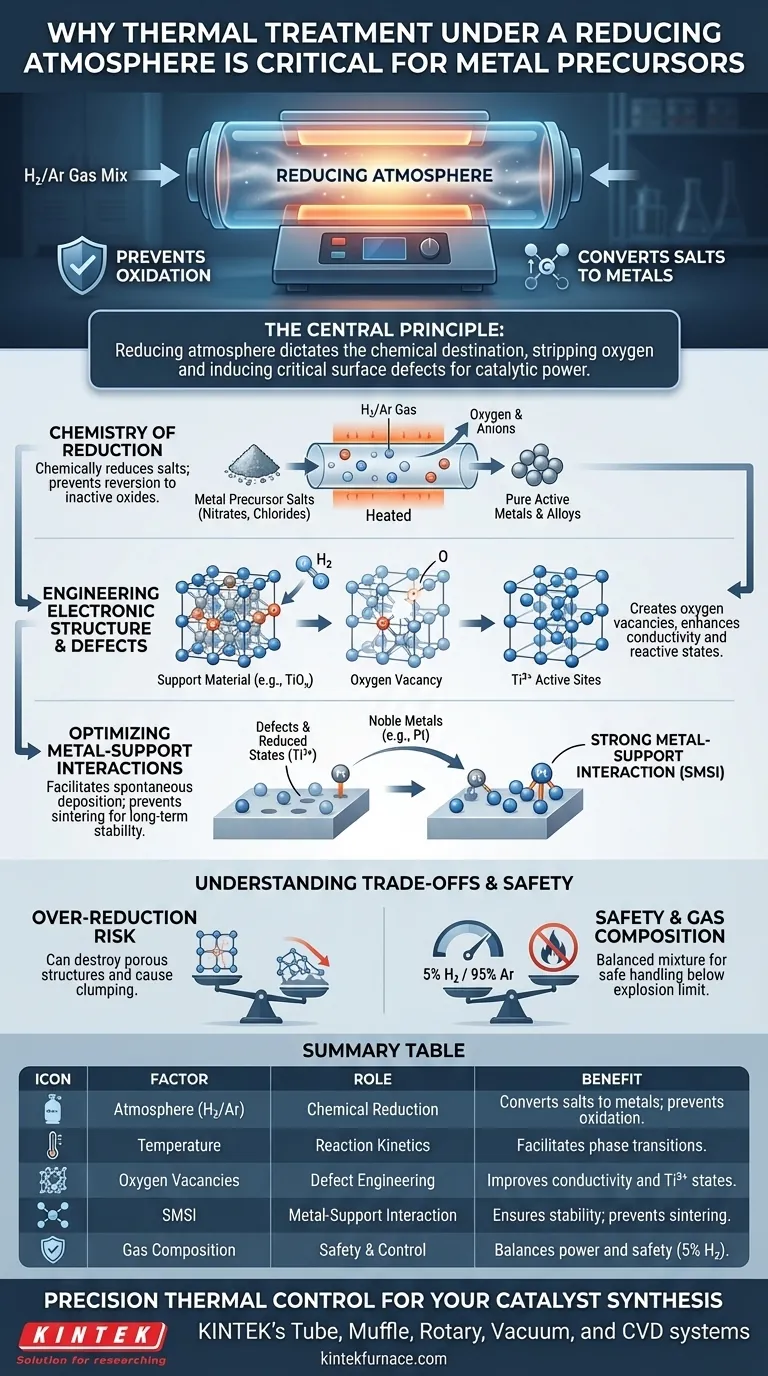
Thermal treatment under a reducing atmosphere is chemically essential to convert metal precursor salts into their pure metallic states or specific alloy structures. By introducing a reducing agent like hydrogen, you actively prevent uncontrolled oxidation that naturally occurs at high temperatures, ensuring the material develops the precise electronic structure required for high-performance electrochemical applications.
The Central Principle
High temperatures facilitate reaction kinetics, but a reducing atmosphere dictates the chemical destination. It strips away oxygen atoms to transform passive salts into active metals and induces critical surface defects that define the material's catalytic power.

The Chemistry of Reduction and Synthesis
Converting Precursors to Active Metals
The primary function of a reducing gas, such as a hydrogen-argon mix, is to chemically reduce precursor salts.
Without this atmosphere, heating metal salts would simply result in calcination or oxidation. The reducing gas strips away anionic components (like nitrates or chlorides) and oxygen, leaving behind the desired metallic phase or alloy.
Preventing Uncontrolled Oxidation
At elevated temperatures, metals are thermodynamically prone to reacting with ambient oxygen.
