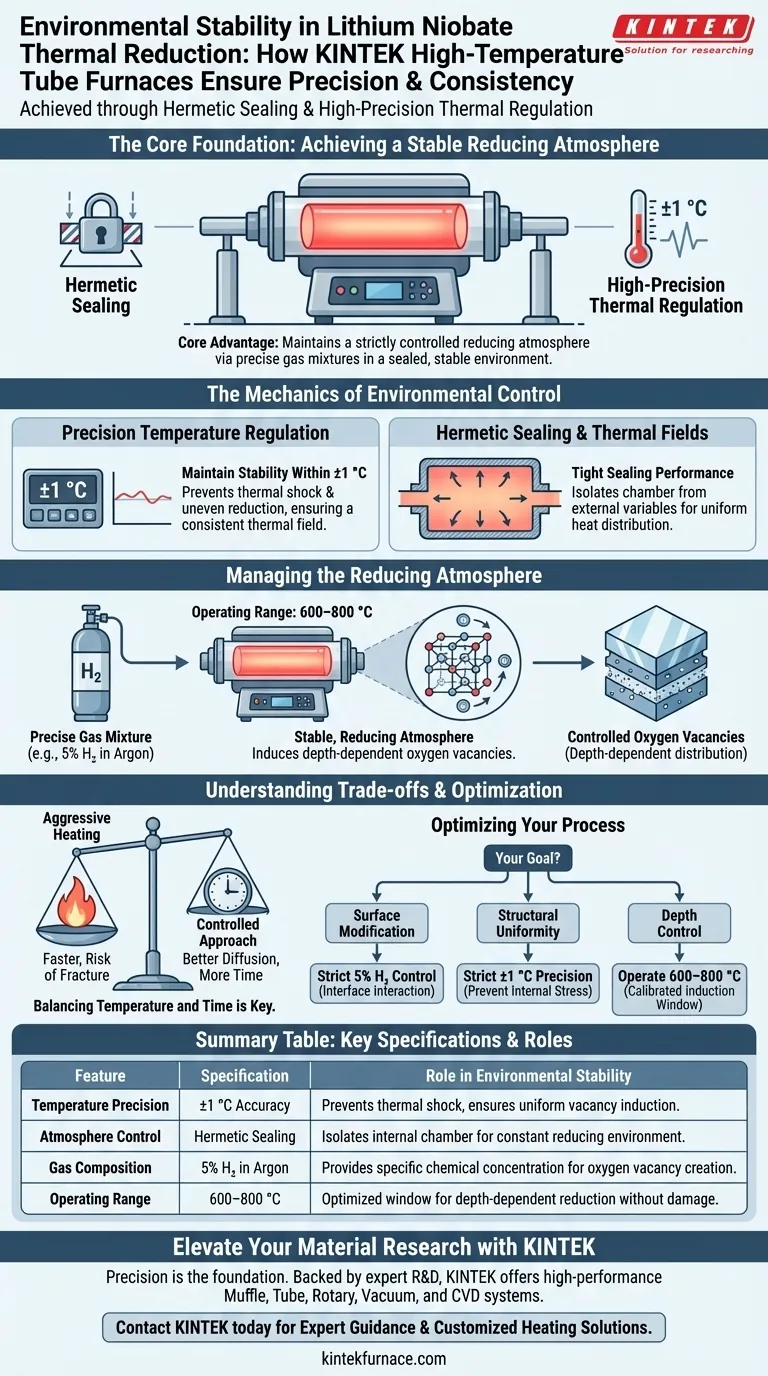
High-temperature laboratory tube furnaces achieve environmental stability through a combination of hermetic sealing and high-precision thermal regulation. These systems utilize tight seals to isolate the internal chamber and advanced control systems to maintain temperature accuracy within ±1 °C, ensuring a consistent thermal field for sensitive chemical changes.
The core advantage of these furnaces lies in their ability to maintain a strictly controlled reducing atmosphere. By introducing precise gas mixtures into a sealed, stable thermal environment, researchers can accurately induce depth-dependent oxygen vacancies without compromising the crystal's structural integrity.

The Mechanics of Environmental Control
Precision Temperature Regulation
To process lithium niobate crystals effectively, maintaining a specific thermal window is non-negotiable.
