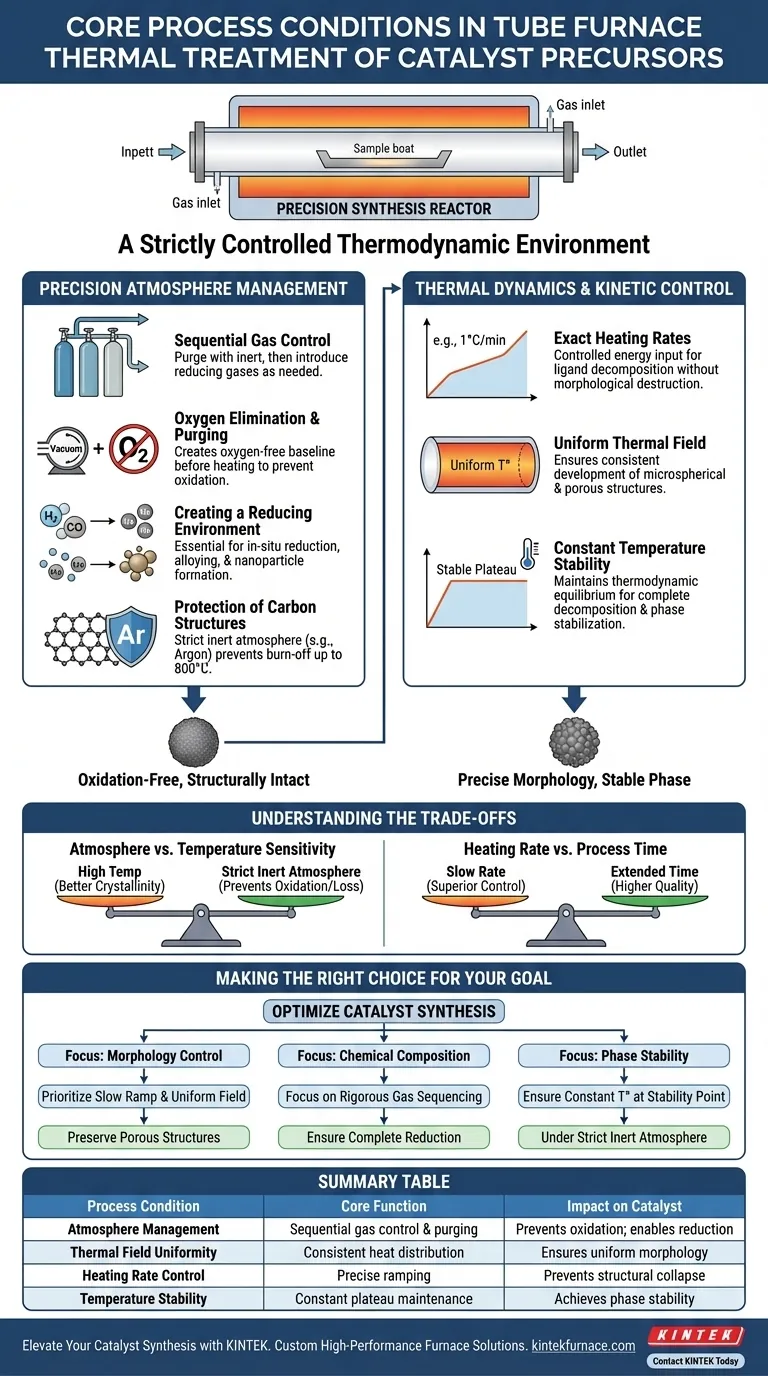
A tube furnace provides a strictly controlled thermodynamic environment defined by precise atmosphere regulation and rigorous thermal management. Specifically, it enables the sequential introduction of inert and reducing gases to eliminate oxygen, while simultaneously maintaining exact heating rates and a uniform thermal field to drive complex chemical transformations like ligand decomposition and metal reduction.
The tube furnace functions not merely as a heating element, but as a precision synthesis reactor. It synchronizes gas composition with thermal kinetics to ensure that precursor decomposition and nanoparticle formation occur without oxidation or structural collapse.

precision Atmosphere Management
Sequential Gas Control
The primary function of the tube furnace is to manipulate the reaction atmosphere through the sequential introduction of gases. The process typically begins with inert gases to purge the system, followed by reducing gases when specific chemical reactions are required.
