Optimizing a vertical tube furnace is a process of aligning its operational parameters and physical components with the specific requirements of your heat treatment task. This involves refining temperature control for uniformity, maximizing thermal efficiency, and leveraging the unique design advantages of the vertical orientation to achieve consistent, repeatable results.
True optimization goes beyond simply reaching a target temperature. It is about understanding how the furnace's control system, physical design, and material components interact to create a stable and uniform thermal environment that precisely matches the demands of your application.
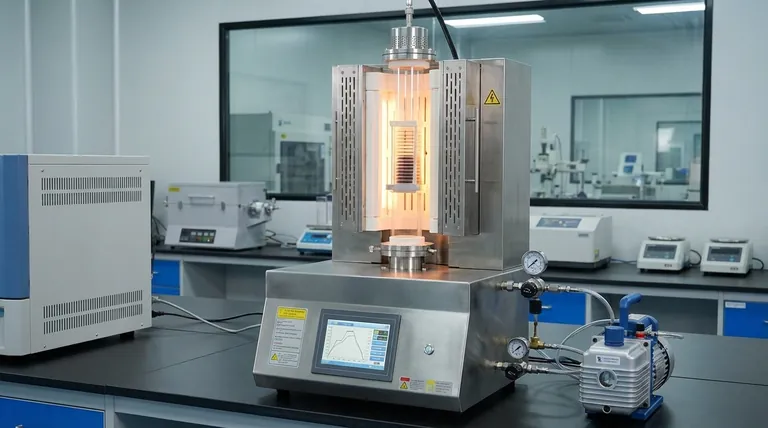

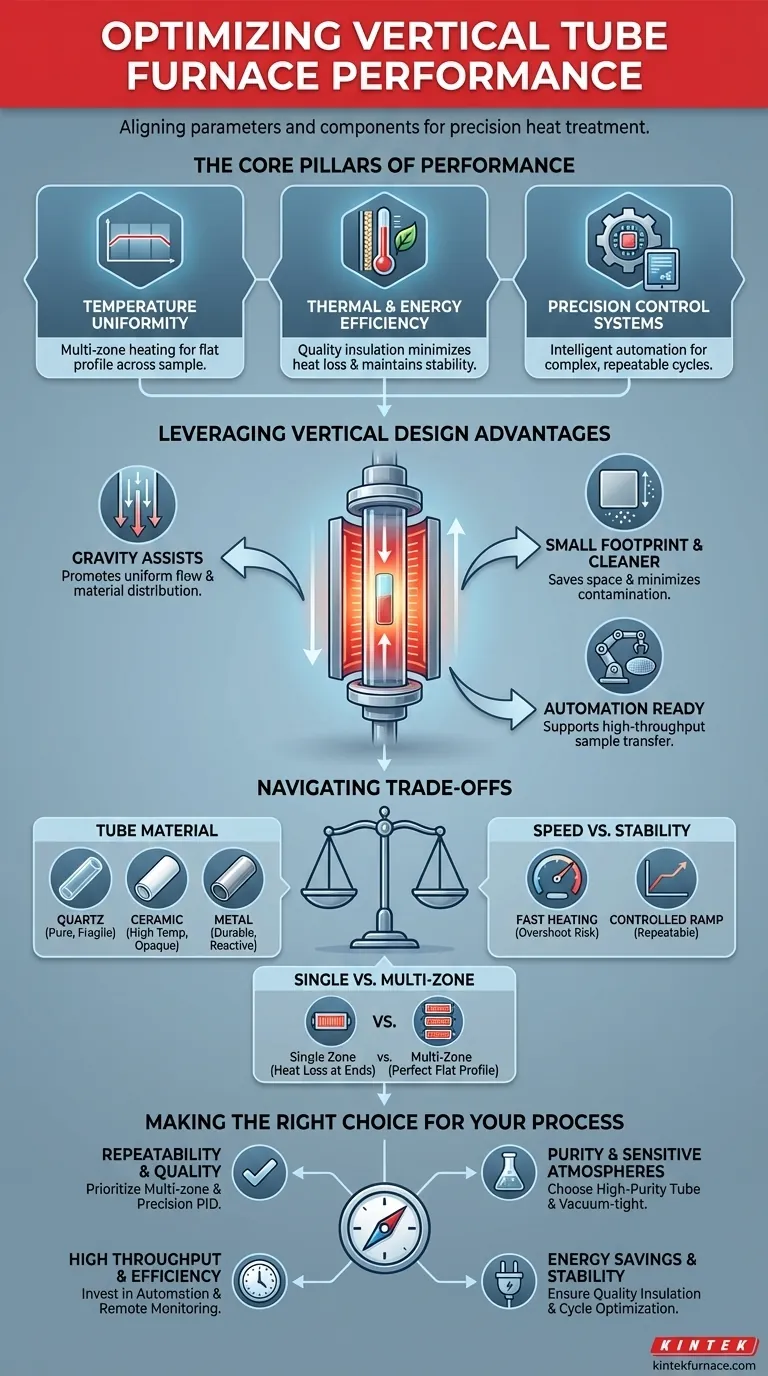
The Pillars of Furnace Performance
Optimizing performance begins with mastering the three core pillars: temperature uniformity, thermal efficiency, and control system precision. Neglecting any one of these can compromise the outcome of your process.
