To operate a split tube furnace safely, you must integrate personal protective measures with rigorous operational protocols. This involves wearing heat-resistant gloves and safety glasses, ensuring the workspace is properly ventilated and free of flammables, adhering strictly to temperature limits and gas flow procedures, and receiving comprehensive training on both standard operation and emergency shutdowns.
A split tube furnace's power and versatility come with inherent thermal, electrical, and atmospheric risks. True safety is not a checklist but a systematic culture that respects the equipment, the environment, and the established procedures at all times.
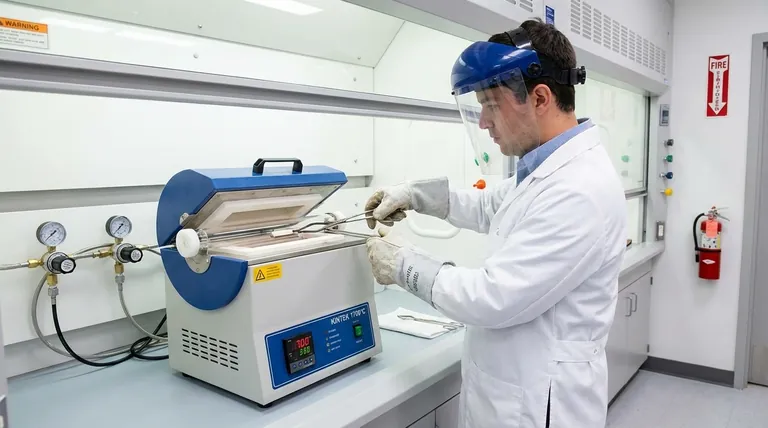

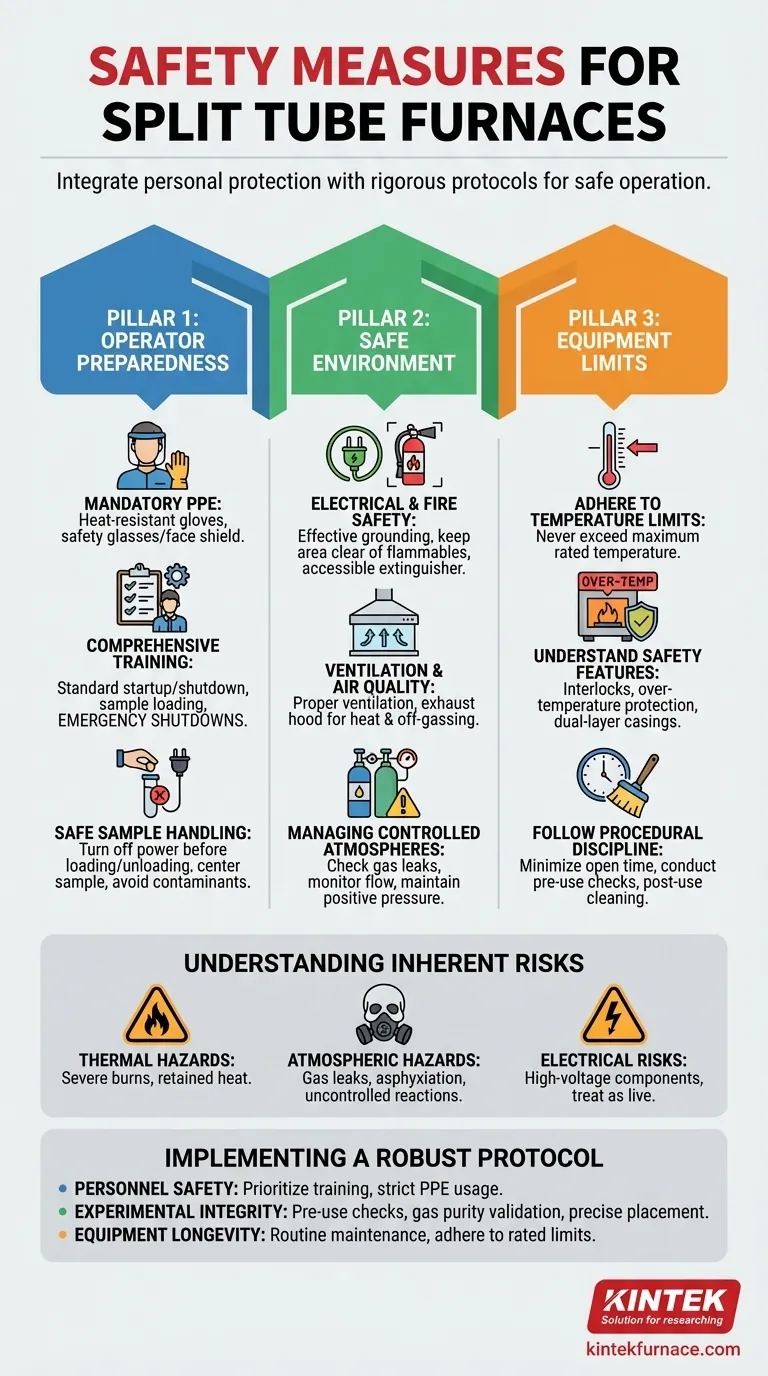
The Three Pillars of Furnace Safety
Safe operation rests on three distinct but interconnected pillars: the operator's preparedness, the safety of the immediate environment, and a deep respect for the equipment's operational limits. Neglecting any one of these pillars compromises the entire system.
