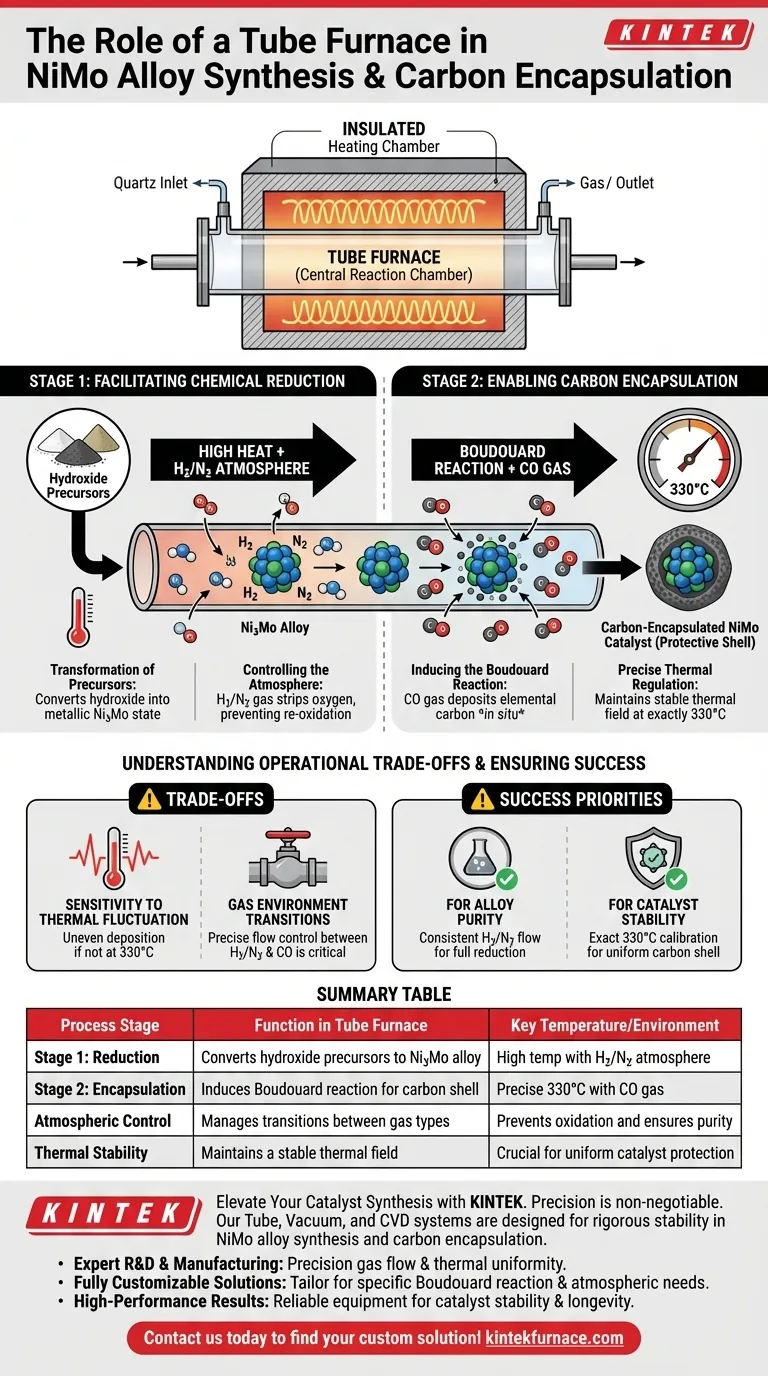
The tube furnace serves as the central reaction chamber for synthesizing and stabilizing NiMo alloy catalysts. Its specific role is to provide a strictly controlled high-temperature environment that first reduces hydroxide precursors into a metallic Ni3Mo state and subsequently maintains the precise thermal conditions required to encase the alloy in a protective carbon shell.
The tube furnace functions as a dual-stage reactor: it first facilitates the chemical reduction of precursors under a specific gas atmosphere and then stabilizes the temperature at exactly 330°C to drive the Boudouard reaction for carbon encapsulation.

Stage 1: Facilitating Chemical Reduction
Transformation of Precursors
The primary function of the tube furnace in the initial stage is to convert hydroxide precursors into a usable metallic form.
