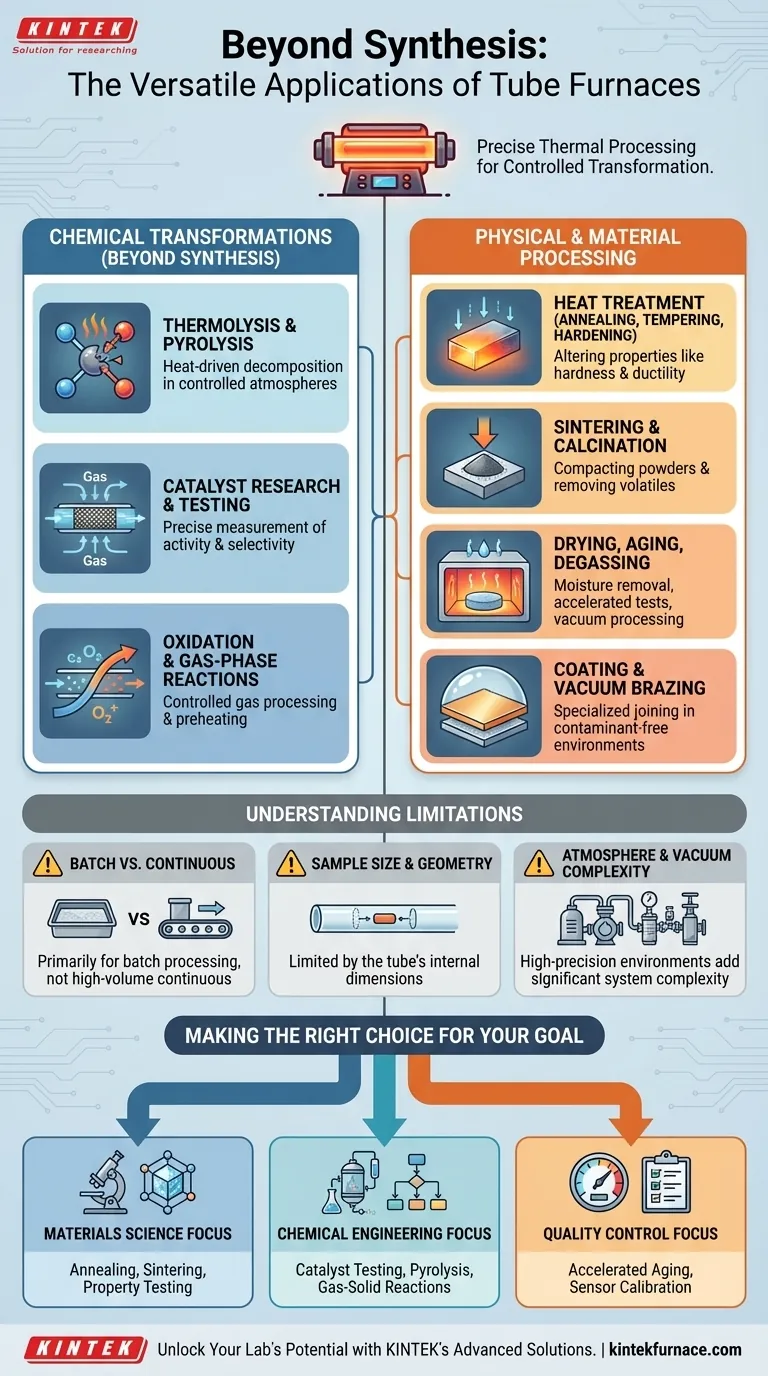
Beyond synthesis and purification, the applications for a tube furnace span a vast range of chemical reactions and physical material treatments. Core uses include chemical decomposition (thermolysis), altering material properties through heat treatment (annealing, tempering), and advanced materials testing for industries like aerospace and energy.
A tube furnace is fundamentally a tool for precise thermal processing. Its value extends far beyond creating or cleaning substances; it is designed to control the physical and chemical transformation of materials in a highly regulated atmosphere.

