In simple terms, a vacuum tube furnace is a high-temperature oven that removes air before the heating process begins. This specialized device uses a sealed tube and a vacuum pump system to create a controlled environment, making it essential for processes where materials must be protected from oxidation or other atmospheric contamination at extreme temperatures.
The true value of a vacuum tube furnace isn't just its ability to get hot; it's the power to control the chemical environment. By removing air, you prevent unwanted reactions, enabling the creation of purer materials with superior properties that would be impossible to achieve in a standard furnace.

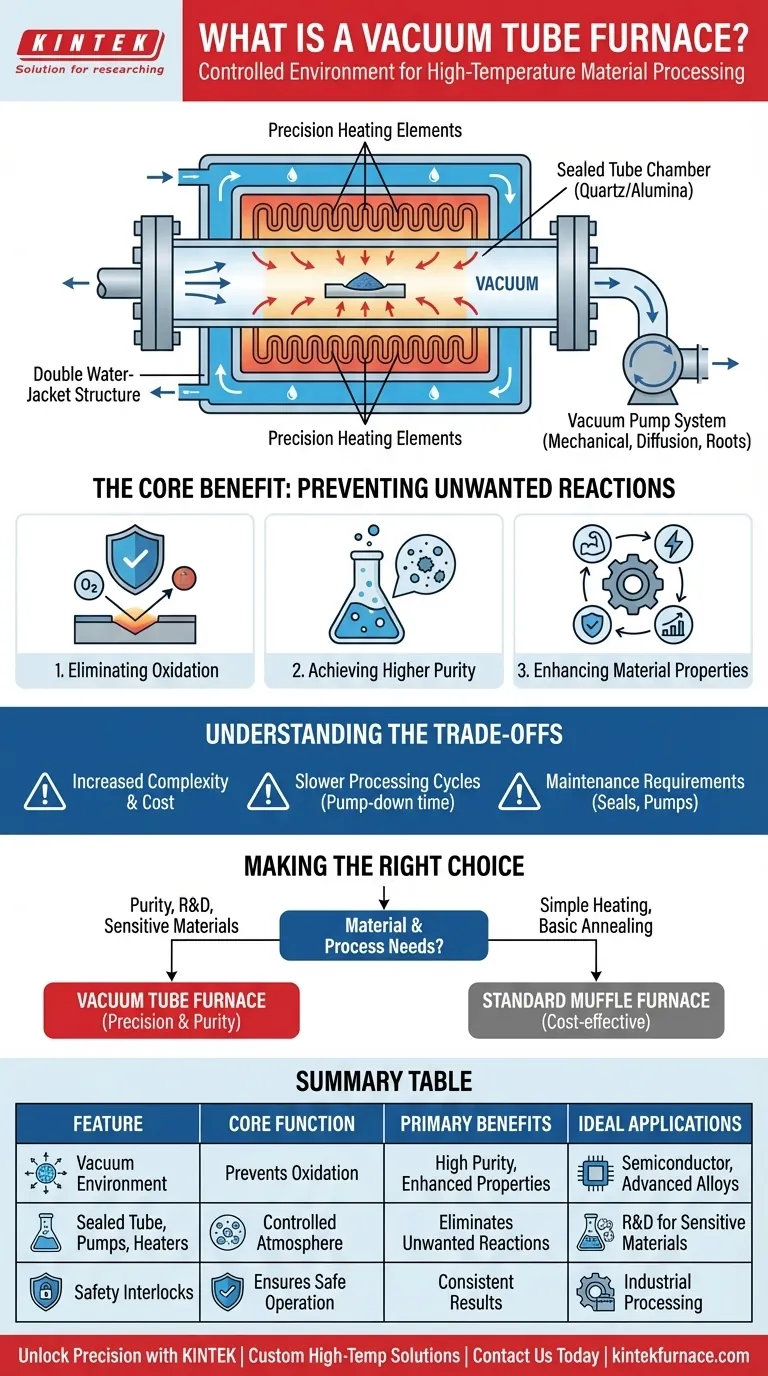
How It Achieves a Controlled Environment
A vacuum tube furnace is not just a heater; it is a complete environmental system. Its design is centered on creating and maintaining a highly controlled, low-pressure atmosphere.
The Sealed Tube Chamber
The core of the furnace is a processing tube, typically made of quartz (for temperatures up to ~1200°C) or corundum/alumina (for higher temperatures). This tube acts as the sealed chamber for the material being processed.