By applying high heat, the furnace drives the chemical transformation necessary to achieve the specific Ni3Mo alloy state.
Controlling the Atmosphere
This reduction process does not occur in standard air; it requires a specialized environment.
The tube furnace allows for the introduction of a hydrogen/nitrogen (H2/N2) atmosphere, which is essential for stripping oxygen from the precursors and preventing re-oxidation.
Stage 2: Enabling Carbon Encapsulation
Inducing the Boudouard Reaction
Once the alloy is formed, the furnace facilitates a secondary process known as the Boudouard reaction.
Carbon monoxide (CO) is introduced into the tube, reacting to deposit elemental carbon directly onto the alloy particles.
Precise Thermal Regulation
The success of this encapsulation relies entirely on thermal stability.
The tube furnace must maintain a precise and stable thermal field at 330°C, as deviation from this temperature can hinder the reaction efficiency.
Formation of the Protective Shell
The result of this thermally controlled reaction is the in situ deposition of carbon.
This forms a protective carbon shell around the Ni3Mo particles, which is critical for the stability and longevity of the catalyst.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Thermal Fluctuation
The reliance on the Boudouard reaction creates a strict dependency on temperature accuracy.
If the tube furnace fails to hold the thermal field at exactly 330°C, the deposition of the carbon shell may be uneven or insufficient, compromising the catalyst's protection.
Gas Environment Transitions
The process requires switching from a reducing atmosphere (H2/N2) to a carbon-rich atmosphere (CO).
This transition demands precise flow control within the furnace to ensure the distinct stages of reduction and encapsulation do not interfere with one another.
Ensuring Synthesis Success
To maximize the quality of your NiMo alloys, consider the following operational priorities:
- If your primary focus is Alloy Purity: Ensure the furnace maintains a consistent H2/N2 flow during the initial heating phase to fully reduce hydroxide precursors.
- If your primary focus is Catalyst Stability: Verify that the furnace calibration is exact at 330°C to guarantee a uniform protective carbon shell via the Boudouard reaction.
Mastering the thermal and atmospheric controls of the tube furnace is the single most important factor in producing high-performance, carbon-encapsulated NiMo catalysts.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Function in Tube Furnace | Key Temperature/Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Stage 1: Reduction | Converts hydroxide precursors to Ni3Mo alloy | High temp with $H_2/N_2$ atmosphere |
| Stage 2: Encapsulation | Induces Boudouard reaction for carbon shell | Precise $330^{\circ}C$ with $CO$ gas |
| Atmospheric Control | Manages transitions between gas types | Prevents oxidation and ensures purity |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains a stable thermal field | Crucial for uniform catalyst protection |
Elevate Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when your research depends on exact thermal fields and atmospheric transitions. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to maintain the rigorous stability required for NiMo alloy synthesis and carbon encapsulation.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Our high-temp furnaces are engineered for precision gas flow and thermal uniformity.
- Fully Customizable Solutions: Tailor your furnace to meet specific research needs, from Boudouard reaction stability to specialized reducing atmospheres.
- High-Performance Results: Ensure catalyst stability and longevity with reliable equipment trusted by lab professionals worldwide.
Ready to achieve superior thermal control for your next synthesis project? Contact us today to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Sun Seo Jeon, Hyunjoo Lee. Degradation of NiMo Catalyst Under Intermittent Operation of Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzer and its Mitigation by Carbon Encapsulation. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202501800
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do laboratory tube furnaces contribute to the sintering of Ba0.95La0.05(Fe1-xYx)O3-δ? Precise Atmosphere Control
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace with an Argon atmosphere required for the carbonization of biomass? Key Insights
- How do three-zone tube furnaces support scalability? Bridge Lab to Industrial Production Seamlessly
- What distinguishes a compact tube furnace from other types? Ideal for Small-Scale Lab Precision
- What are the technical functions of an industrial tube furnace for ZIF-8 carbonization? Master Precise Pyrolysis
- Why is a high-precision dual-zone furnace required for 1T-TaS2 crystals? Achieve Perfect CVT Phase Integrity
- What is a tubular heater used for? Prevent Frost and Damp with Low-Cost Maintenance Heat
- What is the basic working principle of a tube furnace? Master Precise Heating for Material Processing



















