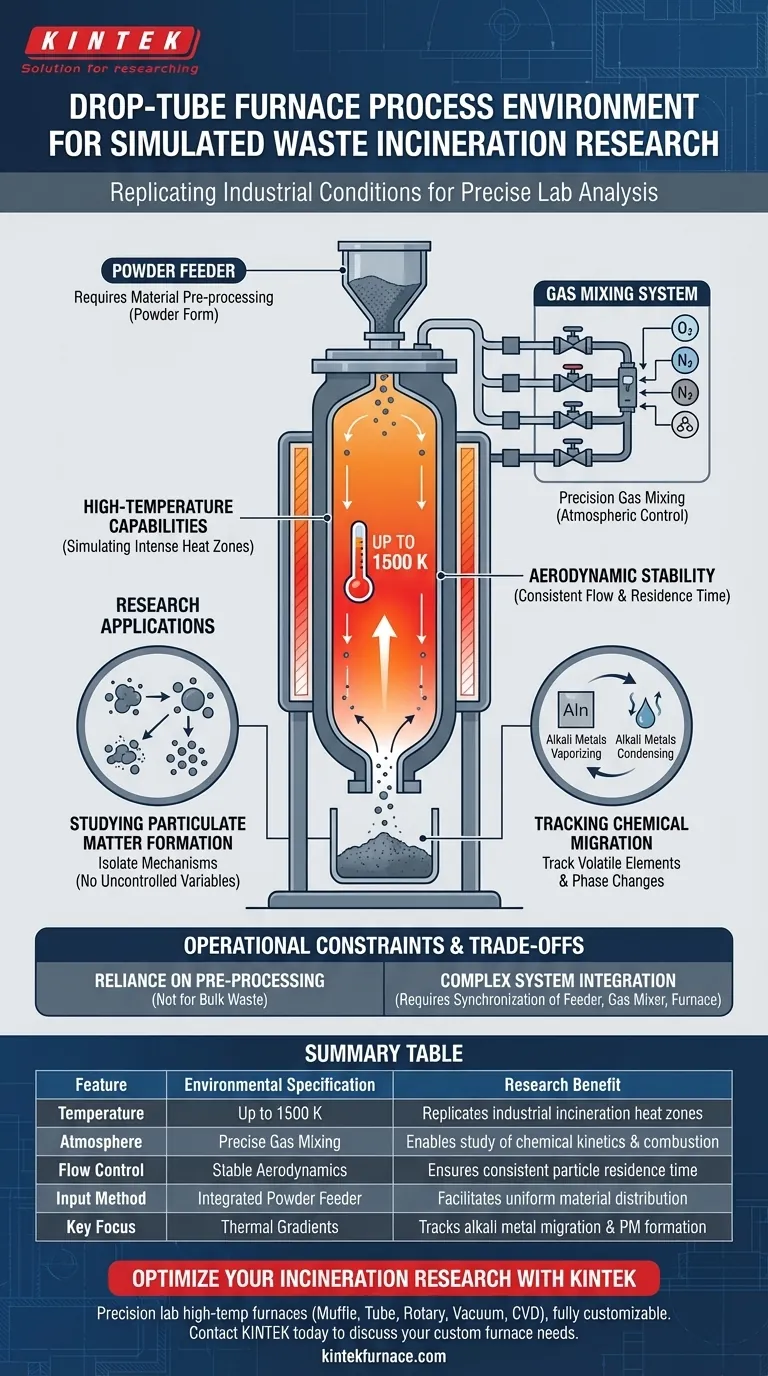
A drop-tube furnace system delivers a precisely controlled, high-temperature reaction environment designed to mimic industrial incineration conditions. By integrating a powder feeder, a gas mixing system, and a vertical reaction furnace body, it generates temperatures reaching up to 1500 K alongside specific aerodynamic profiles. This setup allows researchers to isolate and observe complex thermal and chemical behaviors, such as reaction kinetics, that occur during waste combustion.
The system’s primary value lies in its ability to replicate specific temperature distributions and gas atmospheres found in real-world incinerators. This controlled environment is essential for isolating the mechanisms behind alkali metal migration and the formation of fine particulate matter.

