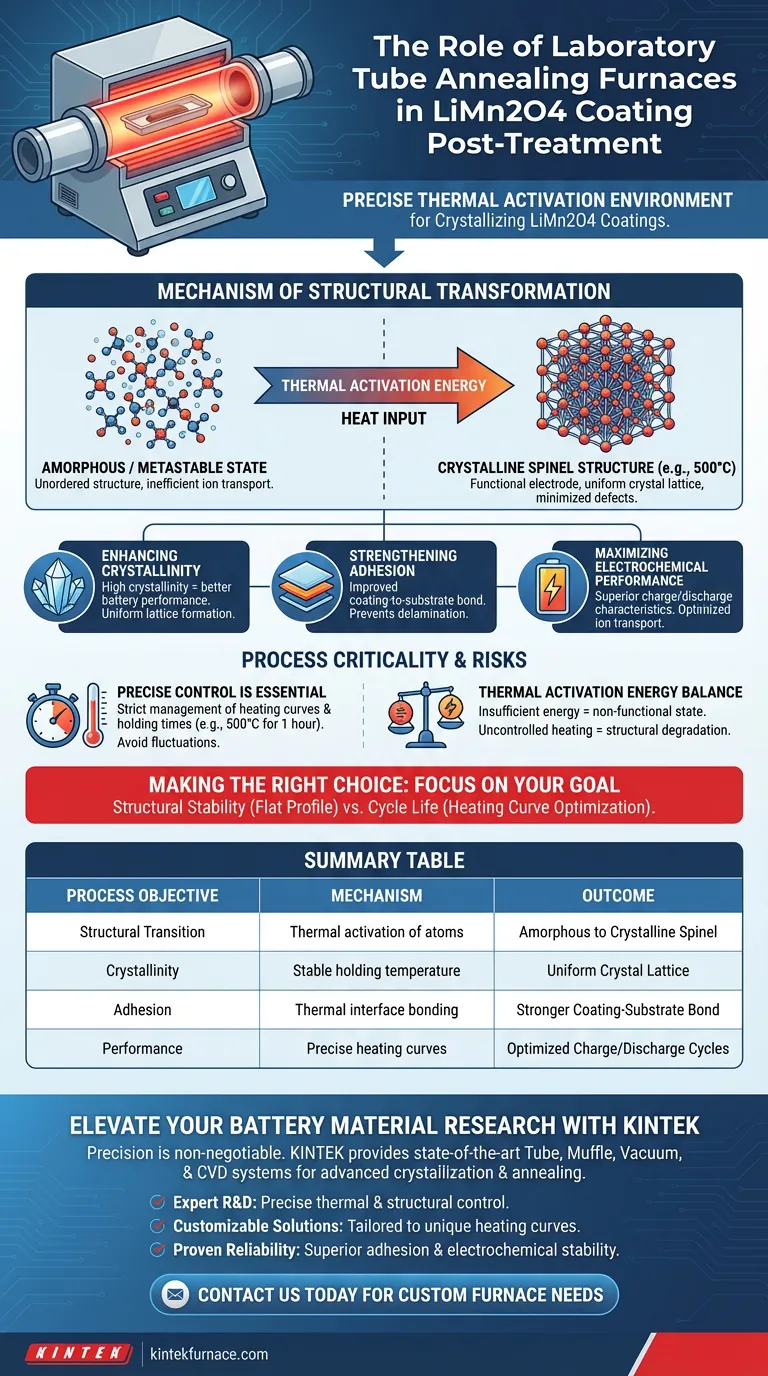
A laboratory tube annealing furnace serves as the precise thermal activation environment required to crystallize LiMn2O4 coatings. It facilitates the essential phase transformation of the material, converting deposited layers from an unstable or amorphous state into a functional, crystalline spinel structure.
The annealing process is the bridge between a raw deposited film and a functional battery electrode. It provides the specific thermal energy needed to lock in the spinel structure, ensuring the material is chemically active and physically robust.
Mechanism of Structural Transformation
From Amorphous to Crystalline
Newly deposited LiMn2O4 layers often exist in an amorphous or metastable state. These states lack the ordered atomic structure necessary for efficient ion transport.
The tube furnace provides the thermal activation energy required to rearrange these atoms. This heat input drives the transition into the required spinel structure.
Enhancing Crystallinity
High crystallinity is correlated with better battery performance. The furnace ensures the formation of a uniform crystal lattice throughout the coating.
By maintaining specific holding temperatures, such as 500 °C, the equipment allows the grain structure to develop fully. This minimizes defects that could impede lithium-ion movement.
Physical and Electrochemical Optimization
Strengthening Adhesion
A coating is only as good as its bond to the substrate. Post-treatment annealing significantly improves the adhesion between the LiMn2O4 layer and the current collector.
The thermal process creates a more intimate interface, preventing delamination during the expansion and contraction cycles of battery use.
Maximizing Electrochemical Performance
The ultimate goal of the annealing process is the optimization of the material's electrical properties. A properly annealed film exhibits superior charge and discharge characteristics.
The precise control of the heating environment ensures the material achieves the specific electrochemical profile required for energy storage applications.
Understanding Process Criticality and Risks
The Necessity of Precise Control
Success depends on the strict management of heating curves and holding times. A digitally controlled furnace is essential to execute these parameters without fluctuation.
For example, a standard protocol may require holding the temperature at exactly 500 °C for one hour. Deviations in this ramp-up or hold time can lead to incomplete crystallization.
Thermal Activation Energy Balance
The process is a balancing act of energy input. Insufficient thermal energy will leave the material in a metastable, non-functional state.
Conversely, while not explicitly detailed in the primary text, uncontrolled heating generally risks structural degradation. The tube furnace mitigates this by regulating the exact energy delivered to the sample.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your LiMn2O4 coatings meet performance standards, focus on the specific parameters of your annealing protocol.
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability: Ensure your furnace can maintain a flat, unwavering temperature profile at 500 °C to guarantee complete conversion to the spinel phase.
- If your primary focus is Cycle Life: prioritize the optimization of the heating curve to maximize coating-to-substrate adhesion, which prevents mechanical failure over time.
Control the temperature, and you control the quality of the final electrode.
Summary Table:
| Process Objective | Mechanism | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Transition | Thermal activation of atoms | Amorphous state to crystalline spinel structure |
| Crystallinity | Stable holding temperature (e.g., 500°C) | Uniform crystal lattice and minimized defects |
| Adhesion | Thermal interface bonding | Stronger coating-to-substrate bond, preventing delamination |
| Performance | Precise heating curves | Optimized charge/discharge cycles and ion transport |
Elevate Your Battery Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when transforming LiMn2O4 coatings into high-performance electrodes. KINTEK provides state-of-the-art Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems specifically engineered to deliver the unwavering temperature profiles required for advanced crystallization and annealing.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D: Our furnaces are designed for precise thermal activation and structural control.
- Customizable Solutions: We tailor systems to your unique heating curves and substrate requirements.
- Proven Reliability: Achieve superior adhesion and electrochemical stability every time.
Ready to optimize your lab's high-temperature processes? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Fabián Ambriz-Vargas, Manuel Quevedo-López. Fine-Tuning Cathode Performance: The Influence of Argon Deposition Pressure on LiMn2O4 Thin Film Electrochemistry for Li-Ion Batteries. DOI: 10.3390/batteries10120449
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How do vertical tube furnaces comply with environmental standards? A Guide to Clean, Efficient Operation



















