In short, an alumina tube furnace is a high-temperature heating device used in laboratories and industry, built around a ceramic tube made of high-purity aluminum oxide (alumina). Its primary function is to heat materials to extreme temperatures, often exceeding 1500°C (2732°F), within a chemically stable and controlled environment.
The core value of an alumina tube furnace lies in the unique properties of its central tube. The alumina provides exceptional heat resistance and chemical inertness, making it the tool of choice for sensitive processes that would contaminate or destroy lesser materials.
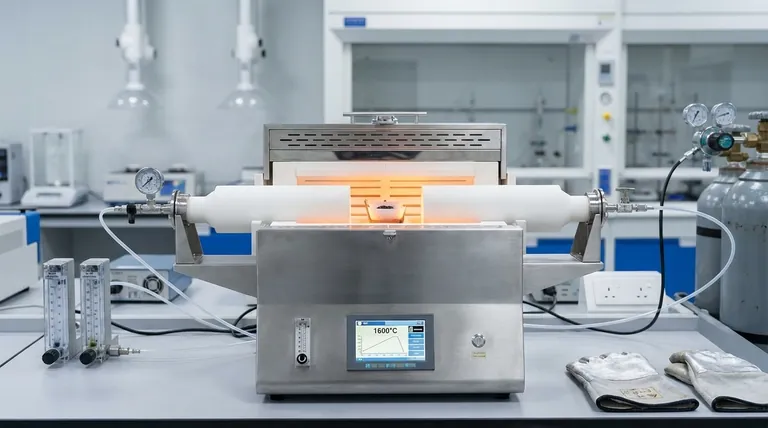

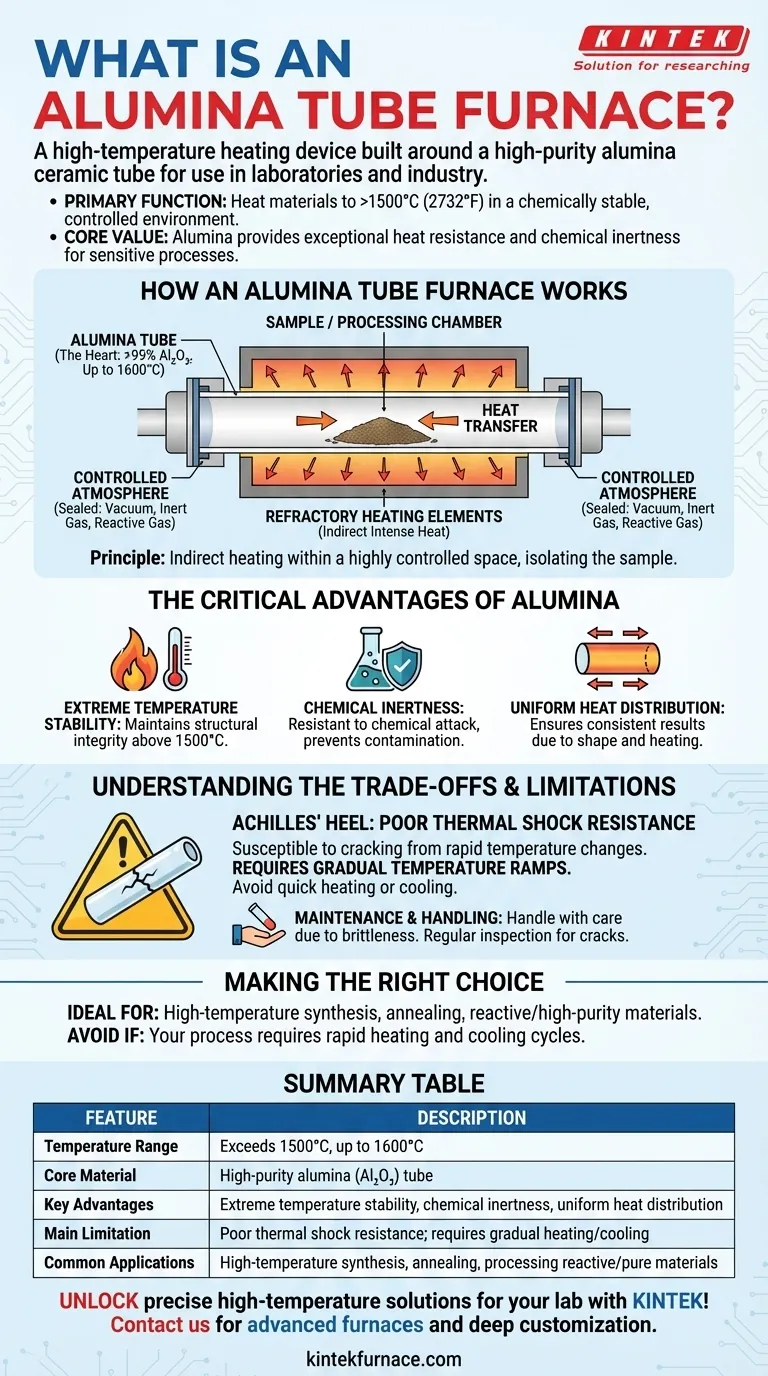
How an Alumina Tube Furnace Works
An alumina tube furnace operates on a simple yet effective principle: indirect heating within a highly controlled space. The design centers on isolating the sample from the heating elements.
