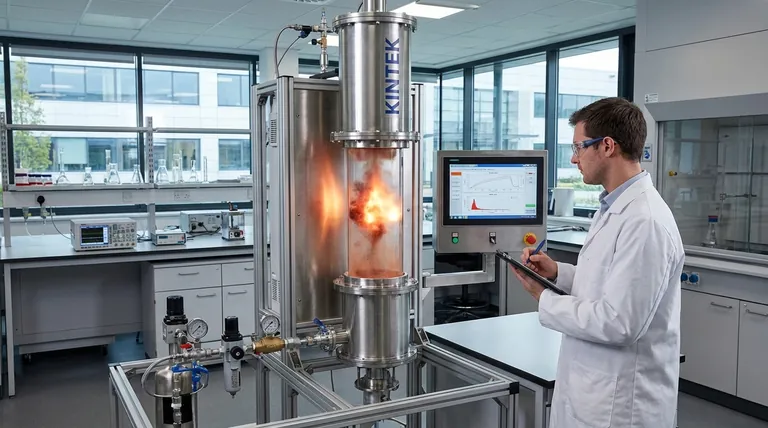
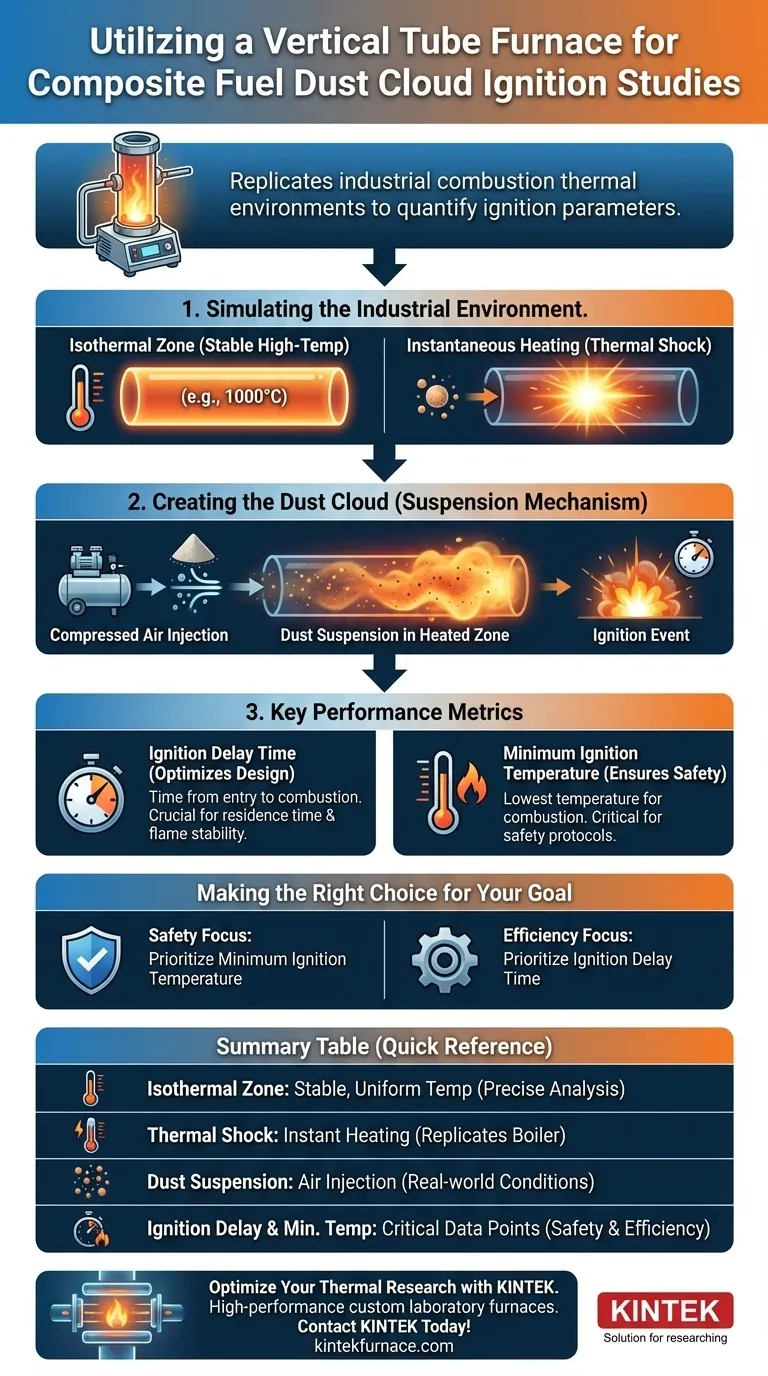
A Vertical Tube Furnace functions as a specialized high-temperature reactor designed to replicate the thermal environment of industrial combustion systems. By utilizing electrical heating to create a stable isothermal zone and integrating a compressed air injection system, the furnace simulates the instantaneous heating shock that powdered fuels experience in a boiler. This controlled setup allows for the precise quantification of critical combustion parameters, specifically the ignition delay time and the minimum ignition temperature of composite fuel dust suspensions.
