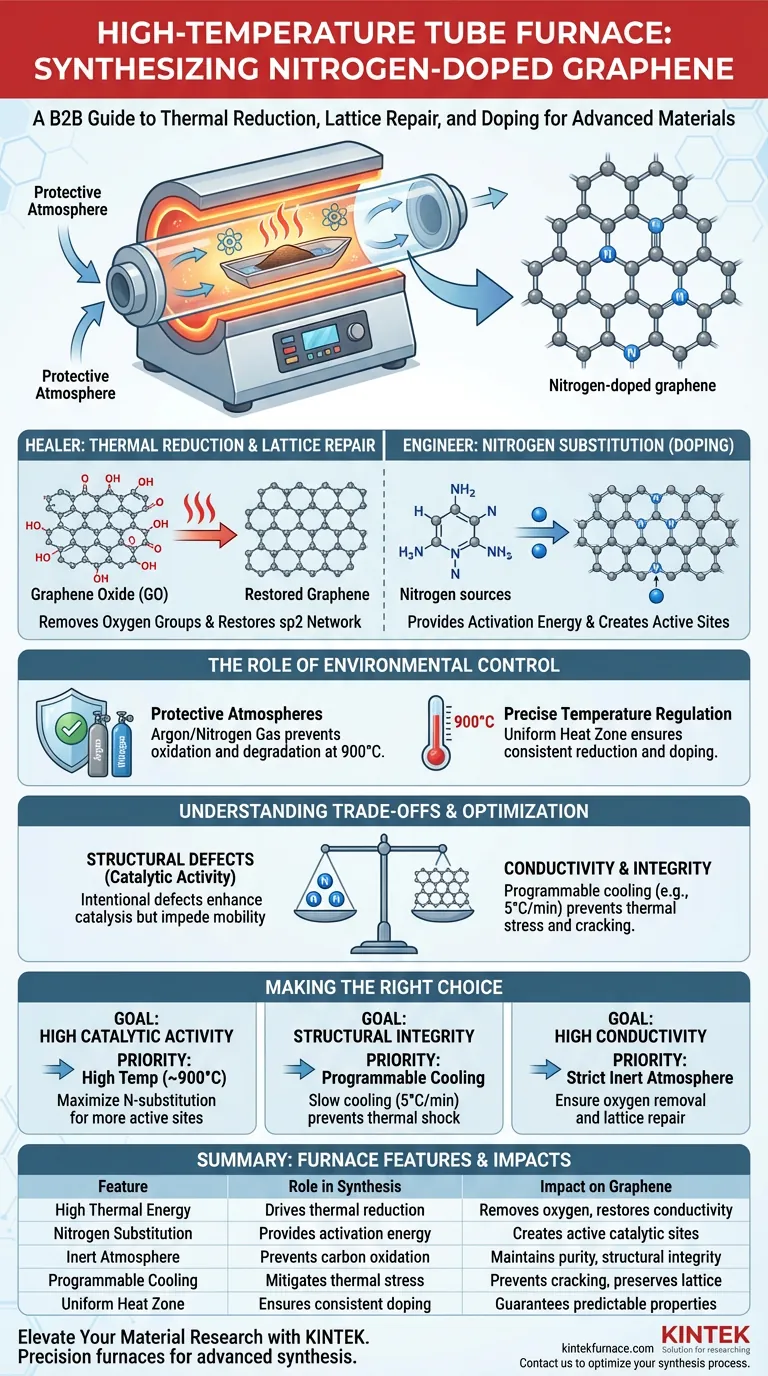
A high-temperature tube furnace is the critical reaction vessel for synthesizing nitrogen-doped graphene, providing the necessary thermal energy to simultaneously reduce graphene oxide and incorporate nitrogen atoms into the carbon lattice. By maintaining a precise temperature, typically around 900 °C, under an inert argon atmosphere, the furnace facilitates the removal of oxygenated functional groups while enabling the substitution of carbon atoms with nitrogen.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace acts as a dual-purpose tool: it functions as a "healer" by thermally stripping oxygen to restore the graphene’s conductive network, and as an "engineer" by supplying the activation energy required to force nitrogen atoms into the structure for enhanced chemical properties.

The Mechanics of Thermal Reduction and Doping
Removing Oxygen Functional Groups
The primary role of the furnace is to drive thermal reduction. Graphene oxide (the precursor) is heavily oxidized and non-conductive. The high heat of the furnace effectively strips away oxygen-containing functional groups that disrupt the material's electronic structure.
