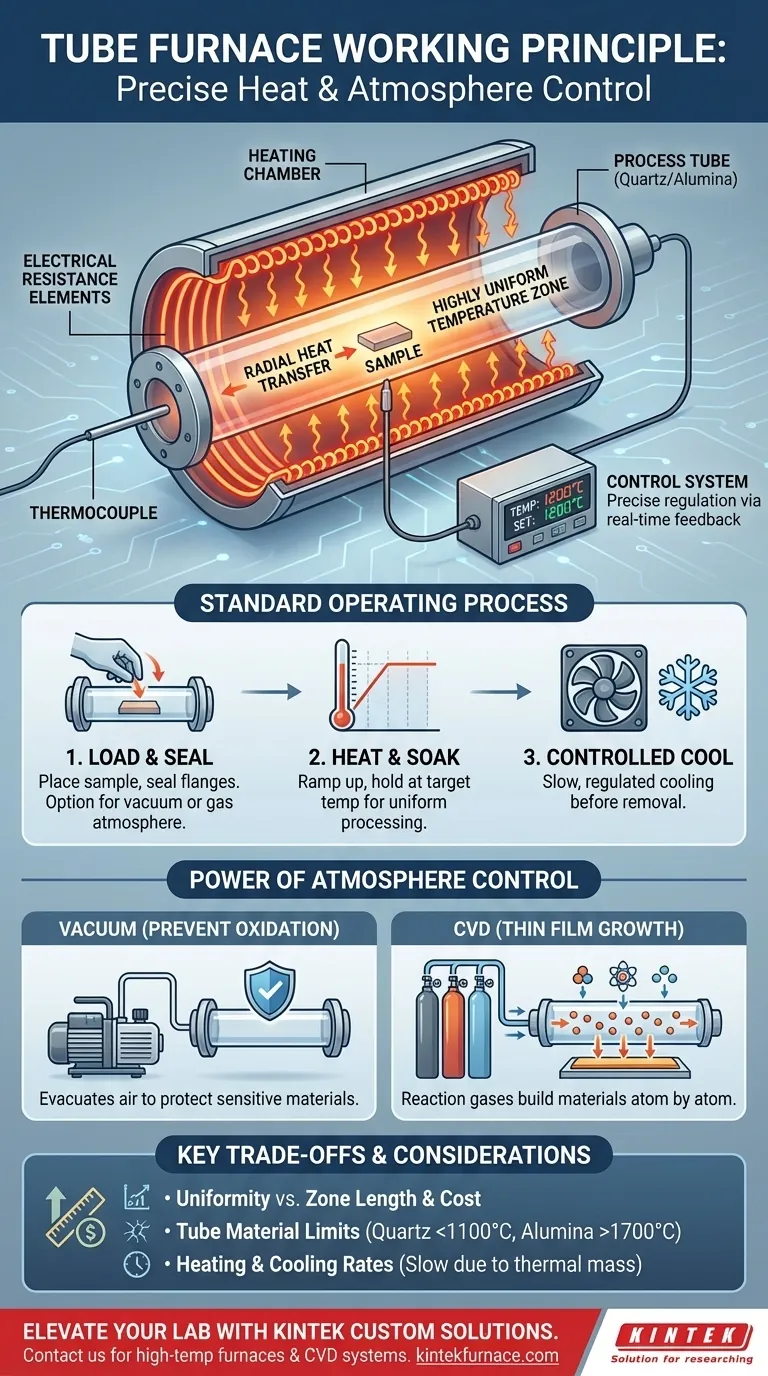
At its core, a tube furnace operates on a simple principle: it generates heat using electrical resistance elements that surround a central tube. This design transfers heat radially inward, creating a highly uniform and precisely controlled temperature zone inside the tube for processing samples or materials.
The true value of a tube furnace lies not just in its ability to reach high temperatures, but in its capacity to create an isolated and exceptionally uniform environment. This control over both heat and atmosphere is what makes it an indispensable tool for advanced research and material processing.

The Core Components of Operation
To understand its function, it's best to break the furnace down into its three primary systems: the heat source, the process tube, and the control system.
The Heating Chamber and Elements
The vast majority of modern lab-scale tube furnaces generate heat through electrical resistance. High-resistance wires or ceramic elements are wound or placed around the process tube.
When an electric current is passed through these elements, they heat up significantly, radiating thermal energy into the furnace chamber and, most importantly, onto the outer surface of the process tube.
