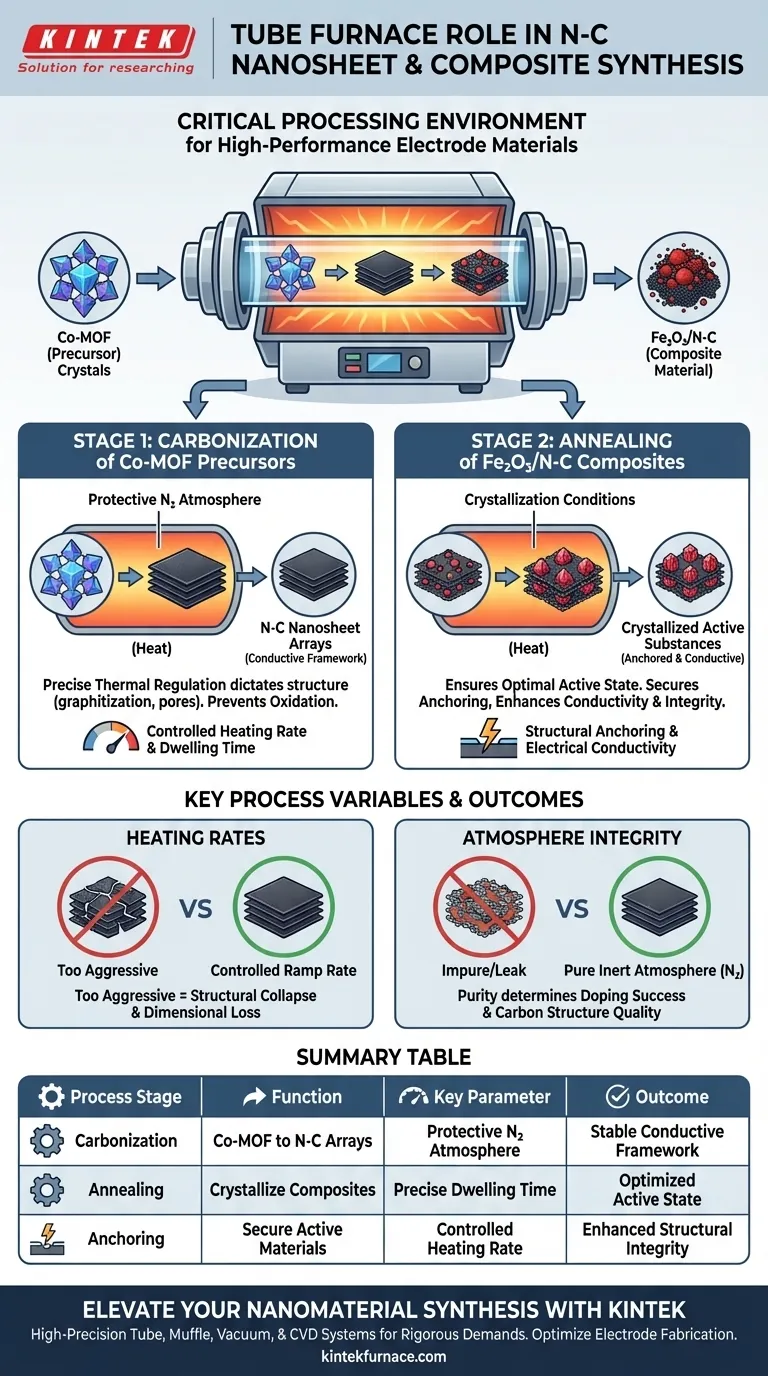
The tube furnace serves as the critical processing environment for converting metal-organic framework (MOF) precursors into high-performance nitrogen-doped carbon (N-C) nanosheet arrays. It specifically facilitates two distinct stages: the initial carbonization of Co-MOF precursors under a protective nitrogen atmosphere and the subsequent annealing of Fe2O3/N-C composite materials to crystallize active substances.
The tube furnace provides the precise thermal control necessary to anchor active materials onto a conductive framework, ensuring the final electrode possesses both high structural integrity and superior electrical conductivity.

