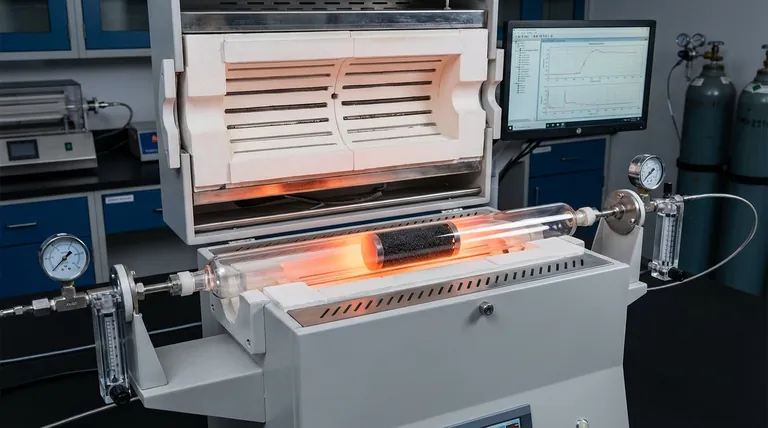
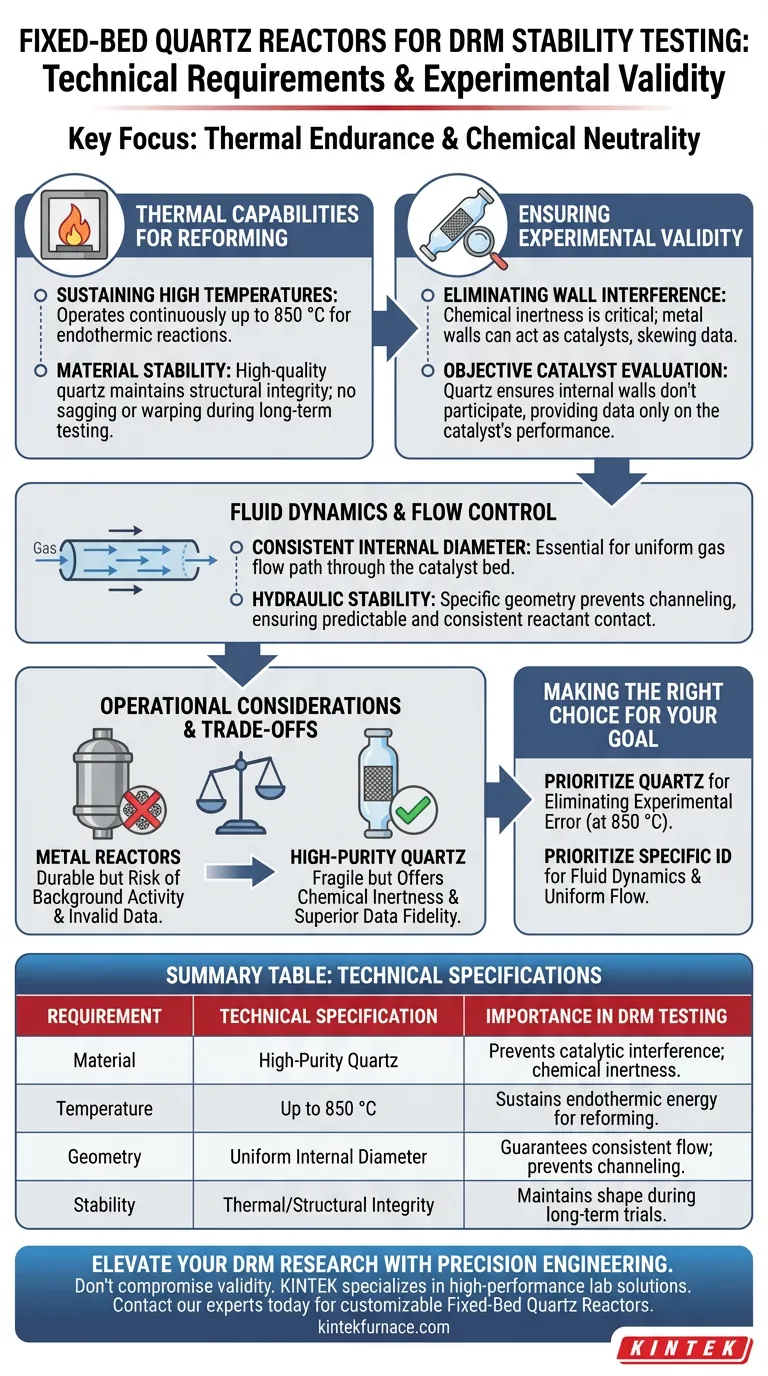
The technical requirements for a fixed-bed quartz reactor in Dry Reforming of Methane (DRM) center on thermal endurance and chemical neutrality. Specifically, the apparatus must possess a defined internal diameter to enforce a constant gas flow path and be constructed of quartz capable of withstanding operating temperatures up to 850 °C without physical deformation or chemical interaction.
