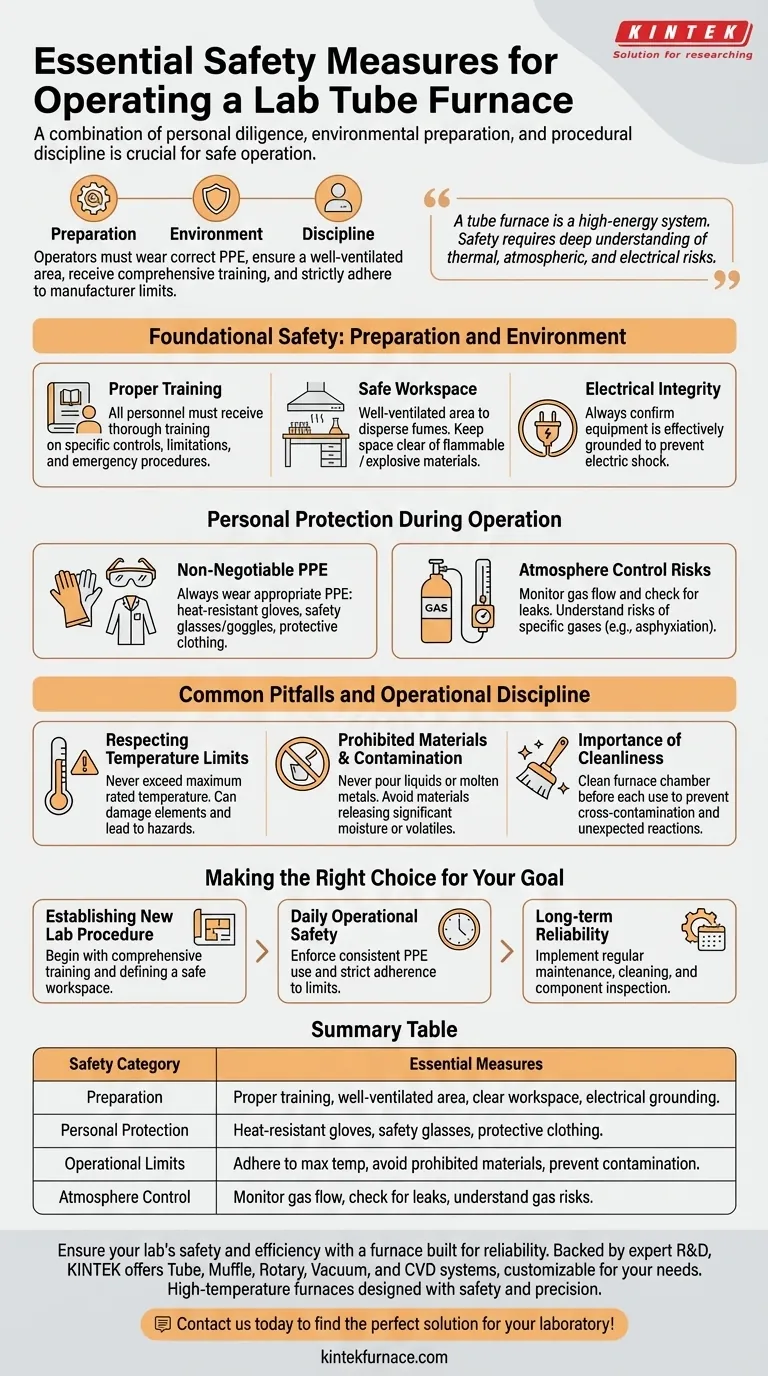
The most essential safety measures for operating a lab tube furnace are a combination of personal diligence, environmental preparation, and procedural discipline. Operators must wear the correct Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), ensure the furnace is in a well-ventilated area, receive comprehensive training on its specific operation, and strictly adhere to the manufacturer's temperature and material limits.
A tube furnace is not just a piece of equipment; it is a high-energy system. True safety extends beyond a simple checklist and requires a deep understanding of the thermal, atmospheric, and electrical risks involved at every stage of operation.

Foundational Safety: Preparation and Environment
Before the furnace is ever turned on, the operator and the workspace must be properly prepared. Neglecting this foundation introduces unacceptable risk.
The Mandate for Proper Training
All personnel who will operate the furnace must receive thorough training. This is non-negotiable.
Training must cover the specific model's controls, limitations, and emergency shutdown procedures. Understanding the instruction manual is the absolute minimum requirement.
Setting Up a Safe Workspace
The physical environment is your first line of defense. The area must be well-ventilated to safely disperse any hazardous fumes or process gases.
Keep the space surrounding the furnace completely clear of flammable or explosive materials. This simple housekeeping rule prevents a minor incident from becoming a major catastrophe.
Ensuring Electrical Integrity
A tube furnace is a high-power electrical device. Always confirm the equipment is effectively grounded to prevent the severe risk of electric shock.
Personal Protection During Operation
When the furnace is running, direct interaction requires specific safeguards. PPE is the final barrier between you and a potential hazard.
Non-Negotiable Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Always wear appropriate PPE when working with or near an operating furnace.
This includes, at a minimum, heat-resistant gloves, safety glasses or goggles, and appropriate protective clothing to shield against high temperatures.
Managing Atmosphere Control Risks
Many processes require specific atmospheres using inert or reactive gases. This introduces risks beyond heat.
Always monitor gas flow rates and check connections to prevent dangerous leaks. Ensure you understand the specific risks of the gases being used, including asphyxiation from inert gases in enclosed spaces.
Common Pitfalls and Operational Discipline
Adherence to operational limits is critical for both safety and the longevity of the equipment. Most failures occur when operators deviate from established protocols.
Respecting Temperature Limits
Never operate the furnace beyond its maximum rated temperature.
Exceeding this limit can damage the heating elements and internal lining, creating an immediate safety hazard and leading to costly repairs.
Prohibited Materials and Contamination
The furnace chamber is a controlled environment. Never pour any liquids or molten metals directly into the furnace tube.
Avoid heating materials that may release significant moisture or volatile gases unexpectedly, as this can cause rapid pressure changes and damage the process tube.
The Importance of Cleanliness
A clean furnace is a safe and effective furnace. The interior chamber must be kept clean before each use.
This prevents cross-contamination between samples and removes residual materials that could react unexpectedly at high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Implementing a robust safety protocol requires focusing on different aspects of the process depending on your immediate objective.
- If your primary focus is establishing a new lab procedure: Begin with comprehensive operator training and meticulously defining a safe, clear workspace according to manufacturer guidelines.
- If your primary focus is daily operational safety: Enforce the consistent and correct use of all required PPE and maintain strict adherence to the furnace's material and temperature limits.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Implement a non-negotiable schedule for regular maintenance, cleaning, and inspection of all electrical, gas, and heating components.
A proactive culture of safety is the most effective tool for preventing accidents in any high-temperature laboratory environment.
Summary Table:
| Safety Category | Essential Measures |
|---|---|
| Preparation | Proper training, well-ventilated area, clear workspace, electrical grounding. |
| Personal Protection | Heat-resistant gloves, safety glasses, protective clothing. |
| Operational Limits | Adhere to max temperature, avoid prohibited materials, prevent contamination. |
| Atmosphere Control | Monitor gas flow, check for leaks, understand gas-specific risks. |
Ensure your lab's safety and efficiency with a furnace built for reliability. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique needs. Our high-temperature furnaces are designed with safety and precision in mind. Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