Mechanisms of Synthesis and Transformation
Carbonization of Precursors
The primary function of the tube furnace in this context is the carbonization of Co-MOF precursors.
This process transforms the raw precursor material into three-dimensional N-C nanosheet arrays.
To prevent unwanted oxidation and ensure proper chemical conversion, this stage must be conducted under a protective nitrogen atmosphere.
Precise Thermal Regulation
Success in this synthesis relies on the furnace's ability to maintain precise control over the heating rate and dwelling time.
These thermal parameters dictate the evolution of the material's structure.
By regulating these variables, the furnace determines the final properties of the carbon framework, influencing factors like graphitization and pore structure.
Enhancing Composite Properties via Annealing
Crystallization of Active Substances
Beyond carbonization, the tube furnace is utilized for the annealing of Fe2O3/N-C composite materials.
During this heat treatment, the furnace creates the thermodynamic conditions required to facilitate the crystallization of active substances.
This step ensures that the chemical components reach their optimal active state for electrochemical performance.
Structural Anchoring and Conductivity
A critical outcome of this annealing process is the secure anchoring of active substances onto the conductive carbon framework.
This connection is vital for maintaining the electrode's structural integrity, preventing degradation during use.
Furthermore, this integration optimizes the electrical conductivity of the composite, which is essential for its application in energy storage or conversion devices.
Understanding the Process Variables
The Importance of Heating Rates
While the tube furnace enables high temperatures, the heating ramp rate is just as critical as the final temperature.
If the heating rate is too aggressive, it can compromise the dimensional accuracy and lead to structural collapse of the nanosheets.
Atmosphere Integrity
The effectiveness of the carbonization process is entirely dependent on the purity of the inert atmosphere.
Even minor leaks or fluctuations in the nitrogen flow within the tube furnace can lead to oxidation, ruining the N-C doping mechanism and degrading the carbon structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your synthesis, align your furnace parameters with your specific material objectives:
- If your primary focus is N-C Nanosheet Formation: Prioritize precise control over heating rates and nitrogen flow to ensure the Co-MOF precursors convert into a stable, conductive 3D array.
- If your primary focus is Composite Performance: Focus on the annealing stage parameters to guarantee active substances (like Fe2O3) are fully crystallized and securely anchored to the carbon backbone.
Mastering the tube furnace parameters allows you to engineer the interface between the active material and the conductive support, directly dictating the lifespan and efficiency of your electrode.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Function in Tube Furnace | Key Parameter | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonization | Converts Co-MOF precursors into 3D N-C arrays | Protective N2 Atmosphere | Stable conductive framework |
| Annealing | Crystallizes Fe2O3/N-C composites | Precise Dwelling Time | Optimized active substance state |
| Anchoring | Secures active materials to carbon backbone | Controlled Heating Rate | Enhanced structural integrity |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise thermal control is the difference between structural collapse and high-performance conductivity. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-precision Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of carbonization and annealing.
Whether you are synthesizing N-C nanosheets or complex composites, our customizable lab high-temp furnaces ensure the atmosphere purity and ramp-rate accuracy your research requires.
Ready to optimize your electrode fabrication? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Zhiqiang Cui, Rui Tong. Rationally Designed PPy-Coated Fe2O3 Nanoneedles Anchored on N-C Nanoflakes as a High-Performance Anode for Aqueous Supercapacitors. DOI: 10.3390/cryst15040346
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the technical advantages of using a vacuum tube furnace for S53P4-NO2 glass? Achieve 100% Amorphous Results
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace used for SNCB preparation? Optimize Nitrogen-Doped Porous Carbon Synthesis
- What functions does a support frame provide in tube furnace modernization? Gain Stability and Experimental Flexibility
- How does an alumina-lined vertical tube furnace provide a stable environment for corrosion experiments? Get Expert Data
- What process environment does a drop-tube furnace system provide? Expert Simulated Waste Incineration Research
- Why is precise temperature control important in split tube furnaces? Ensure Reliable Material Processing
- What are the differences between solid tube and split type tube furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What is the necessity of a precision tube resistance furnace in molten salt electrolysis research? Ensure Unrivaled Precision & Reproducibility!



