Repairing the Lattice
As oxygen groups are removed, the carbon atoms must rearrange themselves. The thermal energy provided by the furnace allows the material to repair its sp2 hybridized network. This restoration of the honeycomb lattice is essential for recovering the material's electrical conductivity and structural stability.
Facilitating Nitrogen Substitution
Doping is an energy-intensive process. The furnace provides the activation energy needed for nitrogen atoms—sourced from residues like ammonium, nitrates, or external precursors like melamine—to physically replace carbon atoms within the graphene lattice. This atomic substitution creates the "active sites" that give nitrogen-doped graphene its unique catalytic properties.
The Role of Environmental Control
Maintaining Protective Atmospheres
At 900 °C, carbon burns instantly in the presence of air. The tube furnace enables the use of a strictly controlled protective atmosphere, typically Argon (Ar) or Nitrogen gas. This prevents the graphene from oxidizing (burning up) and ensures that the chemical reactions remain focused on doping and reduction rather than degradation.
Precise Temperature Regulation
The synthesis process is highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. The tube furnace provides a uniform heat zone, ensuring that the reduction and doping occur intimately and evenly across the sample. Without this uniformity, you would achieve inconsistent doping levels, leading to material with unpredictable electronic properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Thermal Stress
While high heat is necessary for doping, rapid temperature changes can destroy the material. Differences in thermal expansion coefficients between the graphene and its substrate can lead to cracking or peeling. A tube furnace with programmable cooling (e.g., 5°C per minute) is often required to mitigate this stress, rather than simply turning the heat off.
Structural Defects vs. Doping
There is a fine line between doping and damage. While the furnace repairs the sp2 network, the introduction of nitrogen atoms intentionally creates defects in the lattice. These defects are useful for catalysis but can impede pure electron mobility. The furnace temperature and duration must be tuned to balance the density of these defects against the overall crystallinity of the graphene.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your nitrogen-doped graphene synthesis, consider these operational priorities:
- If your primary focus is high catalytic activity: Prioritize temperatures near 900°C to maximize the substitution of nitrogen into the lattice, creating more active sites.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Utilize the furnace’s programmable cooling features to lower the temperature slowly (e.g., 5°C/min) to prevent thermal shock and cracking.
- If your primary focus is high conductivity: Ensure a strict inert atmosphere (Argon) and sufficient dwell time to maximize the removal of oxygen groups and the repair of the sp2 network.
Success in this process relies not just on reaching high temperatures, but on the precise orchestration of heating rates, atmospheric composition, and cooling protocols.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Synthesis | Impact on Graphene |
|---|---|---|
| High Thermal Energy | Drives thermal reduction | Removes oxygen and restores conductivity |
| Nitrogen Substitution | Provides activation energy | Creates active catalytic sites in the lattice |
| Inert Atmosphere | Prevents carbon oxidation | Maintains material purity and structural integrity |
| Programmable Cooling | Mitigates thermal stress | Prevents cracking and preserves lattice stability |
| Uniform Heat Zone | Ensures consistent doping | Guarantees predictable electronic properties |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the foundation of successful graphene synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of high-temperature doping and thermal reduction.
Our lab furnaces offer the precise temperature regulation and atmosphere control necessary to balance catalytic activity with structural integrity. Whether you need a standard setup or a fully customizable solution for unique high-temp needs, KINTEK is your trusted partner in innovation.
Ready to optimize your synthesis process? Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Hela Kammoun, Ana C. Tavares. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Materials with High Electrical Conductivity Produced by Electrochemical Exfoliation of Graphite Foil. DOI: 10.3390/nano14010123
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What safety measures should be followed when operating a split tube furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Lab Operations
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in NC framework preparation? Master Precision Carbonization
- What are the primary functions of a high-precision tube resistance furnace? Optimize Chloride-Doped Composite Synthesis
- What is the primary purpose of using a tube furnace during the desizing phase? Optimize Carbon Fiber Surface Purity
- What is the purpose of introducing nitrogen flow into a tube furnace? Optimize Your Activated Carbon Calcination
- Why Use a Reducing Gas in Tube Furnace Thermal Treatment? Unlock Pure Metallic Phases and Defects
- What type of processing environment do high-temperature tube and muffle furnaces provide? Master Thermal Precision
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the ammonia reduction annealing process for (NiZnMg)MoN catalysts? Optimize Phase Transitions



















