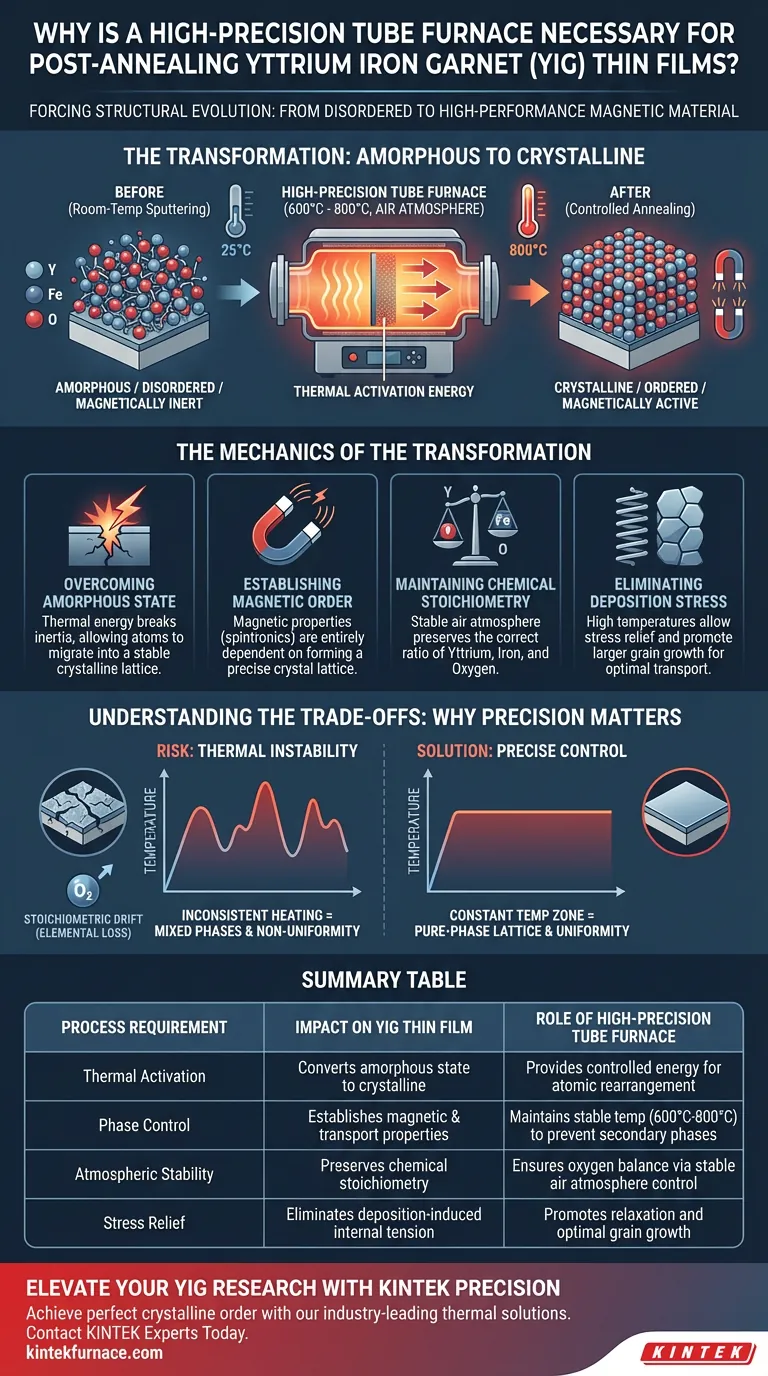
The necessity of a high-precision tube furnace lies in its ability to force a structural evolution, converting Yttrium Iron Garnet (YIG) thin films from a disordered, non-functional state into a high-performance magnetic material.
When YIG films are deposited via sputtering at room temperature, they land on the substrate in an amorphous state. They lack the crystalline structure required for magnetic activity. To fix this, the film must be subjected to a strictly controlled post-annealing process, typically between 600°C and 800°C in an air atmosphere, to supply the thermal activation energy needed for atomic rearrangement.
The Core Insight Room-temperature deposition is only half the battle; the resulting film is structurally disordered and magnetically inert. The tube furnace provides the thermal activation energy required to reorganize random atoms into a precise lattice, physically "switching on" the material's magnetic and transport properties.

The Mechanics of the Transformation
Overcoming the Amorphous State
Freshly sputtered YIG films are amorphous, meaning their atomic structure lacks long-range order. Without this order, the material cannot exhibit its defining characteristics.