A reducing environment acts as a protective shield. It ensures that the catalyst does not revert to a stable, inactive oxide form, which is critical for maintaining intrinsic electrochemical activity, such as in the oxygen evolution reaction (OER).
Engineering Electronic Structure and Defects
Creating Oxygen Vacancies
Beyond simple reduction, this atmosphere allows for precise defect engineering in support materials (e.g., TiOx).
As noted in advanced synthesis protocols, the reducing gas triggers phase transitions and pulls oxygen atoms out of the crystal lattice. This creates oxygen vacancies, which are essential for altering the electronic band structure of the material.
Enhancing Active Sites (Ti3+ Content)
The creation of oxygen vacancies directly increases the concentration of specific electronic states, such as Ti3+.
These states act as highly reactive sites. They significantly improve the material's conductivity and provide the necessary electronic environment for subsequent chemical reactions or metal deposition.
Optimizing Metal-Support Interactions
Facilitating Spontaneous Deposition
A surface pre-treated in a reducing atmosphere is chemically primed to accept noble metals.
The defects and reduced states (like Ti3+) serve as nucleation points. This allows for the spontaneous and uniform deposition of active metals, such as Platinum (Pt), without requiring harsh additional chemicals.
Strong Metal-Support Interaction (SMSI)
The reducing environment is the key to unlocking Strong Metal-Support Interaction (SMSI).
This interaction creates a robust bond between the catalyst nanoparticles and the support material. A strong bond prevents particle migration (sintering) and ensures long-term stability under operating conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Over-Reduction
While reduction is necessary, an overly aggressive reducing atmosphere or excessive temperature can degrade the material.
Too much reduction can cause the collapse of porous structures or lead to the sintering of metal particles into large, inactive clumps. The goal is controlled reduction, not structural destruction.
Safety and Gas Composition
Pure hydrogen poses significant safety risks at high temperatures due to flammability.
Standard protocols mitigate this by using a balanced mixture, often 5% Hydrogen in 95% Argon. This concentration is sufficient to drive the chemical reduction thermodynamics while remaining below the explosion limit for safer handling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve the best results, tailor your thermal treatment parameters to your specific material requirements.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing pure metallic alloys: Ensure your temperature profile is high enough to fully reduce the precursor salts but low enough to prevent particle agglomeration.
- If your primary focus is defect engineering (e.g., Oxygen Vacancies): Calibrate the hydrogen concentration and duration to induce the specific phase transition (like Anatase to Rutile) without fully reducing the support to a bulk metal.
Control the atmosphere, and you control the intrinsic properties of your final catalyst.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Role in Thermal Treatment | Benefit for Metal Precursors |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere (H2/Ar) | Chemical Reduction | Converts salts to pure metals; prevents oxidation. |
| Temperature | Reaction Kinetics | Facilitates phase transitions and atom migration. |
| Oxygen Vacancies | Defect Engineering | Increases Ti3+ states and improves conductivity. |
| SMSI | Metal-Support Interaction | Prevents sintering and ensures long-term stability. |
| Gas Composition | Safety & Control | 5% H2/95% Ar balances reduction power and safety. |
Precision Thermal Control for Your Catalyst Synthesis
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK’s high-performance laboratory solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-precision Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the rigorous demands of reducing gas atmospheres and defect engineering.
Whether you are synthesizing metallic alloys or engineering oxygen vacancies, our fully customizable high-temperature furnaces provide the stability and safety your research deserves.
Ready to elevate your material science? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace for your unique application!
Visual Guide
References
- Iveta Boshnakova, Evelina Slavcheva. Bimetallic Ir-Sn Non-Carbon Supported Anode Catalysts for PEM Water Electrolysis. DOI: 10.3390/inorganics13070210
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What function does a tube furnace serve in converting electrospun fibers into CNFs? Mastering the Carbonization Path
- Why use a laboratory tube furnace with argon for low carbon steel annealing? Ensure Oxidation-Free Material Integrity
- What temperature control features do tube turnouts typically have? Achieve Precise Thermal Management for Your Lab
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the pore regulation of carbon nanofibers? Precision Engineering
- Why is an industrial tube furnace with argon flow required for Ti3AlC2? Expert Sintering Guide
- Why is high-vacuum encapsulation in quartz tubes required? Ensure Precision for Sn-Ag-Bi-Se-Te Composites
- What are the advantages of a vacuum tube? Unlock Superior Performance in Audio & Heat Treatment
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the chemical activation stage of producing activated carbon? Expert Insights



