Achieving Absolute Temperature Uniformity
For most applications, temperature uniformity is the single most critical performance metric. Inconsistent temperatures across your sample can lead to non-homogeneous material properties and failed experiments.
Modern furnaces often use multi-zone heating to achieve a flat temperature profile. By independently controlling multiple heating elements along the length of the tube, the system can compensate for natural heat loss at the ends, ensuring the entire sample experiences the same thermal conditions.
Maximizing Thermal and Energy Efficiency
Efficiency is not just about saving costs; it is also about thermal stability. A well-insulated furnace with efficient heat transfer mechanisms requires less energy to maintain its setpoint.
This stability translates directly to better performance. High-quality insulation minimizes the impact of external temperature fluctuations, while effective heating elements ensure that energy is delivered precisely where it is needed, preventing over- and undershooting of the target temperature.
The Role of Advanced Control Systems
The furnace's control system is its brain. Advanced controllers offer intelligent operation, moving far beyond simple on/off functions to enable complex, pre-programmed thermal cycles.
These systems allow for precise control over heating rates (ramps), holding times (soaks), and cooling profiles. By automating the entire process, they enhance safety, reduce the chance of human error, and ensure that every run is identical, which is essential for both research and industrial production.
Leveraging the Vertical Design Advantage
The vertical orientation of these furnaces is not just an aesthetic choice; it provides distinct advantages that can be leveraged for optimization.
Using Gravity to Your Advantage
In certain processes like crystal growth, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), or sample drying, a vertical setup is superior. Gravity assists in creating uniform flow patterns and ensuring even material distribution, which can be difficult to achieve in a horizontal orientation.
Minimizing Footprint and Contamination
Vertical furnaces have a smaller physical footprint, a significant benefit in crowded laboratories or production facilities.
Furthermore, the vertical design helps to achieve minimal particle generation and contamination. Particulates are more likely to fall away from the sample due to gravity, leading to a cleaner processing environment, which is critical for applications like semiconductor manufacturing.
Automating for Productivity
For high-throughput applications, the vertical design lends itself well to automation. Systems featuring automatic wafer or boat transfer can significantly improve productivity by streamlining the loading and unloading process, supporting continuous and reliable operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Constraints
Perfect optimization requires acknowledging the inherent limitations and making informed choices based on your specific needs.
Choosing the Right Process Tube
The material of the process tube is a critical decision. The references note high-quality materials are used, but they come with trade-offs.
- Quartz: Offers high purity and is excellent for clean processes but is fragile and has a lower maximum temperature compared to ceramics.
- Ceramics (e.g., Alumina): Can withstand very high temperatures and are physically robust but may be less pure than quartz and are opaque.
- Metals: Are highly durable and resistant to thermal shock but can react with certain process atmospheres or samples.
Balancing Speed vs. Stability
Optimizing for the fastest possible heating rate can come at the cost of stability. Aggressive heating profiles can cause the temperature to overshoot the setpoint, compromising the uniformity and repeatability of your process. A slower, more controlled ramp is often better for sensitive materials.
The Limits of Single-Zone Control
While multi-zone furnaces offer the best uniformity, many standard furnaces have only a single heating zone. In these systems, achieving a perfectly flat temperature profile is challenging due to unavoidable heat loss at the tube ends. Understanding this limitation is key to positioning your sample correctly within the "sweet spot" of the furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your optimization strategy should be dictated by your primary goal. Use these guidelines to focus your efforts.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and quality: Prioritize a multi-zone furnace with a precision PID controller to guarantee temperature uniformity across your entire sample.
- If your primary focus is material purity and sensitive atmospheres: Carefully select your process tube material (e.g., high-purity quartz) and ensure the system is vacuum-tight to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and efficiency: Invest in automation features like automatic sample transfer and a control system with remote monitoring and programming capabilities.
- If your primary focus is energy savings and stability: Ensure the furnace is built with high-quality, multi-layer insulation and a controller that can optimize heating cycles to minimize waste.
By aligning the furnace's capabilities with your specific process goals, you move from simply operating a machine to mastering a critical tool for your work.
Summary Table:
| Optimization Aspect | Key Strategies |
|---|---|
| Temperature Uniformity | Use multi-zone heating, position sample in 'sweet spot' |
| Thermal Efficiency | Employ high-quality insulation, optimize heating cycles |
| Control System Precision | Implement PID controllers, automate thermal cycles |
| Vertical Design Benefits | Leverage gravity for uniform flow, minimize contamination |
| Tube Material Selection | Choose quartz for purity, ceramics for high temperature |
Ready to optimize your vertical tube furnace for superior performance? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise alignment with your experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and results—Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















