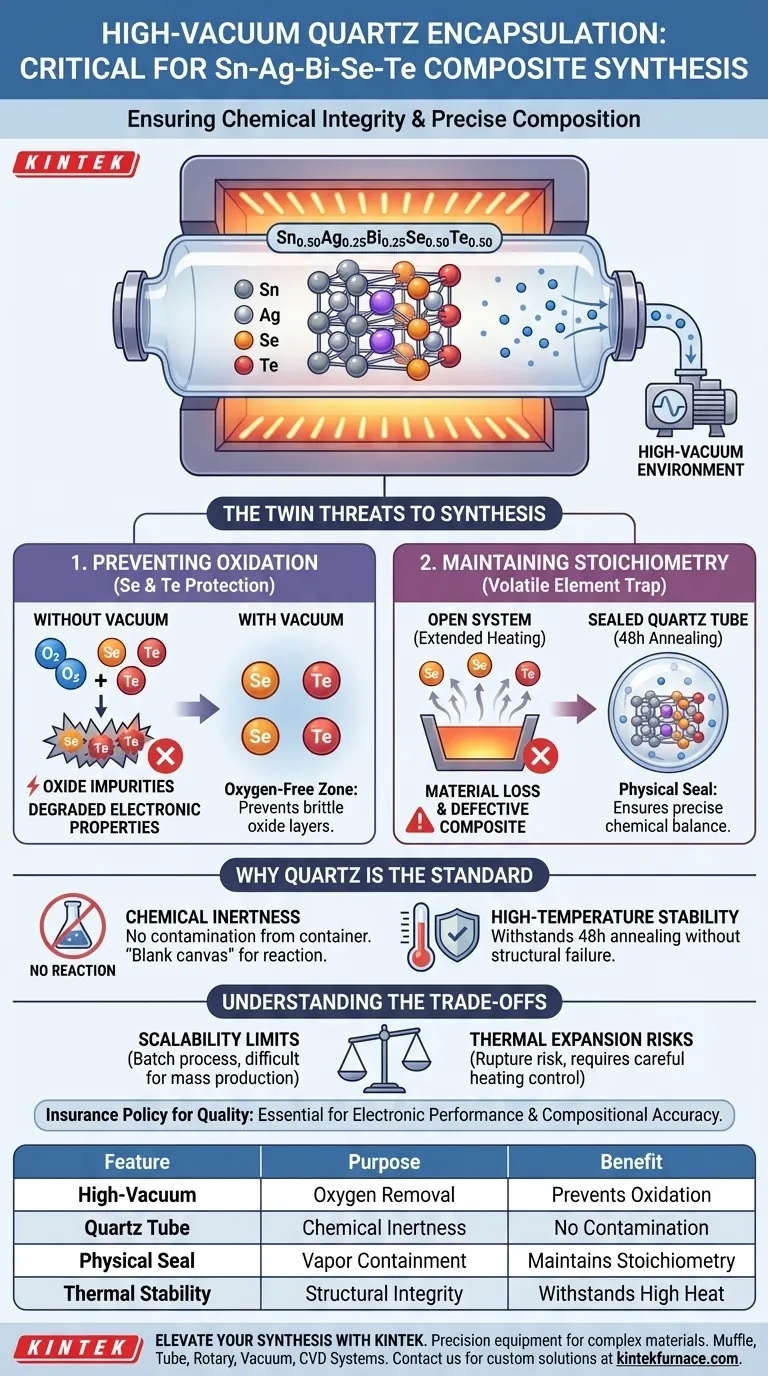
High-vacuum encapsulation is strictly required to maintain the chemical integrity and precise composition of the Sn0.50Ag0.25Bi0.25Se0.50Te0.50 composite. This process creates a controlled, inert environment that prevents the oxidation of sensitive elements like Selenium and Tellurium while physically trapping volatile components to stop them from evaporating during high-temperature processing.
Core Takeaway The process serves two non-negotiable functions: it creates an oxygen-free zone to prevent impurity formation and establishes a sealed system to contain volatile elements. Without this step, the material would degrade through oxidation and lose its specific chemical balance (stoichiometry), rendering the final composite defective.

The Twin Threats to Synthesis
To understand why this step is critical, you must look at what happens to the raw materials when exposed to heat and atmosphere.
Preventing Oxidation of Chalcogenides
Selenium (Se) and Tellurium (Te)—the chalcogenide components of this composite—are highly susceptible to oxidation.
