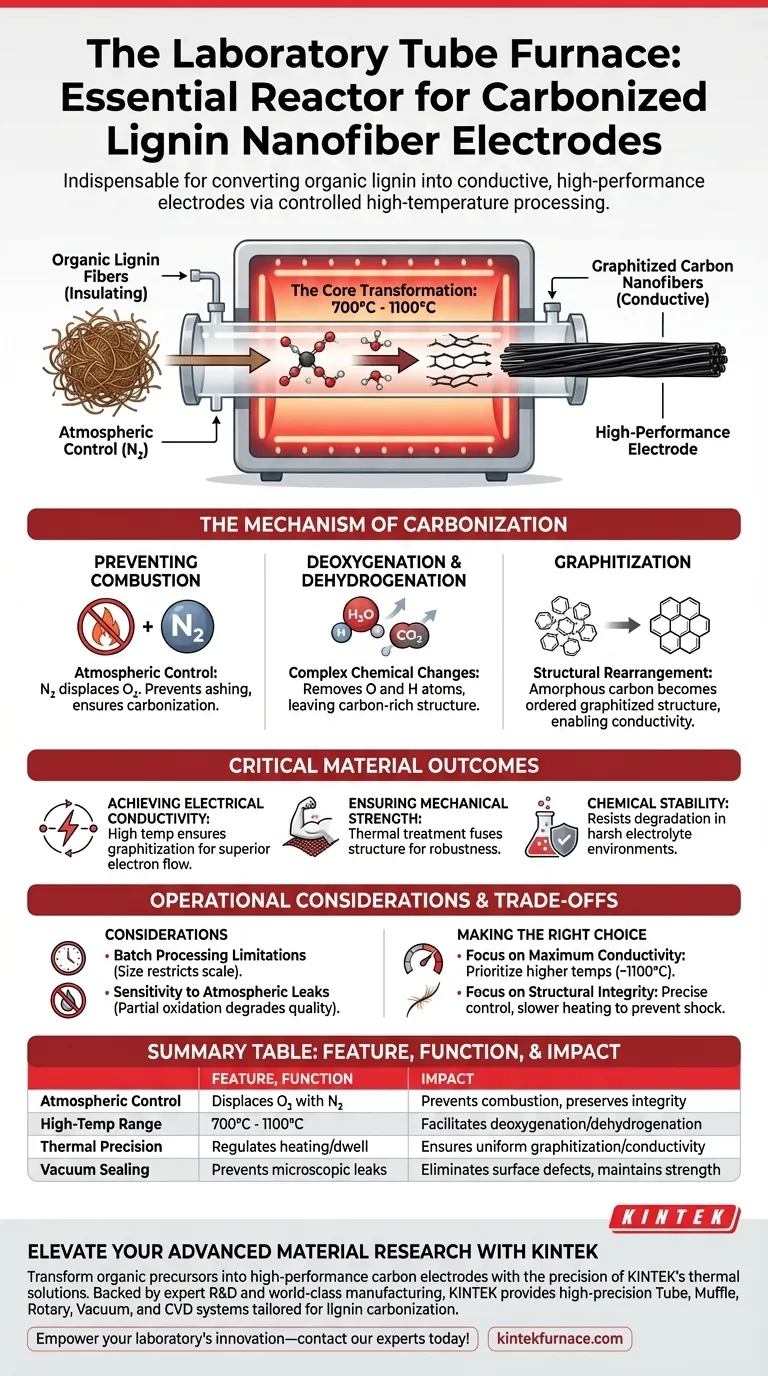
A laboratory tube furnace is the indispensable reactor required to convert organic lignin fibers into functional, conductive carbon electrodes. It provides a strictly controlled, high-temperature environment sealed with an inert gas, which is the only way to fundamentally alter the chemical structure of lignin without destroying it.
The Core Transformation The tube furnace facilitates the critical processes of deoxygenation and dehydrogenation at temperatures between 700°C and 1100°C under a nitrogen atmosphere. This specific environment is required to convert insulating lignin into a graphitized carbon structure, imparting the electrical conductivity and mechanical stability necessary for high-performance electrodes.

The Mechanism of Carbonization
preventing Combustion
The primary function of the tube furnace in this application is atmospheric control.
Lignin is an organic polymer; if heated in regular air, it would simply burn and turn to ash.