The tube furnace supplies specific thermal activation energy. This energy breaks the inertia of the frozen, disordered atoms, allowing them to migrate and lock into a thermodynamically stable, crystalline lattice.
Establishing Magnetic Order
The transition from amorphous to crystalline is not merely structural; it is functional. The magnetic order of YIG—essential for its use in spintronics and microwave devices—is entirely dependent on this crystal lattice.
Until the film undergoes this high-temperature treatment, it possesses no significant magnetic properties. The furnace ensures the formation of the specific single-crystal or polycrystalline phases that dictate the film's performance.
Maintaining Chemical Stoichiometry
The annealing process requires more than just heat; it requires a specific environment. For YIG, this typically involves annealing in air.
A high-precision furnace maintains a stable atmosphere that preserves the film's chemical stoichiometry. This ensures the ratio of Yttrium, Iron, and Oxygen remains correct during the intense heating process, preventing the degradation of the material's magnetic signature.
Eliminating Deposition Stress
Films deposited at room temperature often harbor significant internal stresses. The controlled thermal environment acts as a stress-relief mechanism.
By holding the film at high temperatures, the furnace allows the material to relax. This eliminates internal tension and promotes the growth of larger grain sizes, which is critical for optimizing transport properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Thermal Instability
While high heat is necessary, fluctuating heat is destructive. If the furnace cannot maintain a constant temperature zone, the crystallization will be uneven.
Inconsistent heating rates or unstable dwell times can lead to mixed phases, where parts of the film remain amorphous or crystallize into unwanted secondary phases, ruining the device's uniformity.
Stoichiometric Drift
Precision is also required to prevent elemental loss. While YIG is annealed in air, other similar processes (as noted in comparative materials) often require vacuum or inert gas to prevent volatilization.
For YIG, the challenge is ensuring the oxygen content remains balanced. If the temperature overshoots the target window of 600°C–800°C without precise control, you risk altering the material's composition or damaging the substrate interface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct thermal processing strategy, you must define your end-goal requirements.
- If your primary focus is Basic Crystallization: Ensure your furnace can reliably reach and hold temperatures between 600°C and 800°C to force the amorphous-to-crystalline phase shift.
- If your primary focus is High-Performance Spintronics: Prioritize a furnace with exceptional thermal stability and atmospheric control to ensure a pure-phase lattice with perfect magnetic order.
Success in YIG fabrication depends not just on depositing the right atoms, but on heating them with enough precision to find their intended home.
Summary Table:
| Process Requirement | Impact on YIG Thin Film | Role of High-Precision Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Activation | Converts amorphous state to crystalline | Provides controlled energy for atomic rearrangement |
| Phase Control | Establishes magnetic & transport properties | Maintains stable temp (600°C-800°C) to prevent secondary phases |
| Atmospheric Stability | Preserves chemical stoichiometry | Ensures oxygen balance via stable air atmosphere control |
| Stress Relief | Eliminates deposition-induced internal tension | Promotes relaxation and optimal grain growth |
Elevate Your YIG Research with Precision Thermal Processing
Don't let unstable heating ruin your thin film's magnetic potential. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing. Whether you require standard or fully customizable Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, our high-temperature furnaces are engineered to deliver the precision and atmospheric control your specialized lab work demands.
Ready to achieve perfect crystalline order?
→ Contact KINTEK Experts Today
Visual Guide
References
- Sebastian Sailler, Michaela Lammel. Crystallization dynamics of amorphous yttrium iron garnet thin films. DOI: 10.1103/physrevmaterials.8.043402
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does atmosphere control in a laboratory tube furnace affect Boron Carbide powders? Optimize Your Surface Chemistry
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the conversion of Cu@ZIF-8? Master Precision Material Synthesis
- Why is a laboratory tube furnace considered essential for fabricating carbonized lignin nanofiber electrodes?
- How does the choice of liner material for a laboratory packed-bed tubular reactor impact CO2 hydrogenation experiments?
- What types of containers are used in vacuum tube furnaces? Choose Quartz or Corundum for Optimal Performance
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for the secondary activation of KBC? Achieve Precision Pore Structure
- What are some key features of a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Precision Control for Superior Thermal Processing
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in flash annealing Mg/SiOx? Precision for Advanced Anode Synthesis



















