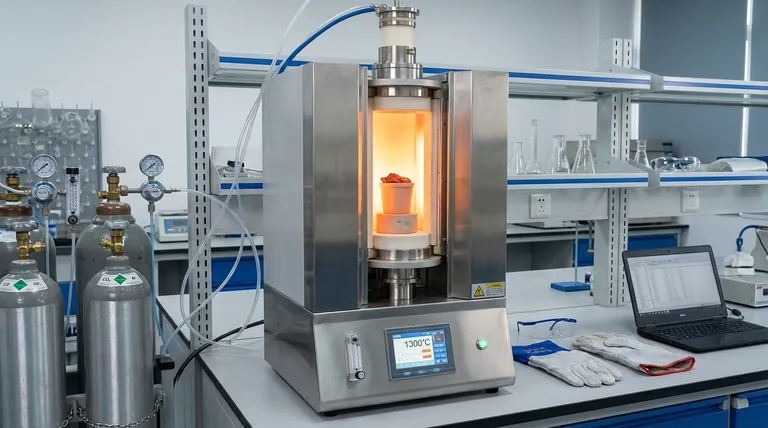
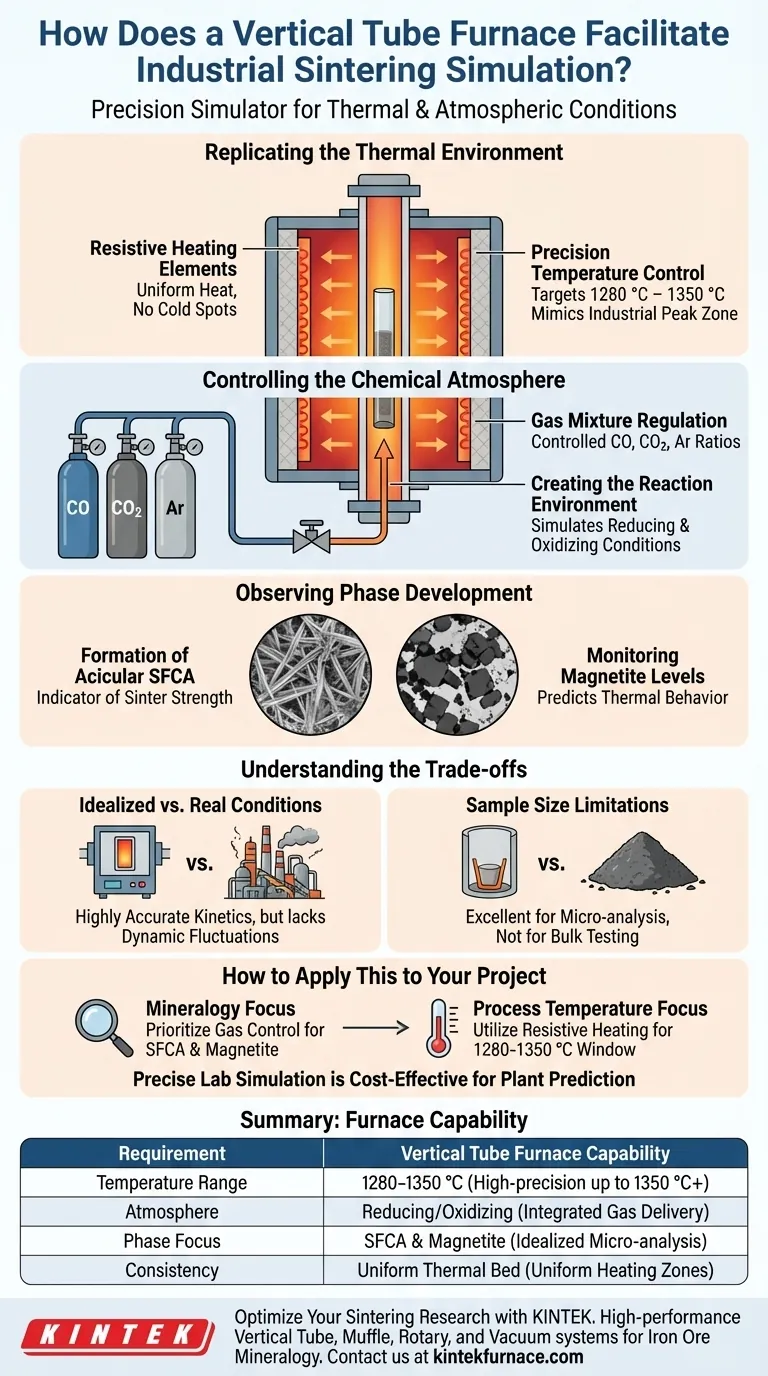
A vertical tube furnace acts as a precision simulator for industrial sintering, replicating the specific thermal and atmospheric conditions found within a sintering machine. It utilizes resistive heating elements to generate exact temperatures and a gas delivery system to create a controlled chemical environment, allowing researchers to study the physical and chemical transformations of iron ores in isolation.
