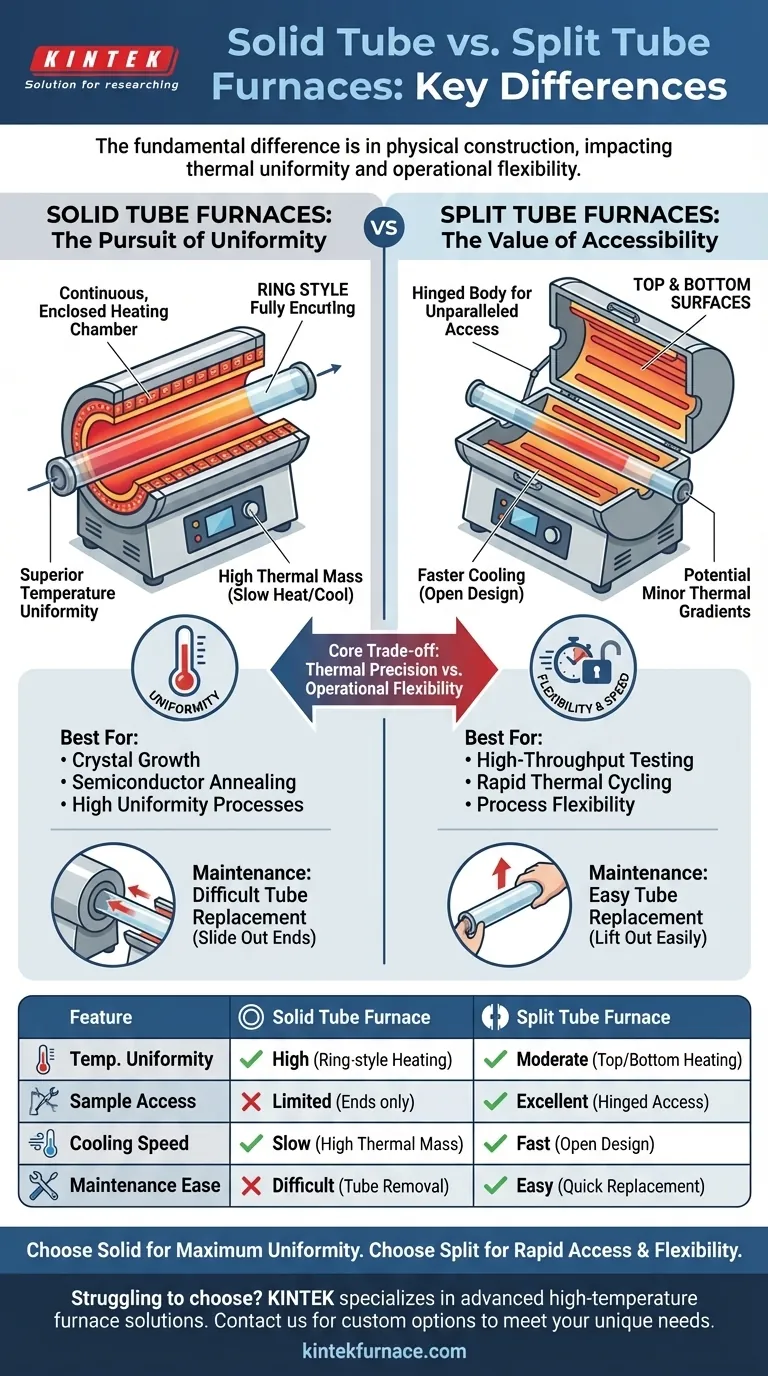
The fundamental difference between solid and split tube furnaces lies in their physical construction, which dictates their primary strengths. Solid tube furnaces utilize a continuous, enclosed heating chamber to deliver superior temperature uniformity. In contrast, split tube furnaces feature a hinged body that opens, providing unparalleled access to the process tube for easier sample handling and faster cooling.
Choosing between a solid and split tube furnace is a direct trade-off between thermal precision and operational flexibility. Your specific application's requirements for temperature stability versus ease of access will be the deciding factor.

The Core Distinction: Heating and Access
The choice between these two furnace types comes down to how they are built and how that construction impacts their use in a laboratory or production setting.
Solid Tube Furnaces: The Pursuit of Uniformity
A solid tube furnace, sometimes called an integral or non-split furnace, features a heating chamber that is a single, continuous cylinder.
The heating elements are typically arranged in a "ring" style, fully encircling the process tube. This design minimizes heat loss and thermal gradients, creating a highly stable and homogenous temperature zone around the entire circumference of the tube.
Access to the chamber is limited to the ends, where the process tube is inserted and removed by sliding it through the length of the furnace.
Split Tube Furnaces: The Value of Accessibility
A split tube furnace is constructed in two semi-cylindrical halves connected by a hinge.
This allows the entire furnace body to be opened, exposing the internal chamber and the process tube directly. This design dramatically simplifies placing or removing the process tube and any samples within it.
Heating elements are typically located on the top and bottom surfaces of the chamber, which is slightly less uniform than a full ring but offers immense practical benefits.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Neither design is universally "better." They are optimized for different priorities, and understanding these trade-offs is critical for making an informed decision.
Thermal Performance: Uniformity vs. Gradients
Solid tube furnaces excel at providing cross-sectional temperature uniformity. The enclosed ring of heating elements ensures the process tube is heated evenly from all sides. This is critical for processes like crystal growth or semiconductor annealing where slight temperature variations can ruin a sample.
Split tube furnaces may introduce minor thermal gradients. The seam where the two halves meet and the top/bottom heating configuration can create slight temperature differences. However, for most applications, this is negligible and can be mitigated with multi-zone control.
It's important to note that temperature uniformity along the length of the tube is primarily controlled by using multiple heating zones (e.g., a three-zone furnace), a feature available on both solid and split models.
Operational Speed: Stability vs. Throughput
Solid tube furnaces have a higher thermal mass and take longer to heat up and cool down. Their enclosed design is built to retain heat, which is excellent for long, stable processes but slows down throughput.
Split tube furnaces enable rapid cooling. By simply opening the furnace body, heat dissipates quickly, allowing you to access your sample much sooner after a process is complete. This is a major advantage for high-throughput testing or rapid thermal cycling.
Maintenance and Usability
Split tube furnaces offer far superior ease of maintenance. If a process tube breaks, warps, or becomes contaminated, it can be lifted out and replaced in moments.
Solid tube furnaces can make tube replacement difficult. Removing a broken or warped tube by sliding it out the end can be a challenging and time-consuming task.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct furnace, align the design's core strength with your primary process requirement.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity: Choose a solid tube furnace for its enclosed, ring-style heating that minimizes thermal gradients.
- If your primary focus is rapid sample exchange and fast cooling: Choose a split tube furnace for its hinged access and ability to quickly dissipate heat.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility and ease of maintenance: The split tube design offers significant advantages in swapping process tubes and accommodating various sample types.
By understanding this core trade-off between thermal precision and operational access, you can confidently select the furnace design that directly supports your goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Solid Tube Furnace | Split Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Uniformity | High (ring-style heating) | Moderate (top/bottom heating) |
| Sample Access | Limited (ends only) | Excellent (hinged access) |
| Cooling Speed | Slow (high thermal mass) | Fast (open design) |
| Maintenance Ease | Difficult (tube removal) | Easy (quick tube replacement) |
| Best For | High uniformity processes | High throughput and flexibility |
Struggling to choose the right tube furnace for your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring precise temperature control, ease of use, and enhanced efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can elevate your laboratory performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















