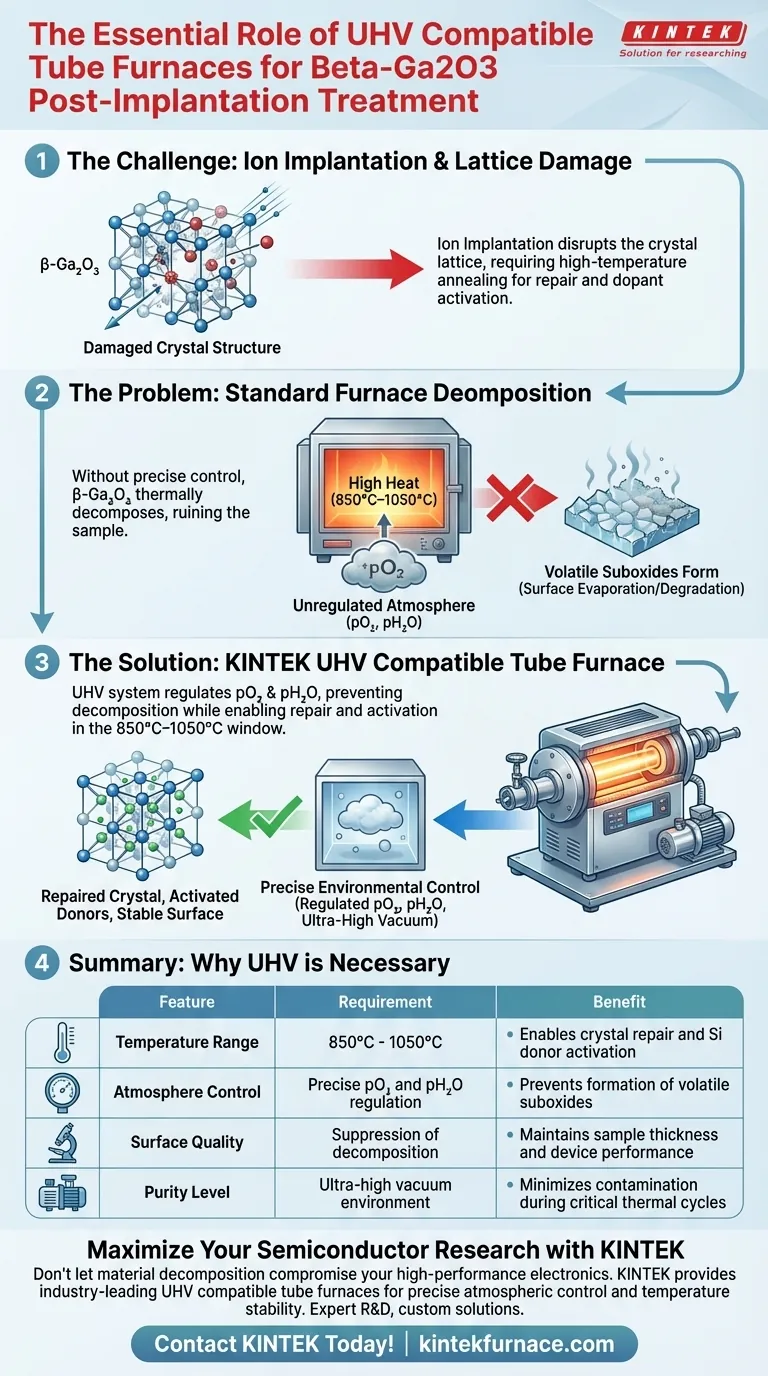
The necessity of an Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV) compatible tube furnace stems from the critical need for environmental purity during the high-temperature processing of beta-gallium oxide ($\beta$-Ga$_2$O$_3$). Specifically, this equipment allows you to repair crystal damage and activate dopants while strictly regulating oxygen partial pressure ($pO_2$) and water vapor ($pH_2$O) to prevent the material from physically decomposing.
Core Takeaway Successful post-implantation treatment of $\beta$-Ga$_2$O$_3$ requires a precise thermal "balancing act." A UHV compatible furnace provides the specific environmental controls necessary to heal the crystal lattice at high temperatures without triggering the chemical breakdown of the substrate into volatile suboxides.
The Dual Objectives of Thermal Treatment
To understand why specialized equipment is required, you must first understand what the thermal process is trying to achieve inside the material.