The Core Component: The Alumina Tube
The heart of the furnace is its tube, which is composed of over 99% pure alumina (Al₂O₃). This high purity gives the tube its remarkable ability to withstand continuous working temperatures up to 1600°C.
Materials or samples are placed inside this tube, which acts as the processing chamber.
The Heating Mechanism
Refractory heating elements are positioned around the exterior of the alumina tube. These elements generate intense heat, which is transferred through the tube wall to the sample inside.
This indirect method ensures the sample is heated uniformly without direct contact with the heating elements, which could cause contamination.
Achieving a Controlled Environment
The tube can be sealed at both ends, allowing operators to control the internal atmosphere. This enables processes to be run under a vacuum, in an inert gas like argon, or in a reactive gas environment, preventing unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation.
The Critical Advantages of Alumina
The choice to use an alumina tube is deliberate and delivers key benefits for specialized applications.
Extreme Temperature Stability
Alumina's primary advantage is its excellent performance at very high temperatures. It maintains its structural integrity and stability where metals or other ceramics would fail.
Chemical Inertness
The high-purity ceramic is highly resistant to chemical attack. This makes it ideal for processing reactive substances without the risk of the tube material leaching into or reacting with the sample.
Uniform Heat Distribution
The cylindrical shape of the tube and the surrounding heating elements promote an even distribution of heat along its length. This ensures consistent and predictable results for the material being processed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, an alumina tube furnace is a specialized tool with a critical vulnerability that demands careful operation.
The Achilles' Heel: Poor Thermal Shock Resistance
The single most important limitation of alumina is its susceptibility to thermal shock. Rapid changes in temperature—either heating up or cooling down too quickly—can cause the ceramic tube to crack.
This requires operators to use programmed, gradual temperature ramps. A furnace cannot be quickly heated or opened at high temperatures without risking catastrophic failure of the tube.
Maintenance and Handling
Due to its brittle nature, the alumina tube must be handled with care. Regular inspection for micro-cracks is essential for safe operation. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for heating and cooling rates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting an alumina tube furnace requires matching its specific strengths and weaknesses to your processing goals.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature synthesis or annealing: The furnace's stability above 1500°C makes it an ideal choice for creating or modifying advanced materials.
- If you are working with highly reactive or high-purity materials: The chemical inertness of the alumina tube is non-negotiable for preventing sample contamination.
- If your process requires rapid heating and cooling cycles: An alumina tube furnace is likely the wrong tool, and you should investigate furnaces with quartz tubes or metallic heating chambers that better tolerate thermal shock.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently determine if an alumina tube furnace is the right instrument for your precise material processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Exceeds 1500°C, up to 1600°C |
| Core Material | High-purity alumina (Al₂O₃) tube |
| Key Advantages | Extreme temperature stability, chemical inertness, uniform heat distribution |
| Main Limitation | Poor thermal shock resistance; requires gradual heating/cooling |
| Common Applications | High-temperature synthesis, annealing, processing reactive/pure materials |
Unlock precise high-temperature solutions for your lab with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced furnaces like Alumina Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your material processing efficiency and achieve contamination-free results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















