Operating a tubular furnace follows a clear sequence of safety checks, power activation, and programming. At its most basic, you will turn on the main air switch and the furnace's power, use the digital controller to set your desired temperature profile, and then press the heating button to begin the cycle.
The key to effectively using a tubular furnace is not just following the startup sequence, but understanding how its design enables precise, uniform heating. Mastering its use means controlling the rate of temperature change to ensure sample integrity, process accuracy, and operational safety.
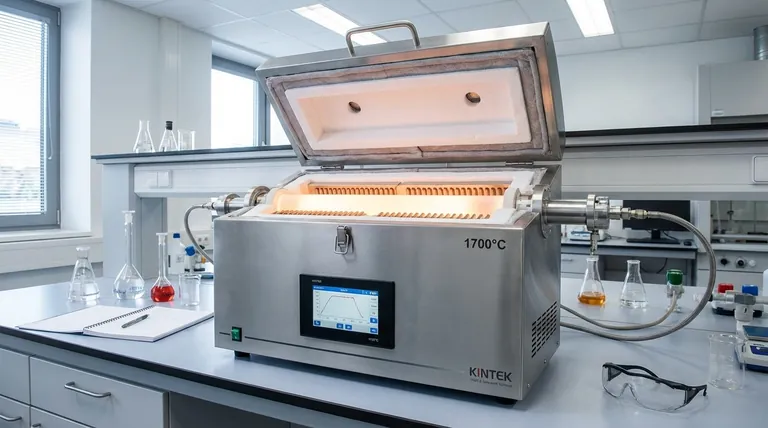

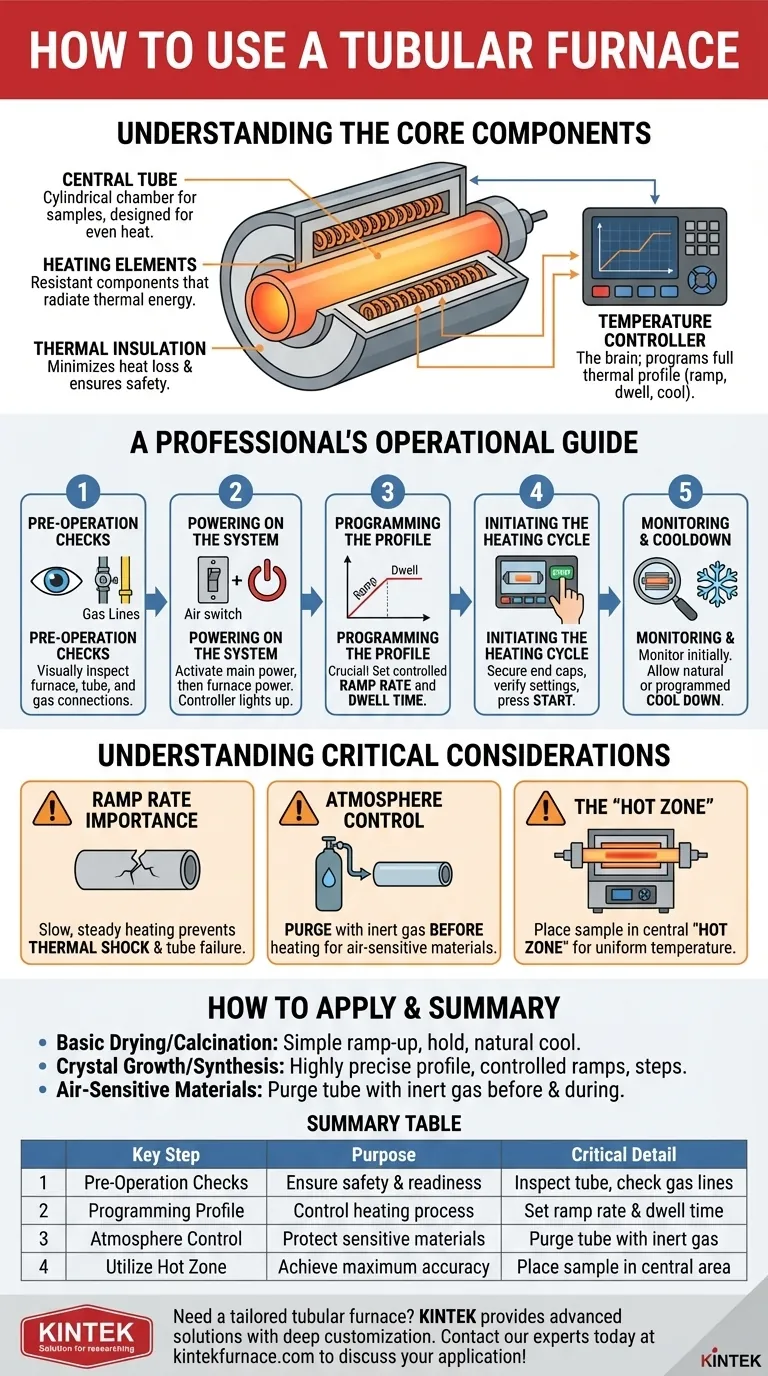
Understanding the Core Components
To use a tubular furnace correctly, you must first understand its fundamental parts and how they work together to create a controlled thermal environment.
