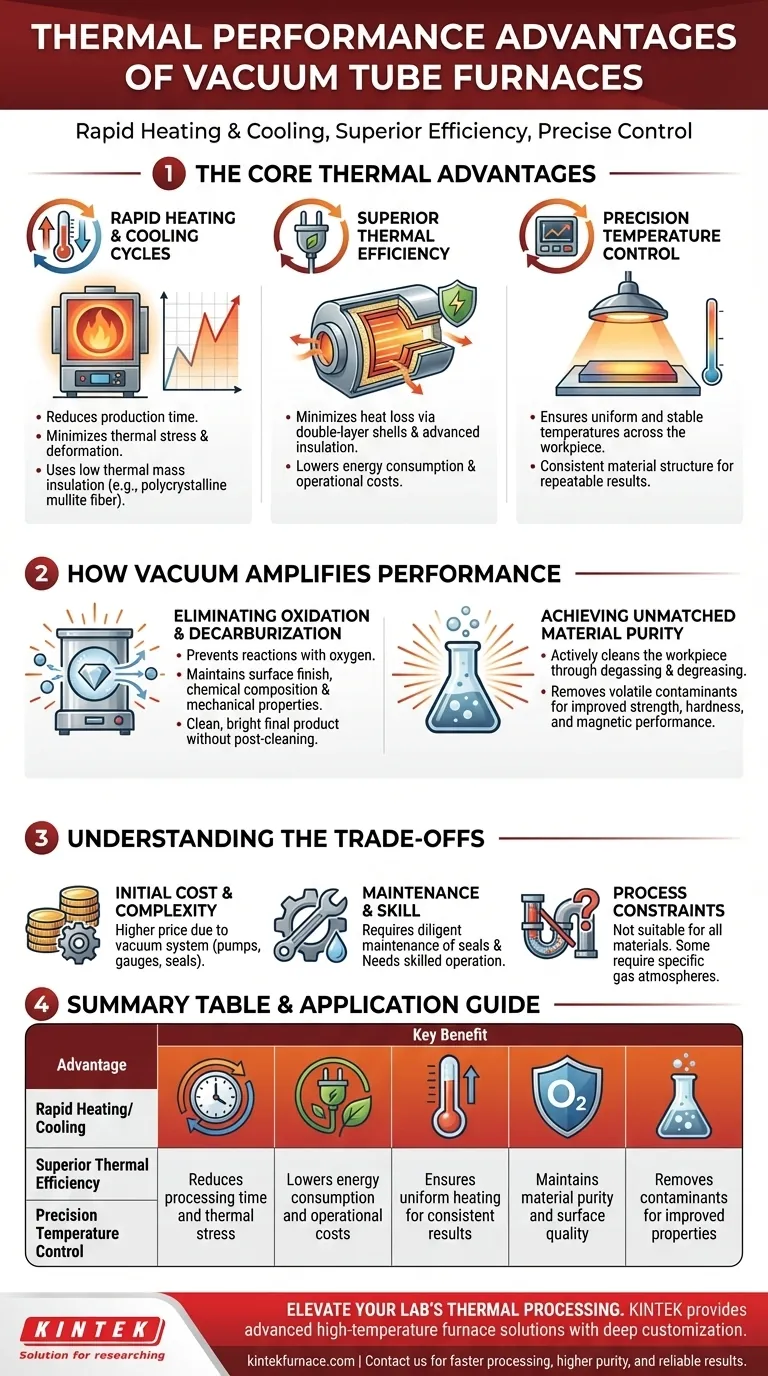
At their core, vacuum tube furnaces deliver significant thermal performance advantages through a combination of rapid heating and cooling rates, superior thermal efficiency, and exceptionally precise temperature control. These capabilities allow for faster processing times and lower energy consumption compared to many conventional atmospheric furnaces.
The true advantage of a vacuum tube furnace is not just its thermal performance, but how the vacuum environment leverages that performance to achieve a level of material purity, quality, and process repeatability that is often unattainable in the presence of air.

The Core Thermal Advantages Explained
Understanding the distinct thermal benefits is the first step. Each contributes directly to efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and the quality of the final product.
Rapid Heating and Cooling Cycles
Vacuum tube furnaces are designed for speed. They often incorporate high-quality insulation, like polycrystalline mullite fiber, which has low thermal mass, enabling them to reach target temperatures very quickly.
This rapid heating directly reduces production time. Furthermore, many models feature controlled, fast cooling capabilities, which can be critical for minimizing thermal stress and preventing deformation in sensitive materials.
Superior Thermal Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a key design principle. Features like double-layer furnace shells and advanced air insulation technology minimize heat loss to the surrounding environment.
This high thermal efficiency means the furnace consumes less power to achieve and maintain the desired temperature, leading to significant operational cost savings over the equipment's lifetime.
Precision Temperature Control and Uniformity
These furnaces provide unparalleled control over the thermal process. This precision ensures that the temperature across the entire workpiece is highly uniform and stable.
For materials science and advanced manufacturing, this is non-negotiable. It guarantees that the material structure is consistent, leading to reliable, repeatable results and stable performance in the final product.
How Vacuum Amplifies Thermal Performance
The vacuum environment is not just an add-on; it is a fundamental component that transforms what is possible with thermal processing. It works in concert with the furnace's heating capabilities to produce superior outcomes.
Eliminating Oxidation and Decarburization
This is arguably the most critical benefit. By removing air, the vacuum prevents the workpiece from reacting with oxygen during heating. This eliminates oxidation and decarburization.
As a result, the material maintains its intended surface finish, chemical composition, and mechanical properties. The final product is clean and bright, without the need for post-process surface cleaning.
Achieving Unmatched Material Purity
A vacuum does more than just prevent reactions; it actively cleans the workpiece. The process can pull volatile contaminants out of the material through degassing and degreasing.
This purification effect is essential for high-performance applications, as it leads to a more uniform and structurally sound material, enhancing properties like strength, hardness, and even magnetic performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum tube furnaces are not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging their specific demands and limitations.
Initial Cost and Complexity
The addition of a vacuum system—including pumps, gauges, and seals—increases the initial purchase price and overall complexity of the equipment compared to a standard atmospheric furnace.
Maintenance and Operational Skill
Vacuum systems require diligent maintenance. Seals must be checked for leaks, and pumps need regular servicing to maintain a high-quality vacuum, which is essential for process repeatability. Operating the equipment effectively also requires a higher level of technical skill.
Process Constraints
Not all materials or processes are suitable for a vacuum. Some applications may require specific partial pressures or reactive gas atmospheres (e.g., nitrogen, argon) that a simple vacuum-only system cannot provide.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use a vacuum tube furnace should be driven by your specific processing goals.
- If your primary focus is material purity and surface quality: The vacuum environment's ability to prevent oxidation and remove contaminants is its most compelling advantage.
- If your primary focus is process speed and throughput: The rapid heating and cooling cycles will significantly reduce your overall production time.
- If your primary focus is property control and repeatability: The precise temperature management ensures consistent, high-quality outcomes for sensitive materials and research applications.
Ultimately, a vacuum tube furnace offers a level of environmental and thermal control that transforms heat treatment from a simple heating process into a precise engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Rapid Heating/Cooling | Reduces processing time and thermal stress |
| Superior Thermal Efficiency | Lowers energy consumption and operational costs |
| Precision Temperature Control | Ensures uniform heating for consistent results |
| Oxidation Prevention | Maintains material purity and surface quality |
| Material Purification | Removes contaminants for improved properties |
Ready to elevate your lab's thermal processing? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum tube furnaces can deliver faster processing, higher purity, and reliable results for your materials science and manufacturing applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