The Process Tube
This is the heart of the furnace. The process tube acts as the chamber that holds the sample, isolating it from the heating elements and the outside world.
These tubes are typically made from materials like quartz, alumina, or corundum, chosen based on the required temperature and chemical compatibility of the experiment. The tube allows for the creation of a specific, controlled atmosphere around the sample.
The Control System
A sophisticated controller is essential for a tube furnace's function. It uses a thermocouple, a temperature sensor placed near the process tube, to provide real-time temperature feedback.
The controller constantly compares this feedback to the user-defined setpoint, adjusting the power sent to the heating elements to maintain a stable and precise temperature, often within a single degree.
The Standard Operating Process
Regardless of the specific application, the workflow for using a tube furnace follows a consistent, multi-stage process designed for precision and safety.
1. Sample Loading and Sealing
First, the sample or substrate is carefully placed inside the process tube. If a specific atmosphere is required, the ends of the tube are then sealed using specialized sealing flanges.
This is the step where a vacuum can be pulled or specific process gases can be introduced, transforming the furnace from a simple heater into a controlled reaction chamber.
2. Heating and Soaking
The control system is programmed with a desired temperature profile. The furnace begins to "ramp up" the heat at a controlled rate to prevent thermal shock to the tube or sample.
Once the target temperature is reached, it is held constant for a specified duration. This period, known as "soaking," is when the actual material processing, reaction, or heat treatment occurs. The uniform heat distribution along the tube is critical during this phase.
3. Controlled Cooling
After the soaking period is complete, the power to the heating elements is shut off. The furnace is then allowed to cool, often at a controlled rate, back to a safe temperature before the sample can be removed.
The Power of Atmosphere Control
Simple heating in air is only one application. The true versatility of a tube furnace is unlocked by its ability to manipulate the environment within the tube.
Vacuum Furnaces: Preventing Oxidation
By using a sealed tube and a vacuum pump, all the air can be evacuated from the chamber. This creates a vacuum atmosphere that is critical for processing air-sensitive materials, preventing unwanted oxidation or contamination during heating.
CVD Furnaces: Building Materials Atom by Atom
In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a tube furnace is used to heat a substrate while specific reaction gases are flowed through the tube. The high temperature causes these gases to react and "deposit" a thin solid film onto the substrate, building a new material one atomic layer at a time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, tube furnaces have inherent limitations that are important to understand.
Temperature Uniformity vs. Zone Length
A longer heated zone generally provides a larger area of stable, uniform temperature. However, this comes at the cost of a larger furnace footprint, higher energy consumption, and increased expense.
Tube Material Limitations
The maximum operating temperature of the furnace is often dictated by the process tube material. Quartz is common and offers good visibility, but it can degrade at temperatures above 1100°C. Alumina can withstand much higher temperatures (up to 1700-1800°C) but is opaque and more brittle.
Heating and Cooling Rates
Due to their significant thermal mass (insulation and heating elements), tube furnaces cannot change temperature instantaneously. Ramping up and, especially, cooling down can be a slow process, which must be factored into experimental planning.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right configuration depends entirely on the intended application.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment in air: A basic, single-zone tube furnace with an unsealed tube is perfectly sufficient.
- If your primary focus is preventing sample oxidation or contamination: You need a system with sealing flanges and a vacuum pump to create a controlled, inert atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is thin film growth or advanced materials synthesis: A specialized CVD furnace with mass flow controllers for precise gas handling is essential.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles empowers you to use a tube furnace not merely as a heater, but as a precise instrument for material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Component/Process | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Generate heat via electrical resistance for radial inward transfer |
| Process Tube | Holds samples, made of quartz/alumina, enables atmosphere control |
| Control System | Uses thermocouple feedback for precise temperature regulation |
| Operating Steps | Load/seal, heat/soak, cool in controlled stages |
| Atmosphere Types | Vacuum for oxidation prevention, CVD for thin film deposition |
| Limitations | Trade-offs in zone length, tube material temp limits, slow ramp/cool rates |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with a custom tube furnace solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for uniform heating and atmosphere control. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your research and material processing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace? Precision Heating for Lab and Industrial Applications
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- Why are tubular furnaces important in material testing and research? Unlock Precision for Advanced Materials Development
- In which industries is the tube furnace commonly used? Essential for Materials Science, Energy, and More
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment



