The core objective of using quartz is to isolate variables. By utilizing a material that remains inert at high temperatures, you ensure that any observed catalytic activity is solely a result of the catalyst bed, not the reactor walls.

Thermal Capabilities for Reforming
Sustaining High Temperatures
DRM is an endothermic reaction requiring significant thermal energy. The reactor must be rated to operate continuously at temperatures as high as 850 °C.
Material Stability
At these elevated temperatures, many materials soften or degrade. High-quality quartz is required to maintain structural integrity, ensuring the reactor does not sag or warp during long-term stability testing.
Ensuring Experimental Validity
Eliminating Wall Interference
The most critical requirement for the reactor material is chemical inertness. In high-temperature reforming environments, metallic reactor walls can sometimes act as a catalyst, skewing data.
Objective Catalyst Evaluation
Quartz ensures that the internal walls do not interfere with the reaction process. This neutrality is essential for the objective evaluation of specific catalyst systems, such as manganese-modified nickel-based catalysts, ensuring the resulting data reflects only the catalyst's performance.
Fluid Dynamics and Flow Control
Consistent Internal Diameter
To obtain reliable data, the gas flow through the catalyst bed must be uniform. The reactor requires a specific, uniform internal diameter to guarantee a constant flow path for the reaction gases.
Hydraulic Stability
Variations in the tube's diameter can cause channeling or uneven flow distribution. A fixed, specific geometry ensures that the reactants contact the catalyst bed predictable and consistently throughout the test.
Operational Considerations and Trade-offs
The Necessity of Inertness
While metal reactors are more durable, they often fail the requirement for inertness in DRM testing. Using a material other than quartz risks introducing "background activity," where the reactor itself contributes to methane conversion, rendering stability data invalid.
Fragility vs. Accuracy
The trade-off for the high accuracy provided by quartz is its physical fragility compared to steel alloys. While it offers excellent high-temperature resistance and superior data fidelity, it requires careful handling to avoid breakage during setup and operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your DRM stability tests yield publishable, accurate results, prioritize the following based on your specific needs:
- If your primary focus is eliminating experimental error: Prioritize high-purity quartz construction to prevent the reactor walls from participating in the reaction at 850 °C.
- If your primary focus is fluid dynamics: specific internal diameter is critical to maintaining a constant flow path and ensuring the gas velocity remains uniform across the catalyst bed.
Select a reactor that acts as a transparent vessel for the chemistry, rather than a participant in it.
Summary Table:
| Requirement | Technical Specification | Importance in DRM Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Material | High-Purity Quartz | Prevents catalytic wall interference; ensures chemical inertness. |
| Temperature | Up to 850 °C | Sustains the endothermic energy required for methane reforming. |
| Geometry | Uniform Internal Diameter | Guarantees consistent gas flow paths and prevents channeling. |
| Stability | Thermal/Structural Integrity | Maintains reactor shape during long-term stability trials. |
Elevate Your DRM Research with Precision Engineering
Don’t let reactor wall interference compromise your experimental validity. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Our customizable Fixed-Bed Quartz Reactors and High-Temperature Systems are designed to provide the chemical neutrality and thermal stability required for accurate catalyst evaluation.
Whether you need Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, KINTEK offers the precise tools necessary to drive your innovation forward.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature lab setup? Contact our technical experts today to discuss your unique project needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Alua M. Manabayeva, С.А. Тунгатарова. Dry Reforming of Methane over Mn-modified Ni-based Catalysts. DOI: 10.1007/s10562-024-04676-0
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for LK-99 sintering? Achieve Precise Superconductor Phase Transformation
- What task is performed by industrial high-temperature tube or atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Carbon Aerogel Synthesis
- Why are high-temperature tube furnaces used for TiZrMoSn0.8Hf0.2 alloys? Essential Benefits for Material Science
- What heating temperatures can tube furnaces achieve? Unlock Precision Up to 1800°C for Your Lab
- Why is an industrial-grade tube furnace essential for reducing SrMo1−xMnxO4? Master SOFC Anode Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in vertical silicon transistor fabrication? Master Precision Oxidation
- What is a laboratory tube furnace? Master Precision Heating and Atmosphere Control
- What are the key features of high temperature tube furnaces? Unlock Precision for Material Science



