The Vertical Tube Furnace provides a controlled, isolated environment to model the rapid heating of suspended fuel dusts, enabling the accurate measurement of when and at what temperature a specific composite fuel will ignite under simulated industrial conditions.

Simulating the Industrial Environment
To understand the utility of a Vertical Tube Furnace, one must look at the specific conditions it attempts to mimic: the interior of an industrial boiler.
Creating the Isothermal Zone
The core feature of this apparatus is the generation of a high-temperature isothermal zone.
Through precise electrical heating, the furnace maintains a constant, uniform temperature profile. This uniformity is essential for isolating temperature as a variable, ensuring that observed ignition characteristics are due to fuel properties rather than environmental fluctuations.
Modeling Instantaneous Heating
In a real-world boiler, fuel dust does not heat up slowly; it is subjected to immediate, intense thermal shock.
The Vertical Tube Furnace replicates this by introducing the fuel into the pre-heated isothermal zone. This allows researchers to observe how the fuel behaves under the stress of rapid heating, a critical factor in combustion efficiency.
The Mechanics of Dust Suspension
Studying "composite fuel dust clouds" requires more than just heat; it requires the fuel to be suspended in the air, just as it would be during injection into a combustion chamber.
Compressed Air Injection
To achieve this suspension, the furnace is integrated with a compressed air injection system.
This system disperses the powdered fuel into the heated tube. The air acts as both the oxidizer required for combustion and the carrier mechanism that creates the dust cloud.
Analyzing the Suspension
Once the dust is suspended in the isothermal zone, the furnace acts as a reactor.
It creates the physical conditions necessary to study how the solid fuel particles interact with the heated air, leading to the chemical reactions that cause ignition.
Key Performance Metrics
The primary utility of this setup is the generation of hard data regarding two specific combustion characteristics.
Ignition Delay Time
The furnace allows for the measurement of the time gap between the fuel's entry into the heated zone and the moment of actual ignition.
Understanding this delay is vital for optimizing boiler design, as it dictates residence time and flame stability.
Minimum Ignition Temperature
The apparatus is also used to determine the lowest temperature required to initiate combustion for a specific composite fuel.
This metric is critical for establishing safety protocols and operational baselines for industrial systems using these fuels.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the Vertical Tube Furnace is a powerful tool, it represents an idealization of reality.
Controlled vs. Chaotic Environments
The furnace provides a stable, "controlled" environment to ensure measurement precision.
However, real industrial boilers are dynamic and often chaotic. While the furnace accurately simulates the thermal process (instantaneous heating), it may not perfectly replicate the complex aerodynamic turbulence found in full-scale machinery.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The data derived from a Vertical Tube Furnace is essential for both safety engineering and process optimization.
- If your primary focus is Operational Safety: Prioritize the Minimum Ignition Temperature data to establish safe operating thresholds and prevent accidental combustion in lower-temperature zones.
- If your primary focus is Combustion Efficiency: Focus on the Ignition Delay Time to optimize the injection timing and ensure the fuel has sufficient residence time in the boiler for complete burnout.
By isolating the variables of heat and suspension, the Vertical Tube Furnace translates the complex physics of combustion into measurable, actionable data.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Description | Industrial Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Isothermal Zone | Stable, uniform high-temperature region | Isolates temperature as a variable for precise fuel analysis |
| Thermal Shock | Instantaneous heating via pre-heated tube | Replicates the rapid heating fuel experiences in a boiler |
| Dust Suspension | Compressed air injection system | Mimics real-world fuel injection and oxidation conditions |
| Ignition Delay | Time between entry and combustion | Critical for optimizing residence time and flame stability |
| Min. Ignition Temp | Lowest temperature to initiate combustion | Essential for establishing operational safety protocols |
Optimize Your Thermal Research with KINTEK
Take the guesswork out of combustion analysis. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for your specific laboratory needs. Whether you are studying fuel characteristics or advanced material synthesis, our customizable high-temp furnaces deliver the precision your data demands.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact KINTEK Today to Consult with Our Experts
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision tube furnace necessary for YIG thin films? Unlock Superior Magnetic Performance
- What are the technical requirements for a fixed-bed quartz reactor? Ensure Pure Data in Dry Reforming of Methane
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- How does a high-precision horizontal tube furnace facilitate the activation stage of catalysts? Optimize Pore Integrity
- What factors affect the price of a vacuum tube furnace? Key Drivers and Smart Investment Tips
- How are tubular furnaces utilized in semiconductor manufacturing? Precision Thermal Processing for High-Yield ICs
- How is tantalum disulfide prepared using a tube furnace? Master the Two-Step Synthesis for High-Quality Crystals
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature tube furnace for the post-deposition annealing of ITO? Optimize Film Performance



