The Central Tube
This is the cylindrical chamber at the heart of the furnace where you place your material. Its shape is specifically designed to promote even heat distribution around the sample.
The Heating Elements
These components, typically made of a resistant material, surround the central tube. When electricity passes through them, they heat up, radiating thermal energy inward to heat the tube and its contents.
The Temperature Controller
This is the brain of the system. It's a digital interface that allows you to set a precise temperature, but more importantly, to program a full thermal profile, including the rate of heating (ramp rate), how long to hold a temperature (dwell time), and the rate of cooling.
The Thermal Insulation
The entire assembly is enclosed in high-performance insulation. This minimizes heat loss, improves energy efficiency, and keeps the exterior of the furnace cool enough to be safe, channeling all the energy toward your sample.
A Professional's Operational Guide
Moving beyond the basics, a professional approach involves a more deliberate and safety-conscious workflow.
Step 1: Pre-Operation Checks
Before applying power, visually inspect the furnace. Ensure the process tube is correctly inserted, free of cracks, and that there are no obstructions in or around the unit. If you are using a controlled atmosphere, verify all gas lines are securely connected.
Step 2: Powering On the System
First, activate the main power source, which may be a wall-mounted breaker or an "air switch." Then, turn on the main power switch on the furnace itself. The temperature controller should light up.
Step 3: Programming the Temperature Profile
This is the most critical step for process success. Instead of just setting a final temperature, you must program the ramp rate—how quickly the furnace heats up, measured in degrees per minute or hour. A slow, controlled ramp is essential. Then, program the dwell time and any subsequent cooling steps.
Step 4: Initiating the Heating Cycle
Once your program is set and you have placed your sample in the tube, secure the end caps. Double-check your program settings on the controller's display, and then press the "Heat," "Run," or "Start" button to begin the cycle.
Step 5: Monitoring and Cooldown
The furnace will now run the program automatically. However, it is good practice to monitor the initial phase to ensure it is operating as expected. Once the cycle is complete, allow the furnace to cool down according to your program or naturally before attempting to remove your sample.
Understanding Critical Considerations
Simple operation can lead to poor results or equipment damage. Understanding tratamento trade-offs is crucial for professional use.
The Importance of Ramp Rate
Heating the furnace tube too quickly can cause thermal shock, leading to cracks and catastrophic failure. Always use a slow and steady ramp rate, especially with ceramic or quartz tubes, to allow the material to expand evenly.
Atmosphere Control
Many applications require an inert or reactive gas atmosphere to prevent oxidation or facilitate a reaction. If this is your goal, you must purge the air from the tube with your chosen gas before you begin heating and maintain a slight positive pressure throughout the cycle.
The "Hot Zone"
While tubular furnaces provide excellent temperature uniformity, there is always a central area promoção a "hot zone," where the temperature is most accurate and stable. For precise work, you must know the location of your furnace's hot zone and place your sample directly within it.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your operational procedure should be guided by your specific scientific or industrial goal.
- If your primary focus is basic material drying or calcination: A simple temperature ramp-up to a set point, a hold, and a natural cool-down is often sufficient.
- If your primary focus is crystal growth or advanced material synthesis: You will need to program a highly precise profile with controlled ramp rates, multiple temperature steps, and a controlled cooling rate.
- If your primary focus is working with air-sensitive materials: Your procedure must include steps for purging the tube with an inert gas before heating and maintaining that atmosphere during the run.
By moving beyond simple operation to understand the principles of controlled heating, you can ensure safe, repeatable, and successful results from your tubular furnace.
Summary Table:
| Key Step | Purpose | Critical Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Operation Checks | Ensure safety and readiness | Inspect tube, check gas lines for atmosphere control |
| Programming Profile | Control the heating process | Set ramp rate and dwell time to prevent thermal shock |
| Atmosphere Control | Protect sensitive materials | Purge tube with inert gas before heating |
| Utilize Hot Zone | Achieve maximum accuracy | Place sample in the furnace's most uniform temperature area |
Need a tubular furnace tailored to your specific process? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring precise temperature control and process accuracy. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and get a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















