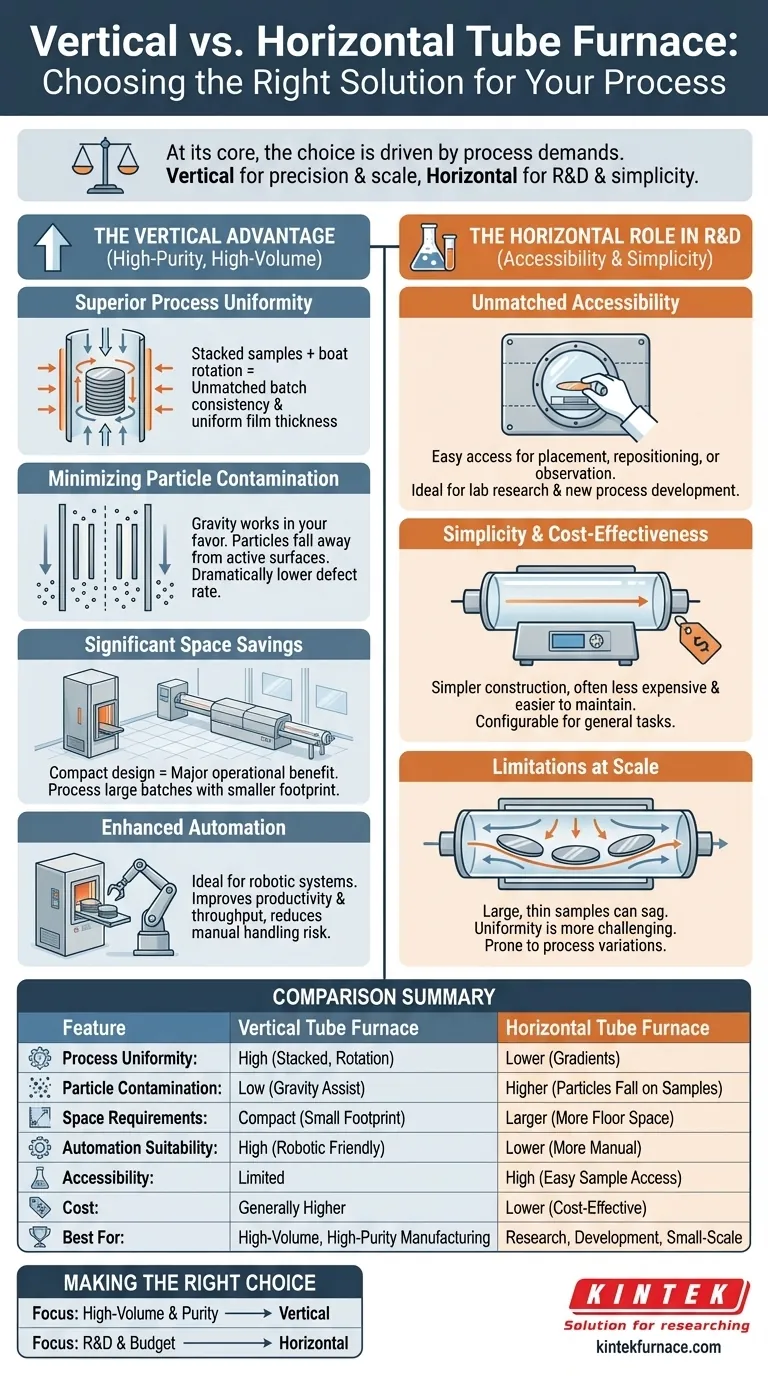
At its core, the choice between a vertical and horizontal tube furnace is a decision driven by the demands of your process. A vertical furnace is chosen for its superior process uniformity, significantly reduced particle contamination, and smaller physical footprint. These advantages have made it the mainstream choice for high-purity, high-volume applications like semiconductor manufacturing.
While both furnace types heat materials effectively, the orientation fundamentally changes the outcome. Vertical furnaces are optimized for precision and purity at scale, whereas horizontal furnaces prioritize accessibility and simplicity for research and smaller-scale work.