The Anatomy of the Thermal Environment
High-Temperature Capabilities
The core function of the drop-tube furnace is to provide a thermal regime capable of reaching 1500 K. This high-temperature capacity is critical for simulating the intense heat zones found in actual waste incineration plants, ensuring that laboratory results are relevant to industrial processes.
Replicating Thermal Distributions
Beyond raw heat, the system is designed to simulate specific temperature distributions. Rather than a static heat source, the furnace body allows researchers to model the thermal gradients a particle experiences as it moves through a combustion chamber.
Control of Atmospheric and Aerodynamic Conditions
Precision Gas Mixing
The environment is defined by its chemical composition as much as its temperature. Through an integrated gas mixing system, researchers can create specific atmospheres. This allows for the precise study of how different gas compositions affect combustion efficiency and pollutant formation.
Aerodynamic Stability
To ensure accurate data, the system provides precisely controlled aerodynamic conditions. By managing the flow within the reaction body, the system ensures that the residence time and trajectory of the powder particles are consistent and measurable.
Research Applications and Utility
Studying Particulate Matter Formation
The controlled environment is specifically optimized for investigating the mechanisms of particulate matter formation. By isolating the reaction zone, researchers can observe how solid waste transforms into fine particles without the interference of uncontrolled variables.
Tracking Chemical Migration
The system is a core tool for studying alkali metal migration. The ability to control both temperature and atmosphere allows scientists to track how these volatile elements behave, vaporize, and condense during the incineration process.
Operational Constraints and Trade-offs
Reliance on Material Pre-processing
The system explicitly integrates a powder feeder, which implies a limitation on the state of the feed material. To utilize this precise environment, waste materials must typically be processed into a powder form, meaning the system is less suited for studying bulk, unrefined waste streams.
Complexity of System Integration
Achieving this high-fidelity simulation requires the tight integration of three distinct subsystems: the feeder, the gas mixer, and the furnace body. The accuracy of the research depends entirely on the synchronization of these components; a fluctuation in gas flow or feed rate can compromise the aerodynamic control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
To leverage a drop-tube furnace effectively, align its capabilities with your specific investigative goals:
- If your primary focus is Pollutant Control: Utilize the system to isolate the specific mechanisms of particulate matter formation and alkali metal migration.
- If your primary focus is Process Optimization: Use the gas mixing and thermal controls to simulate specific incineration atmospheres and temperature distributions to test efficiency.
The drop-tube furnace provides the essential bridge between theoretical combustion chemistry and industrial-scale waste processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Environmental Specification | Research Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Up to 1500 K | Replicates industrial incineration heat zones |
| Atmosphere | Precise Gas Mixing | Enables study of chemical kinetics and combustion |
| Flow Control | Stable Aerodynamics | Ensures consistent particle residence time |
| Input Method | Integrated Powder Feeder | Facilitates uniform material distribution |
| Key Focus | Thermal Gradients | Tracks alkali metal migration and PM formation |
Optimize Your Incineration Research with KINTEK
Precision is the foundation of breakthrough environmental research. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab high-temp furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique simulation requirements. Whether you are studying particulate matter formation or alkali metal migration, our systems provide the aerodynamic stability and thermal control necessary for accurate data.
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Mingkai Cheng, Sheng Chen. The influence of alkali metals on PM10 emission characteristics during waste combustion. DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/3159/1/012001
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the sintering of phosphor ceramic blocks? Master Optical Purity
- What are the primary functions of a tube furnace for ZIF-derived materials? Optimize Carbonization & Porosity
- How can the performance of a vertical tube furnace be optimized? Boost Efficiency and Precision in Heat Treatment
- What is the purpose of performing thermal annealing in vacuum-sealed glass tubes for nickel oxide films?
- Why are vacuum tube furnaces considered valuable in various fields? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- Why Use a Programmable Tube Furnace for Ni-WOx/SAPO-11 Calcination? Ensure Catalyst Purity & Performance
- What are the types of Tube Furnaces based on tube shape? Choose Between Solid and Split for Your Lab
- What is the function of a vacuum tube furnace in NbC-Cr7C3@graphene/Fe synthesis? Expert Guide to In-Situ Synthesis



