At the elevated temperatures required for synthesis, these elements react aggressively with any available oxygen.
The high-vacuum environment effectively eliminates oxygen from the reaction chamber. This prevents the formation of brittle oxide layers or impurities that would degrade the electronic properties of the material.
Maintaining Stoichiometry
The preparation of this specific composite involves a lengthy 48-hour annealing process.
During this extended period of high heat, volatile elements naturally tend to vaporize and escape.
The physical seal of the quartz tube traps these vapors. This ensures that the elements remain within the reaction zone and re-integrate into the material, guaranteeing that the final product maintains the exact intended stoichiometric ratio (Sn0.50Ag0.25Bi0.25Se0.50Te0.50).
Why Quartz is the Standard
The choice of quartz as the encapsulation material is not arbitrary; it is a functional requirement for the reaction conditions.
Chemical Inertness
Quartz provides a "blank" canvas for the reaction.
It does not react chemically with Tin, Silver, Bismuth, Selenium, or Tellurium. This ensures that the tube itself does not introduce foreign contaminants into the composite.
High-Temperature Stability
The annealing process requires sustained high temperatures that would melt or degrade softer glasses.
Quartz maintains its structural integrity under these conditions, ensuring the vacuum seal remains unbroken throughout the 48-hour cycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While encapsulation is necessary for high-quality synthesis, it introduces specific challenges that must be managed.
Scalability Limits
High-vacuum encapsulation is inherently a batch process.
Each tube must be prepared, evacuated, sealed, and annealed individually. This makes the technique excellent for research and high-precision synthesis but difficult to scale for mass production compared to continuous flow methods.
Thermal Expansion Risks
The process relies on a closed system subjected to high heat.
If the internal vapor pressure of the volatile elements rises too quickly or the temperature exceeds the quartz's limits, the ampoule can rupture. Careful control of heating ramp rates is required to balance reaction speed with safety.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When preparing Sn-Ag-Bi-Se-Te composites, high-vacuum encapsulation acts as an insurance policy for your material's quality.
- If your primary focus is electronic performance: The vacuum is critical to prevent oxide impurities that act as scattering centers and reduce carrier mobility.
- If your primary focus is compositional accuracy: The physical seal is vital to prevent the loss of volatile Se and Te, ensuring your actual formula matches your theoretical calculation.
In the synthesis of complex chalcogenides, controlling the atmosphere is just as critical as controlling the ingredients.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose in Synthesis | Benefit for Sn-Ag-Bi-Se-Te |
|---|---|---|
| High-Vacuum | Oxygen removal | Prevents oxidation of sensitive Selenium and Tellurium |
| Quartz Tube | Chemical inertness | Ensures no contamination from the container during heating |
| Physical Seal | Vapor containment | Maintains precise stoichiometry during 48-hour annealing |
| Thermal Stability | Structural integrity | Withstands high temperatures without seal failure or rupture |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in chalcogenide synthesis demands the highest standards of temperature and atmospheric control. KINTEK provides the expertise and equipment necessary for complex material preparation. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique research or production needs.
Don't let oxidation or stoichiometry loss compromise your results. Let our specialized lab high-temp furnaces provide the stable, inert environment your materials require.
Ready to optimize your synthesis process? Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Zhenyu Tan, Degang Zhao. Enhanced Thermoelectric Properties in Cubic Sn0.50Ag0.25Bi0.25Se0.50Te0.50 via MWCNTs Incorporation. DOI: 10.3390/cryst15040365
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How is a tubular furnace utilized in the homogenization annealing of Ti-20Zr alloys? Precision Thermal Profiles
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the sintering process of modified graphite felt? Precision Control
- What is the specific role of a tube furnace in the synthesis and carbon-encapsulation of NiMo alloys? Explained
- What is sintering, and how is it performed in horizontal furnaces? Unlock Precision in Powder Processing
- What is the recommended procedure for using a vacuum tube type experimental furnace with a specific atmosphere? Master Precise Control for Your Experiments
- Why is controlling the residence time within a tube furnace critical for the synthesis of amorphous NiFe2O4 catalysts?
- What safety measures should be taken when operating a lab tube furnace? Essential Steps for Risk-Free Laboratory Work
- How does the working temperature range affect the choice of a tube furnace? Match Your Lab's Thermal Needs for Precision and Cost-Efficiency



