The tube furnace allows for a nitrogen protective atmosphere, displacing oxygen to ensure the material undergoes carbonization rather than combustion.
Deoxygenation and Dehydrogenation
Inside the furnace, the stabilized lignin fibers undergo complex chemical changes.
The heat drives off non-carbon elements, specifically removing oxygen and hydrogen atoms from the polymer chain.
This process, known as deoxygenation and dehydrogenation, leaves behind a carbon-rich skeletal structure.
Graphitization
As the temperature rises, the remaining carbon atoms rearrange themselves.
They transition from a disordered amorphous state into an ordered graphitized carbon structure.
This structural reordering is the key factor that turns the fiber from an insulator into a conductor.
Critical Material Outcomes
Achieving Electrical Conductivity
The utility of an electrode is defined by how well it conducts electricity.
The tube furnace's ability to reach and maintain temperatures up to 1100°C ensures a high degree of graphitization.
This directly results in the superior electrical conductivity required for electrochemical applications.
Ensuring Mechanical Strength
Carbonized fibers must withstand physical handling and operational stress.
The thermal treatment fuses the carbon structure, significantly enhancing the mechanical strength of the final nanofiber mat.
Chemical Stability
Electrodes often operate in harsh chemical environments (electrolytes).
The high-temperature processing renders the carbonized lignin chemically stable, preventing it from degrading during battery or capacitor cycling.
Operational Considerations and Trade-offs
Batch Processing Limitations
While tube furnaces offer precision, they are typically limited by the size of the tube.
This often restricts production to batch processing rather than continuous manufacturing, which can be a bottleneck for scaling up production.
Sensitivity to Atmospheric Leaks
The quality of the electrode is entirely dependent on the integrity of the seal.
Even a microscopic leak in the atmospheric sealing can introduce oxygen.
This results in partial oxidation, which creates surface defects that may degrade conductivity and mechanical integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring your tube furnace protocols for lignin carbonization, consider your specific performance targets:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Conductivity: Prioritize temperatures at the higher end of the range (near 1100°C) to maximize graphitization and electron mobility.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Ensure precise temperature control and potentially slower heating rates to prevent thermal shock and fiber breakage during the volatile release phases.
The laboratory tube furnace is not just a heater; it is a precision instrument that dictates the final electrochemical identity of your material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Lignin Carbonization | Impact on Electrode Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric Control | Displaces oxygen with inert Nitrogen gas | Prevents combustion/ashing; preserves material integrity |
| High-Temp Range | Operates between 700°C and 1100°C | Facilitates deoxygenation and dehydrogenation |
| Thermal Precision | Regulates heating rates and dwell times | Ensures uniform graphitization and electrical conductivity |
| Vacuum Sealing | Prevents microscopic oxygen leaks | Eliminates surface defects and maintains mechanical strength |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Research with KINTEK
Transform your organic precursors into high-performance carbon electrodes with the precision of KINTEK’s thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-precision Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for the rigorous demands of lignin carbonization and nanofiber fabrication.
Whether you need customizable atmospheric control for oxygen-free processing or high-temperature stability for maximum graphitization, our lab furnaces are built to deliver consistent, reproducible results. Empower your laboratory’s innovation—contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace for your unique research needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Reima Herrala, Jaana Vapaavuori. Functionalizing Lignin‐Based Nanofiber Electrodes with Gold Using Electrochemically Assisted Aqueous Reduction. DOI: 10.1002/admi.202400748
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of a horizontal electric furnace? Achieve Superior Process Control and Accessibility
- What is the temperature of a tube furnace? Selecting the Right High-Temp Solution for Your Lab
- Why is an Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV) compatible tube furnace necessary for beta-Ga2O3? Protect Your Semiconductor Integrity
- What role does a vacuum tube furnace play in AlCrSiWN coating annealing? Enhance Stability and Hardness
- What advantages does a drop tube furnace offer over other types of furnaces? Unlock Precision in Particle Thermal Analysis
- What factors influence the processing time in a rotary tube furnace? Master Control for Efficient Heat Treatment
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a three-zone furnace? Ensure Precision and Efficiency for Your Thermal Processes
- Why choose a vertical tube furnace over a horizontal tube furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Purity



















