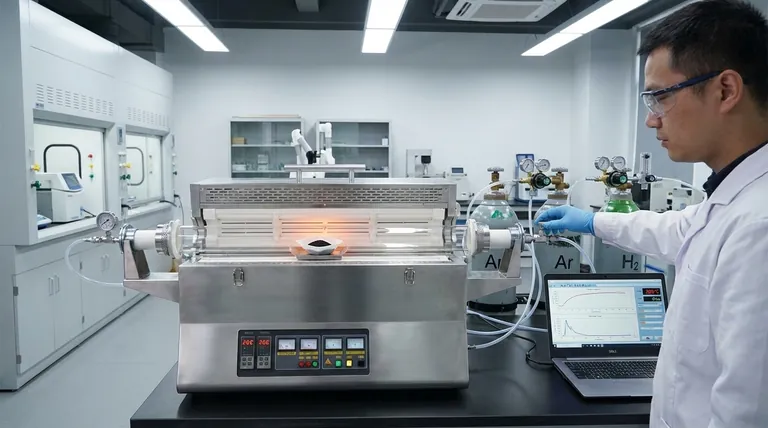
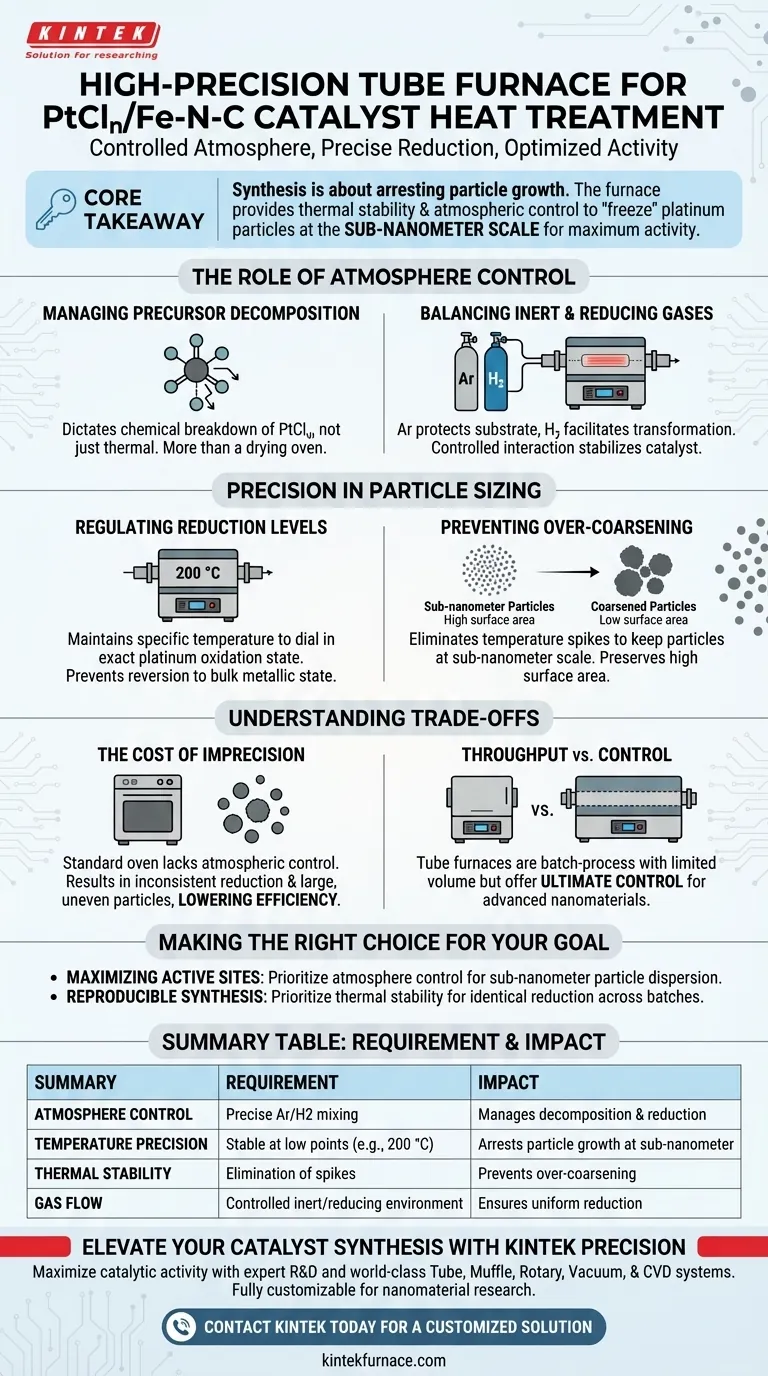
A high-precision tube furnace is strictly required to create a stable, controlled environment—using inert gases like argon or reducing gases like hydrogen—that manages the delicate thermal decomposition of platinum precursors. Operating at specific temperatures, such as 200 °C, the furnace enables precise regulation of platinum reduction levels, ensuring the formation of sub-nanometer particles while preventing the performance-degrading coarsening that occurs in less controlled environments.
