In essence, a tubular heater is a low-wattage electric heater designed to provide gentle, constant background heat. Its primary purpose is not to warm a room for occupancy, but to maintain a minimum temperature to prevent frost, dampness, and condensation in enclosed or infrequently used spaces. Common applications include greenhouses, sheds, wardrobes, and conservatories.
A tubular heater is not a replacement for a conventional room heater. Instead, it is a highly efficient, specialized tool for low-cost, continuous "set-and-forget" temperature maintenance in smaller areas where preventing cold and damp is the main objective.
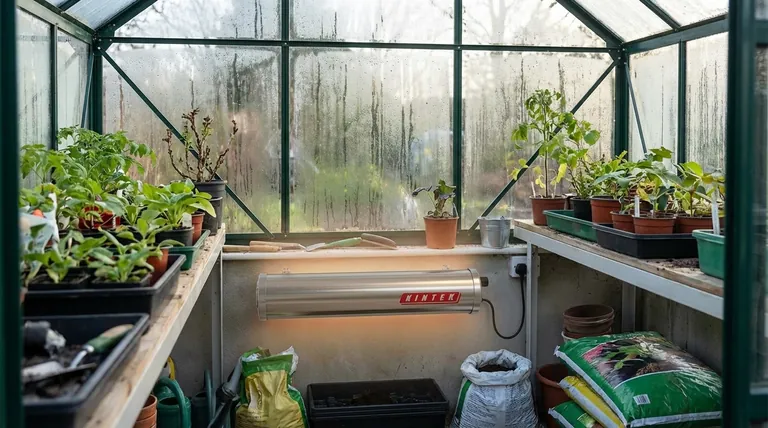

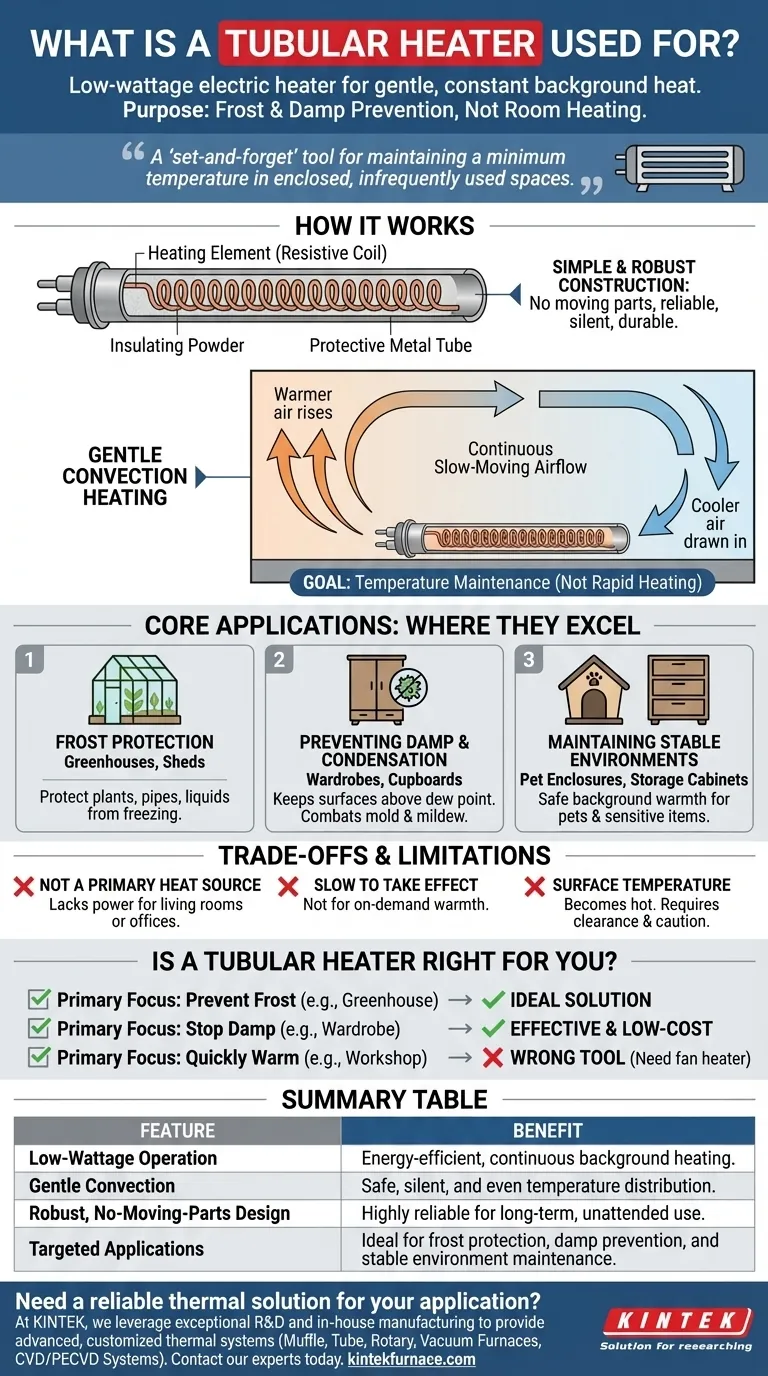
How a Tubular Heater Works
A tubular heater's effectiveness comes from its simple design and low-energy operation. It works by creating a slow, gentle convection current rather than producing intense, directional heat.
