
Plasma technology is one such method. It uses a high-energy electrical field to create a plasma that breaks down complex molecules into their constituent elements. This is a highly effective but also more complex and expensive solution reserved for specific, hard-to-treat waste streams.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Considerations
No exhaust treatment method is a perfect "set and forget" solution. Each comes with its own operational requirements, costs, and potential failure modes that you must manage.
The Limits of Combustion
Afterburners are powerful but require significant energy to maintain their high operating temperature. More importantly, incomplete combustion—caused by insufficient temperature or oxygen—can create new, equally hazardous byproducts like carbon monoxide (CO).
The Limits of Adsorption and Scrubbing
Scrubber and adsorption systems rely on consumable materials. The activated carbon will eventually become saturated and must be replaced, creating a new solid waste stream. Likewise, the neutralizing liquid in a wet scrubber will be consumed over time. If the media is not replaced, "breakthrough" can occur, where hazardous gas passes through the system untreated.
Critical System Integration
The exhaust treatment system must be matched to your furnace. A poorly designed system can create backpressure, which disrupts the controlled atmosphere inside your process tube and can compromise your experiment or product. All connections must be gas-tight and made from materials that can withstand the temperature of the exhaust gas.
How to Choose the Right Method for Your Process
Your decision must be driven by safety and a clear analysis of your process outputs. Never vent unknown gases directly into a lab or general ventilation.
- If your primary output is high-concentration organic vapors or flammable gases (e.g., from pyrolysis or processes using hydrogen): Your starting point should be a combustion afterburner for complete decomposition.
- If your primary output is corrosive acid gases or low levels of organic solvents: A chemical scrubber or an activated carbon trap is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If you are unsure of your process byproducts: You must perform a risk assessment. Consult your material safety data sheets (MSDS) and consider a formal gas analysis before operating the process and selecting a treatment method.
Ultimately, proper exhaust gas treatment is a non-negotiable component of running a safe and compliant furnace operation.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion (Afterburner) | High-concentration flammable/organic gases | Decomposes gases at >800°C into CO₂ and H₂O |
| Adsorption/Scrubbing | Corrosive vapors, low-concentration organics | Uses activated carbon or chemical solutions for neutralization |
| Plasma Technology | Highly resistant compounds | High-energy plasma breaks down complex molecules |
Ensure your lab's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored exhaust treatment systems. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you neutralize exhaust gas hazards effectively and enhance your operational compliance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment



