By maintaining precise temperatures between 1280 °C and 1350 °C under a controlled atmosphere, the furnace allows for the detailed observation of critical mineral phase development. This setup enables the study of sintering mechanics without the variability and scale of a full industrial plant.

Replicating the Thermal Environment
Precision Temperature Control
The defining feature of the vertical tube furnace in this context is its ability to reach and maintain a specific high-temperature range.
For accurate sintering simulation, the furnace targets a window between 1280 °C and 1350 °C. This narrow band is critical because it mimics the peak thermal zone of an industrial sintering bed where the most significant bonding occurs.
Resistive Heating Mechanism
To achieve these temperatures, the furnace relies on resistive heating elements that surround the central tube.
These elements heat the interior of the chamber uniformly. This ensures that the iron ore samples are subjected to consistent thermal energy, eliminating the cold spots that can occur in less precise heating methods.
Controlling the Chemical Atmosphere
Gas Mixture Regulation
Temperature is only half of the simulation; the chemical environment determines how the ore reacts.
The furnace allows for the introduction of a specific mixture of gases, typically involving Carbon Monoxide (CO), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), and Argon (Ar).
Creating the Reaction Environment
This controlled atmosphere replicates the reducing and oxidizing conditions present in a sintering machine.
By manipulating the ratios of these gases, researchers can simulate the specific partial pressures of oxygen required to trigger the desired chemical changes in the ore.
Observing Phase Development
Formation of Key Minerals
The primary purpose of combining high heat with specific gases is to observe the development of mineral phases that determine the quality of the sinter.
Specifically, this setup facilitates the growth of acicular Silico-Ferrite of Calcium and Aluminum (SFCA). The presence and morphology of SFCA are crucial indicators of sinter strength and reducibility.
Monitoring Magnetite Levels
The furnace also allows for the observation of magnetite formation.
Understanding the balance between magnetite and other phases helps engineers predict the thermal behavior and breakdown characteristics of the sinter before it is processed on an industrial scale.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Idealized vs. Real Conditions
While the vertical tube furnace offers precision, it presents an idealized environment.
Industrial sintering involves dynamic fluctuations in airflow and temperature gradients that a static tube furnace may not perfectly replicate. The data obtained is highly accurate for chemical kinetics but may not fully capture the mechanical irregularities of a moving sinter bed.
Sample Size Limitations
The physical constraints of the tube limit the volume of the sample.
This setup is excellent for micro-structural analysis and phase identification, but it cannot produce bulk quantities of sinter for large-scale physical testing.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The value of a vertical tube furnace depends on the specific parameters you need to isolate.
- If your primary focus is Mineralogy: Prioritize the precise control of the gas atmosphere (CO/CO2/Ar) to study the formation of acicular SFCA and magnetite phases.
- If your primary focus is Process Temperature: Utilize the resistive heating control to test how the ore reacts specifically within the 1280 °C to 1350 °C window.
Precise simulation in the lab is the most cost-effective way to predict performance in the plant.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Sintering Simulation Requirement | Vertical Tube Furnace Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 1280 °C to 1350 °C | High-precision resistive heating up to 1350°C+ |
| Atmosphere | Reducing/Oxidizing (CO, CO2, Ar) | Integrated gas delivery & partial pressure control |
| Phase Focus | SFCA & Magnetite formation | Idealized environment for micro-structural analysis |
| Consistency | Uniform thermal bed | Uniform heating zones to eliminate cold spots |
Optimize Your Sintering Research with KINTEK
Bridge the gap between laboratory simulation and industrial excellence. KINTEK provides high-performance Vertical Tube, Muffle, Rotary, and Vacuum systems, all customizable to meet the rigorous demands of iron ore mineralogy and thermal processing.
Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our furnaces empower your team to master mineral phase development and chemical kinetics. Contact us today to discuss your unique research needs and discover how our advanced heating solutions can streamline your path to plant-scale success.
Visual Guide
References
- Seong‐Jin Kim, Sung‐Mo Jung. Effect of Mill-Scale and Calcined Dolomite on High Al2O3 Sinter and Its Phase Development. DOI: 10.1007/s11663-025-03677-7
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why use a laboratory tube furnace with argon for low carbon steel annealing? Ensure Oxidation-Free Material Integrity
- What is a vacuum tube furnace? Essential for High-Purity Material Processing
- How does the design of tube furnaces ensure uniform heating? Master Precision with Multi-Zone Control
- What is an alumina tube furnace? Essential for High-Temp, Contamination-Free Material Processing
- How to use a tubular furnace? Master Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the performance of carbon nanowire networks? Enhance Electrode Performance
- What types of reactions can tube furnaces be used for besides synthesis and purification? Explore Versatile Thermal Processing Applications



















