At its core, a vacuum tube furnace is considered valuable because it provides an exceptionally high degree of control over the processing environment. This allows for high-temperature treatments in a vacuum or a specific controlled atmosphere, which is essential for preventing oxidation and contamination. This capability makes it an indispensable tool for developing and manufacturing advanced materials in fields ranging from materials science to semiconductor production.
The true value of a vacuum tube furnace is not any single feature, but its ability to create a precisely controlled, isolated micro-environment. This total control over both atmosphere and temperature allows scientists and engineers to create materials with specific, predictable, and superior properties that would be impossible to achieve otherwise.

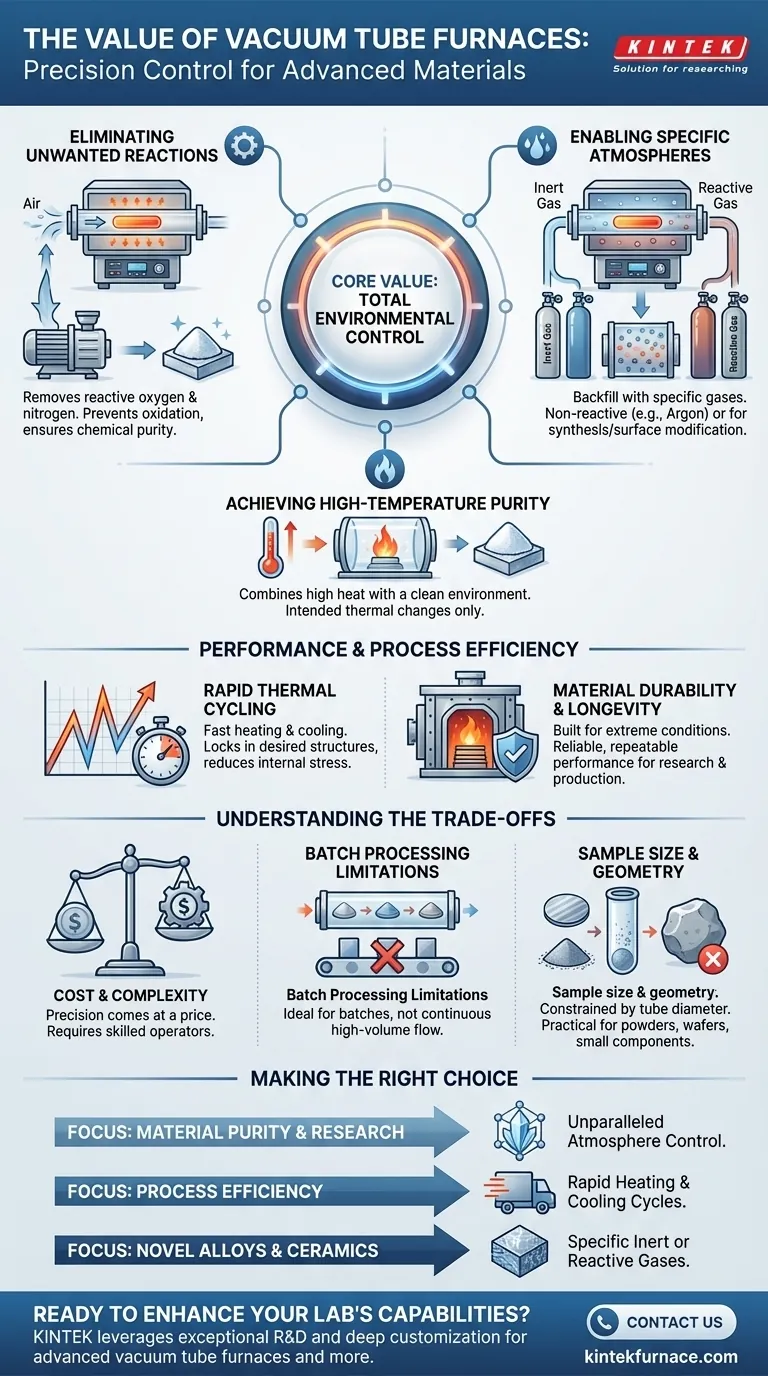
The Foundation of Value: Total Environmental Control
The primary advantage of a vacuum tube furnace is its ability to completely isolate a sample from the outside air. This opens up process capabilities that are critical for modern materials.