Oxygen Elimination and Purging
Before thermal treatment begins, the equipment performs system purging to completely eliminate oxygen. This creates an oxygen-free baseline that prevents the unwanted oxidation of precursor materials during the initial heating phases.
Creating a Reducing Environment
Once purged, the furnace maintains a uniform reducing atmosphere. This environment is essential for inducing the in-situ reduction of metal ions, allowing them to alloy and form highly dispersed metallic nanoparticles on the carrier material.
Protection of Carbon Structures
In applications involving carbon-based precursors, such as the pyrolysis of polypyrrole layers, a strict inert atmosphere (e.g., Argon) is maintained. This prevents the conductive carbon layer from burning off at high temperatures (up to 800 °C), ensuring the final material retains its conductivity.
Thermal Dynamics and Kinetic Control
Exact Heating Rates
The furnace provides precise control over the heating rate, capable of slow ramps (e.g., 1 °C per minute). This controlled energy input is critical for decomposing organic ligands without destroying the underlying morphology of the material.
Uniform Thermal Field
Beyond simple temperature targets, the furnace generates a uniform thermal field distribution within the tube. This uniformity ensures that microspherical morphologies and porous structures—such as those found in Bi2O3 crystals—are developed consistently throughout the sample batch.
Constant Temperature Stability
The equipment maintains constant temperature control at target plateaus. This stability is required to achieve thermodynamic equilibrium, ensuring complete thermal decomposition of precursors and the stabilization of internal crystalline phases.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Atmosphere vs. Temperature Sensitivity
High-temperature treatments offer better crystallinity but pose higher risks of material loss. Without a strictly maintained inert atmosphere, increasing the temperature to improve crystallinity can inadvertently oxidize carbon components or alter the stoichiometry of the catalyst.
Heating Rate vs. Process Time
While a slow heating rate yields superior morphological control and prevents structural collapse, it significantly extends the total processing time. Accelerating the rate to save time risks incomplete ligand decomposition or uneven particle growth, compromising the catalyst's dispersion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your catalyst synthesis, align your furnace settings with your specific material requirements:
- If your primary focus is Morphology Control: Prioritize a slow, precise heating rate and a uniform thermal field to preserve porous structures and particle shape.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Composition: Focus on the rigorous sequencing of gases to ensure complete oxygen elimination and effective reduction of metal ions.
- If your primary focus is Phase Stability: Ensure constant temperature control at the thermodynamic stability point of your target crystal, under a strict inert atmosphere.
Success in catalyst preparation relies on balancing the removal of organic components with the preservation of the active metal structure.
Summary Table:
| Process Condition | Core Function | Impact on Catalyst |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Management | Sequential gas control & oxygen purging | Prevents oxidation; enables in-situ metal reduction. |
| Thermal Field Uniformity | Consistent heat distribution | Ensures uniform morphology and porous structures. |
| Heating Rate Control | Precise ramping (e.g., 1 °C/min) | Prevents structural collapse during ligand decomposition. |
| Temperature Stability | Constant plateau maintenance | Achieves thermodynamic equilibrium and phase stability. |
Elevate Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in thermal kinetics and atmosphere management is non-negotiable for high-performance catalyst production. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of laboratory research and industrial scaling.
Whether you need to maintain a strict inert environment for carbon protection or require precise ramping for delicate nanoparticle formation, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to your unique research needs.
Ready to optimize your material transformation? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution with our technical experts.
Visual Guide
References
- Iveta Boshnakova, Evelina Slavcheva. Bimetallic Ir-Sn Non-Carbon Supported Anode Catalysts for PEM Water Electrolysis. DOI: 10.3390/inorganics13070210
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision tube furnace required for PtCln/Fe-N-C catalysts? Ensure Sub-Nanometer Precision
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace necessary for carbonization of biochar? Unlock High-Performance Electrodes
- What role does a tube furnace play in Se/NC composite synthesis? Mastering the Melt-Diffusion Method
- Why is a tube furnace with precise temperature control required for Pt@A&R-TiO2 calcination? Optimize Catalyst Phase
- What safety protections are included in three-zone split tube furnaces? Ensure Safe, Reliable High-Temp Operations
- What are the main characteristics of horizontal tube furnaces? Optimize Your High-Temp Processing with Uniform Heating
- What role does a tube furnace play in the pyrolysis of covalent triazine frameworks? Optimize Your Carbon Synthesis
- What are the key characteristics of a 70mm tube furnace? Unlock Precision Heating for Your Lab



















