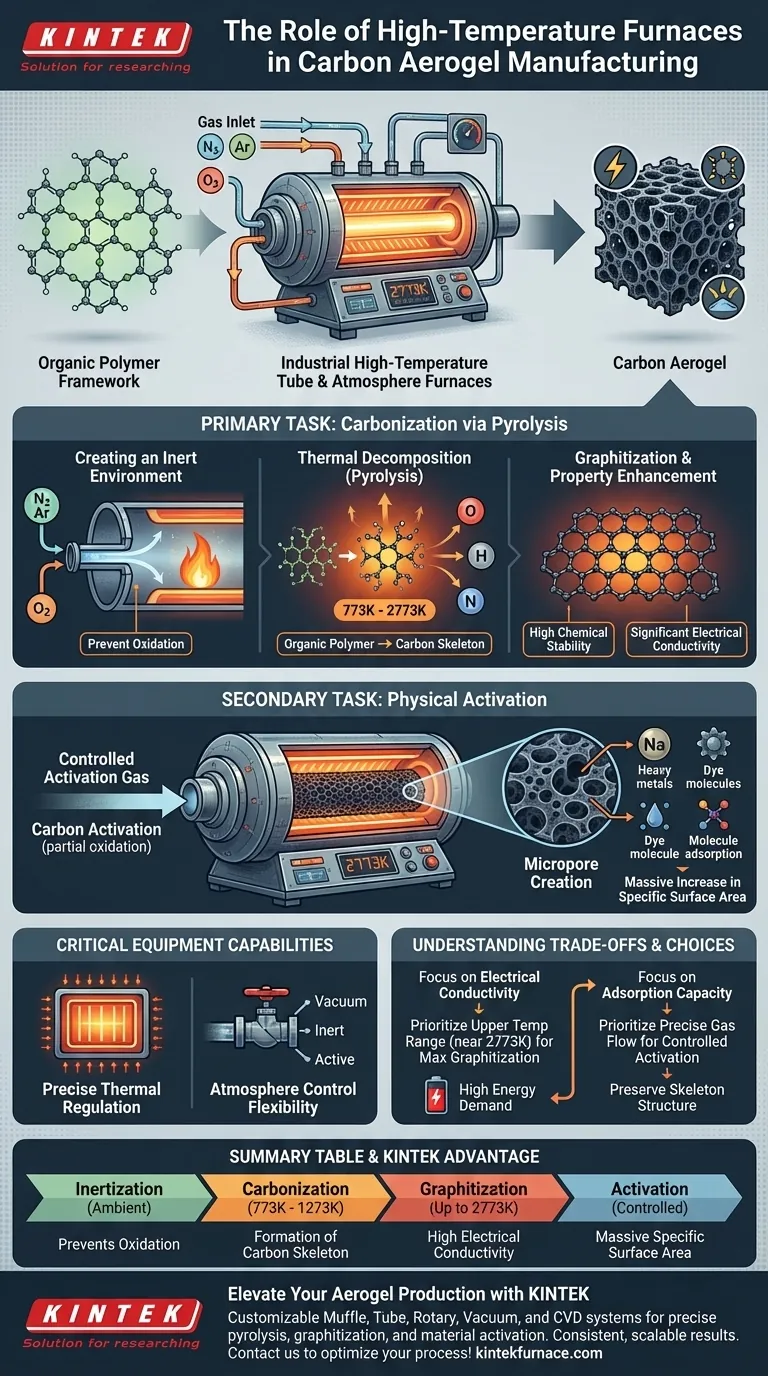
Industrial high-temperature tube and atmosphere furnaces are primarily tasked with the carbonization (pyrolysis) of organic polymer frameworks. These furnaces heat the material to extreme temperatures (773K to 2773K) under a controlled inert atmosphere to strip away non-carbon elements and structurally transform the aerogel.
Core Takeaway The fundamental role of these furnaces is to convert an organic polymer aerogel into a stable carbon aerogel through pyrolysis and graphitization. By precisely controlling heat and gas composition, the equipment dictates the final material's electrical conductivity, chemical stability, and specific surface area.

The Primary Task: Carbonization via Pyrolysis
Creating an Inert Environment
The most critical function of the furnace is to maintain a strict inert atmosphere.
By introducing gases such as nitrogen or argon, the furnace prevents the material from simply burning (oxidizing) as it heats up.
Thermal Decomposition
Once the inert environment is established, the furnace raises the temperature to between 773K and 2773K.