Simple and Robust Construction
At its core, a tubular heater contains a resistive heating element (an electric coil) surrounded by insulating powder and encased in a protective metal tube.
This design has no moving parts, making it extremely reliable, silent, and durable for long-term, unattended operation.
Gentle Convection Heating
The heater's surface warms up, gently heating the air directly around it. This warmer, less dense air rises, drawing cooler, denser air towards the heater from below.
This process creates a continuous, slow-moving circulation of air that gradually raises the ambient temperature of the entire enclosed space by a few degrees.
The Goal: Temperature Maintenance
A tubular heater is not designed for rapid heating. Its function is to consistently emit a small amount of energy to keep the temperature just above freezing or to prevent the air from becoming saturated with moisture.
Core Applications: Where Tubular Heaters Excel
These devices are purpose-built for specific environments where high-power heating is unnecessary or undesirable.
Frost Protection
This is the most common use. In spaces like greenhouses, sheds, or uninsulated utility rooms, a tubular heater can provide just enough warmth to protect plants, pipes, and stored liquids from freezing during cold spells.
Preventing Damp and Condensation
In wardrobes, airing cupboards, or beneath windows, a tubular heater keeps surface temperatures just above the dew point. This prevents moisture in the air from condensing on cold walls or clothes, effectively combating mold, mildew, and musty odors.
Maintaining Stable Environments
They are ideal for providing a safe level of background warmth in pet enclosures like kennels or chicken coops. They also protect sensitive electronics or materials in storage cabinets from the damaging effects of cold and damp.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While excellent for its intended purpose, a tubular heater is the wrong tool for many common heating needs.
Not a Primary Heat Source
A tubular heater lacks the power to heat a living room, office, or any regularly occupied space to a comfortable temperature. It is strictly a supplementary or maintenance heater.
Slow to Take Effect
Because of its low wattage and reliance on gentle convection, it can take many hours to have a noticeable impact on the temperature of a space. It is not suitable for providing on-demand warmth.
Surface Temperature
The surface of the heater becomes hot to the touch. While generally safer than radiant heaters, it must be installed with adequate clearance from flammable materials, and caution is needed in areas with children or pets.
Is a Tubular Heater Right for Your Goal?
Choose this device based on its specific strengths for maintenance, not for active heating.
- If your primary focus is preventing frost in a greenhouse or shed: A tubular heater is an ideal, energy-efficient, and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is stopping dampness in a wardrobe or small cupboard: This is one of the most effective and low-cost methods available for preventing mold and mildew.
- If your primary focus is quickly warming a cold workshop or home office: You need a fan heater or a more powerful convection heater, as a tubular heater will not meet your needs.
By understanding its role as a low-power maintenance device, you can use a tubular heater effectively to protect your spaces and belongings.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Low-Wattage Operation | Energy-efficient, continuous background heating. |
| Gentle Convection | Safe, silent, and even temperature distribution. |
| Robust, No-Moving-Parts Design | Highly reliable for long-term, unattended use. |
| Targeted Applications | Ideal for frost protection, damp prevention, and stable environment maintenance. |
Need a reliable thermal solution for your application?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced, customized thermal systems. Whether your project requires a standard tubular heater or a sophisticated high-temperature furnace, our expertise in Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems ensures a precise solution for your unique requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve optimal temperature control and protection.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control



