Core Takeaway The synthesis of PtCln/Fe-N-C catalysts is not merely about heating; it is about arresting particle growth at a specific stage. The tube furnace provides the necessary thermal stability and atmospheric control to "freeze" platinum particles at the sub-nanometer scale, which is critical for maximizing catalytic activity.

The Role of Atmosphere Control
Managing Precursor Decomposition
The primary function of the tube furnace in this application is to manage how the platinum precursor (PtCln) breaks down.
Unlike simple drying ovens, a tube furnace allows for the introduction of specific gases. This creates a chemical environment that dictates exactly how the precursor decomposes chemically, rather than just thermally.
Balancing Inert and Reducing Gases
The process relies on the ability to switch between or mix inert gases (like argon) and reducing gases (like hydrogen).
This balance is critical. Inert gases protect the substrate, while reducing gases facilitate the transformation of the metal precursors. This controlled interaction ensures the thermal stabilization of the catalyst components during the heat treatment.
Precision in Particle Sizing
Regulating Reduction Levels
The catalytic performance of PtCln/Fe-N-C is directly tied to the oxidation state of the platinum.
By maintaining a highly specific temperature (e.g., 200 °C), the furnace allows researchers to dial in the exact level of platinum reduction required. This precision prevents the metal from fully reverting to a bulk metallic state, which would reduce its chemical activity.
Preventing Over-Coarsening
The most significant risk during heat treatment is "coarsening," where small particles clump together to form larger, less effective particles.
A high-precision furnace prevents this by eliminating temperature spikes. It maintains the thermal conditions necessary to keep particles at the sub-nanometer scale. This preserves the high surface area required for effective catalysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Cost of Imprecision
If a standard muffle furnace or oven were used instead of a high-precision tube furnace, the lack of atmospheric flow control would lead to inconsistent reduction.
Without the precise reducing atmosphere, platinum precursors might either fail to reduce completely or agglomerate rapidly. This results in large, uneven particles that significantly lower the catalyst's efficiency.
Throughput vs. Control
Tube furnaces are generally batch-process tools with limited volume compared to industrial continuous furnaces.
While they offer the ultimate control required for synthesizing advanced nanomaterials like PtCln/Fe-N-C, they are often throughput-limited. However, for high-performance catalysts where atomic-level structure defines value, this trade-off is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your catalyst synthesis, consider your specific performance targets:
- If your primary focus is maximizing active sites: Prioritize atmosphere control to ensure sub-nanometer particle dispersion without agglomeration.
- If your primary focus is reproducible synthesis: Prioritize the furnace’s thermal stability to ensure identical reduction levels across different batches.
The tube furnace is the defining instrument that transitions a material from a simple mixture of precursors to a highly engineered, nanostructured catalyst.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Requirement for PtCln/Fe-N-C Synthesis | Impact on Catalyst Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Precise mixing of Argon and Hydrogen | Manages precursor decomposition and metal reduction |
| Temperature Precision | Stable operation at low points (e.g., 200 °C) | Arrests particle growth at the sub-nanometer scale |
| Thermal Stability | Elimination of temperature spikes | Prevents over-coarsening and loss of surface area |
| Gas Flow | Controlled inert/reducing environment | Ensures uniform reduction levels across the batch |
Elevate Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Maximize your catalytic activity by ensuring perfect atomic-level structures. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of nanomaterial research.
Whether you are synthesizing PtCln/Fe-N-C catalysts or developing next-generation lab high-temp applications, our furnaces provide the atmospheric control and thermal stability your breakthrough deserves.
Ready to optimize your heat treatment? Contact KINTEK today for a customized solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Hiroshi Yano. Sustainable activation of the PtCl <sub> <i>n</i> </sub> /Fe–N–C cathode for PEFCs through repeated subnanometer sizing and coarsening. DOI: 10.1039/d5lf00185d
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- How does a benchtop fixed-bed quartz reactor simulate industrial conditions? Evaluate Pt-Ni Catalyst Stability
- What are the key benefits of using split tube furnaces? Unlock Superior Access and Control for Your Lab
- What is the purpose of using forming gas (N2/H2) in a tube furnace? Achieve High-Purity Cr3+-Activated LiScO2 Phosphors
- How does a tube furnace generate high temperatures? Efficient, Precise Heating for Your Lab
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the carbonization of biomass? Master Precise Pyrolysis for Superior Materials
- What industries commonly use horizontal tube furnaces? Key Applications in Materials Science and Manufacturing
- What is the function of a high-temperature tube furnace? Master Grain Growth for Microcrystalline Alloy Samples
- Why is a specialized tube furnace with a steam inlet required for the steam activation of carbon materials?



