Stainless steel sealing flanges are attached to both ends of the tube. These flanges contain ports for connecting vacuum pumps and gas inlets, creating an airtight seal that isolates the internal environment.
The Vacuum System
To create the vacuum, a system of pumps removes the air from the sealed tube. This often involves a multi-stage process depending on the required vacuum level.
A mechanical pump (or "roughing pump") performs the initial evacuation. For a deeper vacuum, a diffusion pump or Roots pump is used in sequence to remove remaining air molecules, reaching vacuum levels as low as 7 × 10⁻³ Pa.
Precision Heating and Safety
Heating elements surround the outside of the tube, ensuring uniform temperature distribution along its length. The entire furnace assembly is often housed in a double water-jacket structure, which keeps the external surfaces cool and provides structural integrity.
Safety interlocks and over-temperature protection are standard, preventing overheating and ensuring the system operates within safe parameters.
The Core Benefit: Preventing Unwanted Reactions
The primary reason to use a vacuum furnace is to manage chemical reactions that occur at high temperatures. Removing the atmosphere fundamentally changes the outcome of the process.
Eliminating Oxidation
At high temperatures, most materials readily react with oxygen in the air. This process, oxidation, can create unwanted oxide layers, compromise material integrity, or cause surface defects.
By operating in a vacuum, you remove the oxygen, effectively preventing oxidation and preserving the material's intended composition.
Achieving Higher Purity
Air isn't just oxygen; it contains nitrogen, moisture, and other trace gases that can act as contaminants. A vacuum environment removes these impurities from the process chamber.
This results in a final product with significantly higher purity, which is critical for applications like semiconductor manufacturing and producing advanced alloys.
Enhancing Material Properties
The absence of contamination and unwanted side reactions allows for the formation of materials with superior and more consistent properties. This includes enhanced mechanical strength, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vacuum tube furnace is a specialized tool with specific considerations. It is not the right choice for every high-temperature application.
Increased Complexity and Cost
Vacuum systems, including pumps, gauges, and high-integrity seals, are more complex and expensive than the components of a standard atmospheric furnace.
Slower Processing Cycles
Achieving a high vacuum is not instantaneous. The time required for the pumps to evacuate the chamber—known as the "pump-down time"—adds to the total processing cycle, potentially reducing throughput.
Maintenance Requirements
The seals, pumps, and vacuum gauges require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure the system can consistently achieve and hold the desired vacuum level. Leaks can compromise the entire process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace depends entirely on the requirements of your material and your process.
- If your primary focus is material purity and preventing oxidation: A vacuum tube furnace is the correct choice, especially for sensitive materials like advanced alloys, reactive metals, or electronic components.
- If your primary focus is research and development: This furnace is essential for R&D, as it allows for precise control over the atmospheric conditions needed to test and develop new materials.
- If your primary focus is simple heating without atmospheric sensitivity: A standard atmospheric muffle furnace is a more cost-effective and simpler solution for processes like basic annealing or drying.
Ultimately, a vacuum tube furnace is the definitive tool for achieving precision and purity in high-temperature material processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Creates a vacuum environment to prevent oxidation and contamination during high-temperature processes |
| Key Components | Sealed tube (quartz or alumina), vacuum pump system, heating elements, safety interlocks |
| Primary Benefits | Eliminates unwanted reactions, achieves high material purity, enhances properties like strength and conductivity |
| Ideal Applications | Semiconductor manufacturing, advanced alloy production, R&D for sensitive materials |
| Considerations | Higher cost, slower cycles, and regular maintenance due to vacuum system complexity |
Unlock Precision and Purity in Your Lab with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in semiconductor development, materials research, or industrial processing, our vacuum tube furnaces deliver reliable performance and superior results.
Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs and elevate your material processing capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Choose the Right Tube for Your Lab
- What is the primary function of a vacuum-sealed quartz tube in MnBi2Te4 growth? Ensure High-Purity Crystal Synthesis
- What is the primary function of high-purity quartz sealed tubes? Master Sb-Te Alloy Synthesis with Precision Isolation
- What is the working principle of a vacuum tube furnace? Master Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the function of high-vacuum encapsulated quartz tubes for Ce2(Fe, Co)17? Ensure Phase Purity and Stability



