Chemical Transformations Beyond Synthesis
While synthesis involves building molecules, a tube furnace is equally adept at controlled decomposition and reaction analysis.
Thermolysis and Pyrolysis
Thermolysis is the decomposition of a material through heat. A tube furnace provides the precise, uniform temperature required for these reactions.
A classic example is the preparation of ketenes from acetone vapor, a process that requires a specialized high-temperature setup often called a "ketene lamp." Similarly, processes like hydrogen pyrolysis use the furnace to break down substances in a hydrogen-rich atmosphere.
Catalyst Research and Testing
The controlled environment of a tube furnace is ideal for catalyst research. Researchers can pass specific reactant gases over a catalyst bed at a set temperature and flow rate.
This allows for the precise measurement of catalyst activity, selectivity, and lifespan under various operating conditions.
Oxidation and Gas-Phase Reactions
By introducing a controlled flow of a reactive gas, such as oxygen, a tube furnace can be used for specific oxidation reactions.
It's also used for general gas processing and preheating, where a gas must reach a specific temperature before entering another part of a system.
Physical and Material Processing
Many key applications involve changing the physical structure and properties of a material, not its chemical identity.
Annealing, Tempering, and Hardening
These are all heat treatment processes used to alter the properties of metals and other materials.
Annealing reduces hardness and increases ductility, making a material easier to work with. Tempering reduces the brittleness of a hardened material, while hardening increases its strength. The precise temperature control of a tube furnace is critical for achieving the desired outcome.
Sintering and Calcination
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat and pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction. It's essential in ceramics and powder metallurgy.
Calcination involves heating a solid to high temperatures to remove volatile substances, such as driving water out of hydrates or carbon dioxide from calcium carbonate.
Drying, Aging, and Degassing
In a more straightforward application, a tube furnace can serve as a high-performance oven. It's used for drying samples, performing accelerated aging tests, or degassing components by heating them under a vacuum to remove trapped gases.
Coating and Brazing
The controlled atmosphere is also crucial for specialized joining and coating processes. Vacuum brazing uses the furnace to join materials without introducing atmospheric contaminants that could weaken the bond. Certain coating processes also rely on high-temperature, controlled environments.
Understanding the Limitations
While incredibly versatile, a tube furnace is not the right tool for every thermal process.
Batch vs. Continuous Throughput
Most laboratory-scale tube furnaces are designed for batch processing. They are not ideal for high-volume, continuous manufacturing, which requires different industrial furnace designs.
Sample Size and Geometry
The defining characteristic is the tube. This inherently limits the size and shape of the samples you can process. It is perfectly suited for powders, small components, or flowing gases, but not for large, bulky objects.
Atmosphere and Vacuum Complexity
Achieving and maintaining a highly specific atmosphere—such as an ultra-high vacuum or a precise partial pressure of a reactive gas—adds significant complexity and cost. The seals, pumps, and gas delivery systems are as critical as the furnace itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application will determine which function of the tube furnace is most critical.
- If your primary focus is materials science: You will primarily use the furnace for annealing, sintering, and testing the physical properties of new alloys or ceramics.
- If your primary focus is chemical engineering: You will leverage the furnace's controlled environment for catalyst testing, pyrolysis studies, and analyzing gas-solid reactions.
- If your primary focus is quality control or calibration: You will rely on the furnace's thermal stability for accelerated aging studies and the precise calibration of temperature sensors like thermocouples.
Ultimately, the tube furnace is a foundational tool whose versatility is limited only by the process you design for it.
Summary Table:
| Application Type | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Chemical Transformations | Thermolysis, pyrolysis, catalyst research, oxidation, gas-phase reactions |
| Physical/Material Processing | Annealing, tempering, hardening, sintering, calcination, drying, aging, degassing, coating, brazing |
| Limitations | Batch processing, sample size/geometry constraints, atmosphere/vacuum complexity |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line—including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—tailored for precise thermal processing in chemical engineering, materials science, and quality control. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