Pillar 1: Operator Preparedness and Discipline
The most critical safety component is a well-trained and disciplined operator.
Mandatory Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Due to extreme operating temperatures, often reaching up to 1200°C, proper PPE is non-negotiable. Always wear heat-resistant gloves when handling samples or accessing the furnace chamber and safety glasses or a face shield to protect against thermal radiation and potential projectiles.
The Importance of Comprehensive Training
No one should operate a furnace without being fully trained on its specific model. This training must cover standard startup and shutdown sequences, sample loading, and, most critically, emergency shutdown procedures.
Safe Sample Handling
Turn off power before loading or unloading samples to prevent electrical shock. Place samples carefully in the center of the furnace tube to ensure uniform heating and prevent damage to the heating elements. Avoid using contaminated, wet, or oily samples, as they can release harmful vapors and compromise the experiment.
Pillar 2: Creating a Safe Operating Environment
The lab or facility itself must be configured to mitigate risks.
Electrical and Fire Safety
Ensure the furnace has effective electrical grounding to prevent shock. The area around the furnace must be kept clear of all flammable and combustible materials. A properly rated fire extinguisher should be nearby and easily accessible.
Ventilation and Air Quality
Proper ventilation is essential to dissipate heat and remove any potential off-gassing from samples or the furnace itself. A dedicated exhaust hood is often the best solution, especially when working with volatile materials.
Managing Controlled Atmospheres
When using inert or reactive gases, safety becomes even more critical. Regularly check all connections for gas leaks and monitor flow rates continuously. In many applications, it's vital to maintain a slight positive pressure inside the tube to prevent ambient air from entering and reacting with the sample or atmosphere.
Pillar 3: Respecting the Equipment's Limits
A furnace is a powerful tool, not an indestructible one. Pushing it beyond its design limits is a direct path to failure and accidents.
Adhering to Temperature Limits
Never attempt to operate the furnace above its maximum rated temperature. Doing so can severely damage the heating elements, thermocouple, and insulation, creating a significant safety hazard.
Understanding Built-in Safety Features
Modern split tube furnaces often include safety interlocks, over-temperature protection, and dual-layer casings with forced-air cooling to keep the exterior at a safe temperature. Understand what these features do, but never rely on them as a substitute for proper procedure.
Following Procedural Discipline
Always minimize the time the furnace is open to reduce heat loss and thermal shock to the components. Conduct pre-use checks for cleanliness and post-use cleaning to remove any residue that could cause contamination in future runs.
Understanding the Inherent Risks
Recognizing the specific hazards is the first step toward mitigating them. Complacency is the greatest risk of all, as it leads to procedural shortcuts and a disregard for fundamental safety rules.
Thermal Hazards
The most obvious danger is severe burns from touching the furnace's hot interior or samples. Even after shutdown, the furnace retains a tremendous amount of heat for a long time.
Atmospheric Hazards
Incorrectly managed gas flow can lead to dangerous situations. A gas leak can create an asphyxiation or fire risk, while allowing air into a reactive, high-temperature atmosphere can cause an uncontrolled chemical reaction.
Electrical Risks
Split tube furnaces use high-voltage components for their heating elements. Always treat the equipment as a live electrical device, especially during maintenance or when loading and unloading samples.
Implementing a Robust Safety Protocol
Your approach to furnace safety should be tailored to your primary objectives.
- If your primary focus is personnel safety: Prioritize comprehensive training on all procedures, especially emergency shutdowns, and enforce strict PPE usage without exception.
- If your primary focus is experimental integrity: Emphasize pre-use checks for furnace cleanliness, validation of gas purity, and precise sample placement to ensure repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Implement a strict routine maintenance schedule and never operate the furnace beyond its rated temperature or for longer than recommended cycles.
A systematic approach to safety transforms a powerful tool from a potential hazard into a reliable and effective asset for your work.
Summary Table:
| Safety Pillar | Key Measures |
|---|---|
| Operator Preparedness | Wear heat-resistant gloves and safety glasses; receive comprehensive training; handle samples safely |
| Safe Environment | Ensure electrical grounding; maintain ventilation; keep area free of flammables |
| Equipment Limits | Adhere to temperature limits; understand safety features; follow procedural discipline |
Ensure your lab's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your safety protocols and enhance your research outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