The Core Advantages of a Vertical Design
The primary reasons to select a vertical furnace over a horizontal one are rooted in physics. The vertical orientation inherently solves several problems that can plague horizontal systems, especially as sample sizes (like silicon wafers) increase.
Superior Process Uniformity
In a vertical furnace, samples are stacked on top of each other in a carrier, or "boat." This arrangement, often combined with boat rotation, ensures every sample is exposed to a highly consistent thermal environment.
This eliminates the temperature and gas flow gradients that can occur along the length of a horizontal tube, leading to unmatched batch consistency and uniform film thickness across every sample.
Minimizing Particle Contamination
This is perhaps the most critical advantage for high-purity processes. In a horizontal furnace, any microscopic particles generated during processing can fall directly onto the top surface of the samples below.
In a vertical furnace, gravity works in your favor. Particles are pulled downward, away from the active surfaces of the vertically-oriented samples and out of the process zone. This results in a dramatically lower defect rate.
Significant Space Savings
A vertical furnace's footprint is significantly smaller than a horizontal furnace of equivalent capacity. By stacking samples vertically, you can process a large batch without requiring a long, sprawling piece of equipment.
For modern fabrication labs and cleanrooms where every square foot is valuable, this compact design is a major operational benefit.
Enhanced Automation
The vertical layout is exceptionally well-suited for automation. Robotic systems can precisely and cleanly transfer entire boats of wafers into and out of the furnace with minimal human intervention.
This not only improves productivity and throughput but also further reduces the risk of contamination introduced by manual handling.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When to Consider a Horizontal Furnace
A vertical furnace is not universally superior; its advantages come with trade-offs. The horizontal furnace remains a valuable and widely used tool for specific applications where its design offers a clear benefit.
Unmatched Accessibility for R&D
The primary advantage of a horizontal furnace is ease of access. Samples can be easily placed, repositioned, or observed through a viewport during the heating process.
This makes them ideal for laboratory research, new process development, and any application that requires direct manipulation or observation of the sample at temperature.
Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
Horizontal tube furnaces generally have a simpler construction. This often makes them less expensive, easier to maintain, and more configurable for a wide range of general-purpose heating tasks.
For labs with budget constraints or applications that don't require the absolute highest level of purity and uniformity, a horizontal furnace is an extremely practical and cost-effective choice.
Limitations in High-Volume Processing
The main drawback of horizontal furnaces becomes apparent at scale. Large, thin samples like silicon wafers can sag or warp under their own weight at high temperatures when supported only at the edges.
Furthermore, achieving uniform gas flow and temperature across a long boat of samples is inherently more challenging, leading to the process variations that vertical furnaces were designed to solve.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be guided by your primary operational driver. The right furnace is the one that best aligns with the specific requirements of your work.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing and process purity: A vertical furnace is the industry standard for its superior uniformity, low particle count, and automation-friendly design.
- If your primary focus is research, process development, or budget constraints: A horizontal furnace provides the accessibility, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness needed for flexible, small-scale experimental work.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental design trade-offs empowers you to select the furnace that is not just a tool, but a solution tailored to your specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vertical Tube Furnace | Horizontal Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Process Uniformity | High, due to stacked samples and rotation | Lower, prone to gradients along tube length |
| Particle Contamination | Low, as gravity pulls particles away | Higher, particles can fall on samples |
| Space Requirements | Compact, smaller footprint | Larger, requires more floor space |
| Automation Suitability | High, ideal for robotic handling | Lower, more manual intervention needed |
| Accessibility | Limited, harder for direct manipulation | High, easy sample access and observation |
| Cost | Generally higher due to complexity | Lower, more cost-effective for basic use |
| Best For | High-volume, high-purity manufacturing | Research, development, and small-scale work |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with the right furnace solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in semiconductor manufacturing or research, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions



