Repairing Structural Damage
Ion implantation is a violent process at the atomic level. It introduces dopants but simultaneously disrupts the crystal lattice of the semiconductor.
To fix this, the material must undergo high-temperature annealing. The thermal energy allows atoms to migrate back into their correct positions, restoring the structural integrity of the crystal.
Activating Silicon Donors
Structural repair is only half the battle; electrical activation is the other.
The reference highlights that silicon donors—critical for the material's electrical conductivity—must be "activated." This activation occurs effectively only within a specific high-temperature window, typically between 850°C and 1050°C.
The Stability Challenge: Preventing Decomposition
The primary reason a standard furnace is insufficient lies in the chemical instability of $\beta$-Ga$_2$O$_3$ at these necessary activation temperatures.
The Threat of Volatile Suboxides
When $\beta$-Ga$_2$O$_3$ is heated to the 850°C–1050°C range, it becomes thermodynamically unstable.
Without precise environmental control, the material tends to decompose. It breaks down into "volatile suboxides," meaning the surface of your sample effectively evaporates or degrades, ruining the device's potential performance.
Controlling Partial Pressures
This is where the UHV compatible architecture becomes non-negotiable.
The system does not just provide heat; it provides a tightly controlled atmosphere. By regulating the oxygen partial pressure ($pO_2$) and water vapor content ($pH_2$O), the furnace creates an overpressure or equilibrium that counteracts the material's tendency to decompose.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While UHV compatible furnaces are essential for quality, they introduce specific operational considerations.
Complexity vs. Yield
UHV systems are significantly more complex and expensive to operate than standard atmospheric furnaces. However, using simpler equipment often leads to surface degradation, which compromises the electrical properties you are trying to create.
Temperature Constraints
The window for success is narrow. Operating below 850°C may fail to fully activate silicon donors or repair lattice damage. Operating above 1050°C drastically increases the risk of decomposition, requiring even stricter control over the partial pressures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring your annealing process for $\beta$-Ga$_2$O$_3$, consider your primary objectives:
- If your primary focus is Electrical Performance: Ensure your furnace can reach at least 850°C to guarantee the activation of silicon donors.
- If your primary focus is Surface Integrity: Prioritize the precision of the $pO_2$ and $pH_2$O regulation to suppress the formation of volatile suboxides.
By utilizing a UHV compatible tube furnace, you transform a destructive high-heat environment into a constructive one, securing both the structure and function of your semiconductor.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Requirement for $\beta$-Ga$_2$O$_3$ | Benefit of UHV System |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 850°C - 1050°C | Enables crystal repair and Si donor activation |
| Atmosphere Control | Precise $pO_2$ and $pH_2$O regulation | Prevents formation of volatile suboxides |
| Surface Quality | Suppression of decomposition | Maintains sample thickness and device performance |
| Purity Level | Ultra-high vacuum environment | Minimizes contamination during critical thermal cycles |
Maximize Your Semiconductor Research with KINTEK
Don't let material decomposition compromise your high-performance electronics. KINTEK provides industry-leading UHV compatible tube furnaces designed to deliver the precise atmospheric control and temperature stability required for $\beta$-Ga$_2$O$_3$ and other advanced materials.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a full range of Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific research or production parameters.
Ready to achieve superior annealing results? Contact us today to discuss your unique needs with our technical team!
Visual Guide
References
- Katie R. Gann, Michael O. Thompson. Silicon implantation and annealing in <i>β</i>-Ga2O3: Role of ambient, temperature, and time. DOI: 10.1063/5.0184946
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the specific role of a tube furnace in the synthesis of N-C nanosheet arrays? Essential Thermal Processing Guide
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for sulfide solid electrolytes? Boost Your Battery Research Performance
- What are the advantages of using an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace for FTO thin film annealing?
- What are some key features of a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Precision Control for Superior Thermal Processing
- Why is temperature range important when choosing a tube furnace? It Dictates Cost, Materials, and Performance
- How does a Bridgman crystal growth furnace ensure the quality of (Bi2Te3)1-c(Sb2Te)c crystals? Master Precision Growth
- Why are three-zone tube furnaces in high demand? Unlock Precision for Advanced Materials
- What is the necessity of the 500 °C hydrogen environment provided by a tube reduction furnace? Master Catalyst Activation



