This intense heat triggers pyrolysis, a decomposition process that breaks down the organic polymer framework.
Elemental Purification
During pyrolysis, volatile non-carbon elements—specifically oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen—are expelled from the material.
This leaves behind a pure carbon skeleton, effectively transitioning the material from an organic polymer to an inorganic carbon structure.
Graphitization and Property Enhancement
At the higher end of the temperature spectrum, the carbon skeleton undergoes graphitization.
This structural realignment grants the aerogel high chemical stability and significant electrical conductivity, making it suitable for advanced applications like electrodes.
The Secondary Task: Physical Activation
Etching the Microstructure
Beyond standard carbonization, these furnaces are often used for an activation treatment.
By introducing a controlled flow of activation gas (partial oxidation), the furnace facilitates specific reactions that "etch" the material.
Expanding Surface Area
This controlled ablation creates a vast network of micropores within the carbon aerogel.
The result is a massive increase in specific surface area, which enhances the material's adsorption capacity for heavy metals or dye molecules.
Critical Equipment Capabilities
Precise Thermal Regulation
To achieve consistent pore structures, the furnace must utilize advanced controllers for precise temperature management.
High-quality tube furnaces ensure uniform heating, preventing hot spots that could cause uneven shrinkage or structural collapse.
Atmosphere Control Flexibility
The furnace serves as a sealed reaction chamber.
It allows operators to switch between a vacuum, inert gases for carbonization, or active gases for activation, providing versatility in a single piece of equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
High Energy Demand vs. Material Quality
Running furnaces at temperatures up to 2773K is energy-intensive and increases operational costs.
However, higher temperatures are non-negotiable if high electrical conductivity and graphitization are required; lower temperatures yield amorphous carbon with lower conductivity.
Distinction from Precursor Synthesis
It is vital to distinguish this high-temperature step from the earlier "sol-gel" phase.
The sol-gel transition requires constant low-temperature equipment to control particle size; the high-temperature furnace is exclusively for the harsh conditions of carbonization and activation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your furnace protocols based on the specific properties you need in your final carbon aerogel.
- If your primary focus is Electrical Conductivity: Prioritize furnaces capable of reaching the upper limits of the temperature range (near 2773K) to maximize graphitization.
- If your primary focus is Adsorption Capacity: Prioritize furnaces with precise gas flow controls to manage the activation (partial oxidation) process without destroying the skeleton.
Success in carbon aerogel manufacturing relies not just on heating the material, but on the precise orchestration of atmosphere and temperature to engineer the atomic structure.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Temperature Range | Primary Function | Resulting Material Property |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inertization | Ambient | Displacement of oxygen | Prevents oxidation/combustion |
| Carbonization | 773K - 1273K | Thermal decomposition (Pyrolysis) | Formation of carbon skeleton |
| Graphitization | Up to 2773K | Structural realignment | High electrical conductivity |
| Activation | Controlled | Partial oxidation/etching | Massive specific surface area |
Elevate Your Aerogel Production with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a collapsed structure and a high-performance carbon aerogel. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your specific pyrolysis and graphitization requirements. Whether you need extreme thermal uniformity or precise atmosphere control for material activation, our laboratory and industrial furnaces are engineered to deliver consistent, scalable results.
Ready to optimize your carbonization process? Contact us today to find the perfect high-temperature solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Yong Zhong, Xuguang Liu. Carbon Aerogel for Aqueous Phase Adsorption/Absorption: Application Performances, Intrinsic Characteristics, and Regulatory Constructions. DOI: 10.1002/sstr.202400650
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene? Boost Your Lab Results
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate sulfur melt-diffusion? Precision Heating for PCFC/S Cathodes
- What makes a vertical tube furnace easy to operate? Discover Intuitive Automation for Precision Heating
- How does a Tube Furnace facilitate precise control during CVD? Master Stoichiometry and Phase Purity
- What is the function of a tube furnace during the CVD growth of WS2 monolayers? Expert Thermal Control Guide
- Why is a vacuum-sealed quartz tube required during the high-temperature annealing of CoTeO4 to enhance crystallinity?
- What role do laboratory tube or muffle furnaces play in simulating SCM435 steel behavior? Optimize Material Research
- What are the thermal performance advantages of vacuum tube furnaces? Achieve Faster, Purer Heat Treatment



