Eliminating Unwanted Reactions
Many advanced materials are highly reactive with oxygen and nitrogen, especially at elevated temperatures. Processing them in open air would lead to oxidation, which fundamentally changes their properties and degrades performance.
By first evacuating the air to create a vacuum, the furnace removes these reactive elements. This ensures the material being processed maintains its chemical purity.
Enabling Specific Atmospheres
Once a vacuum is established, the furnace can be backfilled with a specific gas. This is crucial for processes that require a particular environment.
An inert gas, like argon, can be introduced to provide a completely non-reactive atmosphere for sensitive materials. Alternatively, a reactive gas can be used to intentionally create a specific chemical reaction on the material's surface, a process known as synthesis or surface modification.
Achieving High-Temperature Purity
High temperatures accelerate chemical reactions. While the heat is necessary for processes like annealing or sintering, it also makes materials more susceptible to contamination.
A vacuum tube furnace solves this problem by combining high-temperature capability with a clean, controlled environment. This synergy ensures that the only changes happening to the material are the ones intended by the thermal process.
Performance and Process Efficiency
Beyond environmental control, the design of modern vacuum tube furnaces is optimized for efficient and reliable operation, directly impacting product quality and lab productivity.
Rapid Thermal Cycling
Many models are designed for rapid heating rates, allowing them to reach target temperatures quickly and reducing overall process time.
Just as important is the ability for fast cooling. Controlled, rapid cooling can "lock in" a desired crystal structure in a material and reduce internal stresses that can cause deformation or failure, ultimately improving the final product's quality and durability.
Material Durability and Longevity
These furnaces are built to withstand extreme conditions. The use of high-quality, corrosion-resistant materials in their construction ensures they have a long service life, even when used with reactive gases at high temperatures.
This robust design translates to reliable, repeatable performance, which is critical for both research and production environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful, vacuum tube furnaces are specialized equipment with inherent limitations that must be considered.
Cost and Complexity
The precision and control offered by these furnaces come at a price. They are more complex and expensive than standard atmospheric furnaces and require skilled operators to manage the vacuum systems and gas controls.
Batch Processing Limitations
By their nature, tube furnaces are batch processors. They are ideal for treating a set amount of material at one time but are not suited for continuous, high-volume manufacturing lines where materials flow without interruption.
Sample Size and Geometry
The "tube" shape itself is a physical constraint. These furnaces are perfect for processing powders, wafers, small components, or other samples that fit within the diameter of the processing tube. They are not practical for large or irregularly shaped objects.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum tube furnace depends entirely on your specific material and process requirements.
- If your primary focus is material purity and research: The unparalleled control over atmosphere to prevent oxidation and contamination is the most critical feature.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: The value lies in the rapid heating and cooling cycles that shorten production time while improving final material quality.
- If your primary focus is creating novel alloys or advanced ceramics: The ability to introduce specific inert or reactive gases at high temperatures is the most powerful capability.
Ultimately, a vacuum tube furnace is an investment in precision, giving you the power to define the properties of your materials from the ground up.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental Control | Isolates samples in vacuum or specific gases to prevent oxidation and contamination. |
| Temperature Management | Allows rapid heating and cooling for efficient thermal cycling and material property control. |
| Material Applications | Ideal for materials science, semiconductor production, and advanced ceramics development. |
| Limitations | Batch processing, higher cost, and sample size constraints compared to other furnaces. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precision high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced vacuum tube furnaces, along with Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can drive your material innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