Tube furnaces employ high-precision control systems capable of maintaining stability within ±1 °C. This prevents thermal fluctuations that could lead to uneven reduction or thermal shock within the crystal lattice.
Hermetic Sealing and Thermal Fields
The physical construction of the furnace plays a critical role in stability.
Tight sealing performance is essential to isolate the processing chamber from external atmospheric variables. This isolation allows the furnace to maintain a stable thermal field, ensuring that the heat distribution remains uniform across the entire sample during the reduction process.
Managing the Reducing Atmosphere
Controlling Gas Concentration
Once the thermal field is stabilized, the chemical environment must be fine-tuned.
The furnace introduces a precisely proportioned argon-hydrogen gas mixture, typically containing 5% Hydrogen (H2). Because the chamber is tightly sealed, the concentration of this reducing atmosphere remains constant throughout the treatment.
Inducing Oxygen Vacancies
The ultimate goal of this stability is the manipulation of the crystal's properties at the atomic level.
Operating within the 600–800 °C range, the controlled environment allows for the precise induction of oxygen vacancies. The stable atmosphere ensures these vacancies are distributed in a depth-dependent manner, rather than randomly, which is critical for the material's final application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Balancing Temperature and Time
While high temperatures facilitate the reduction process, they require careful management of time and ramp rates.
Aggressive heating can accelerate the process but risks destabilizing the crystal growth or causing fractures. A controlled, slower approach—similar to methods used in other crystal growth processes—ensures better diffusion but significantly increases total processing time.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
The precision of the gas mixture is a double-edged sword.
Because the system relies on a specific concentration (e.g., 5% H2), deviations in gas flow or seal integrity can drastically alter the reduction results. If the seal fails, the introduction of oxygen will immediately neutralize the reducing atmosphere, ruining the specific vacancy distribution.
Optimizing Your Reduction Process
To achieve the best results with lithium niobate thermal reduction, match your operational parameters to your specific material goals:
- If your primary focus is surface modification: Ensure your gas mixture is strictly maintained at the 5% H2 level to control the interaction at the crystal interface.
- If your primary focus is structural uniformity: Prioritize the precision of the thermal controller to keep fluctuations strictly within the ±1 °C limit, preventing internal stress.
- If your primary focus is depth control: Operate precisely within the 600–800 °C window, as this temperature range is specifically calibrated for depth-dependent vacancy induction.
True environmental stability is the result of aligning rigorous seal integrity with unwavering thermal precision.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Specification | Role in Environmental Stability |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Precision | ±1 °C Accuracy | Prevents thermal shock and ensures uniform vacancy induction. |
| Atmosphere Control | Hermetic Sealing | Isolates internal chamber to maintain a constant reducing environment. |
| Gas Composition | 5% H₂ in Argon | Provides the specific chemical concentration for oxygen vacancy creation. |
| Operating Range | 600–800 °C | Optimized window for depth-dependent reduction without structural damage. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the foundation of successful lithium niobate thermal reduction. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the most rigorous laboratory standards.
Our furnaces provide the unwavering thermal stability and airtight sealing required for sensitive chemical processes. Whether you need a standard setup or a fully customizable solution for unique research needs, our team is ready to support your goals.
Ready to optimize your reduction process? Contact KINTEK today for expert guidance and customized heating solutions.
Visual Guide
References
- Yunjia Bao, Dongfeng Xue. Machine‐Learning‐Assisted Understanding of Depth‐Dependent Thermal Conductivity in Lithium Niobate Induced by Point Defects. DOI: 10.1002/aelm.202400944
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for MoS2 and WS2 thin films? Achieve 2H Crystalline Phase Excellence
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the initial pyrolysis of date palm leaf biomass? Key Insights
- What synthesis environment does a vacuum tube furnace provide for C@TiC nanoparticles? Master Oxygen-Free Pyrolysis
- How does a high vacuum tube furnace ensure accuracy in Sn-Ag-Cu-Mn-Er solder experiments? Optimize Wetting Analysis
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for Ti3AuC2 annealing? Achieve Perfect Atomic Exchange
- How does a tube furnace generate high temperatures? Efficient, Precise Heating for Your Lab
- How does the temperature curve control in a quartz tube sintering furnace affect Ag-P electrode in-situ doping?
- What role does a tube furnace play in producing activated carbon? Master Walnut Shell Activation for High Adsorption



















