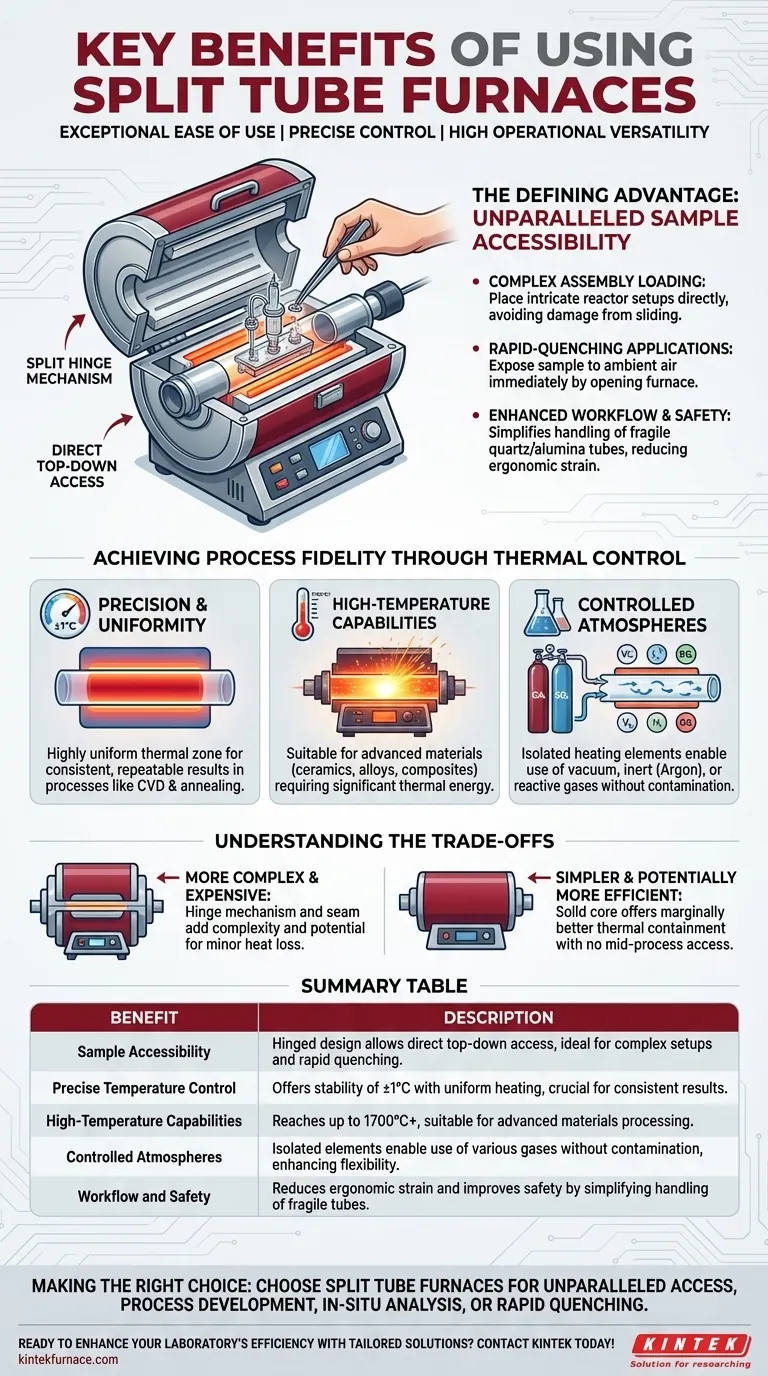
At their core, split tube furnaces provide exceptional ease of use, precise temperature control, and high operational versatility. Their defining feature—a hinged body that opens to allow direct access to the work tube—solves critical challenges in laboratory and industrial high-temperature processing, making them indispensable for complex or delicate applications.
The central advantage of a split tube furnace is not merely heating, but access. While any tube furnace offers a controlled thermal environment, the split design fundamentally changes how you interact with your sample, enabling rapid setup, in-situ adjustments, and fast cooling cycles that are impossible with conventional solid-core designs.

The Defining Advantage: Unparalleled Sample Accessibility
The most significant benefit of a split tube furnace stems directly from its mechanical design. Unlike solid tube furnaces that require samples to be loaded from one end, a split tube furnace is built in two halves connected by a hinge.
The "Split Hinge" Mechanism
This design allows the entire furnace chamber to be opened like a clamshell. This provides complete, top-down access to the internal work tube and the sample within it.
Why This Matters for Your Process
This direct access is critical for processes where the sample assembly is complex or delicate. You can place intricate reactor setups, probes, or pre-assembled components directly into the tube before closing the furnace, avoiding the risk of damage that comes with sliding them down a long tube.
It also enables rapid-quenching applications. By simply opening the furnace, the sample can be exposed to ambient air for immediate cooling, a crucial step in many material synthesis and phase-transformation studies.
Enhancing Workflow and Safety
For operators, this design simplifies the loading and unloading of process tubes. It reduces the ergonomic strain and difficulty associated with handling long, fragile quartz or alumina tubes, creating a more efficient and safer workflow.
Achieving Process Fidelity Through Thermal Control
Beyond accessibility, split tube furnaces are engineered for high-performance thermal processing, ensuring your results are repeatable and accurate.
Precision and Uniformity
Modern split tube furnaces offer exceptional temperature control, often with a stability of ±1°C. Their cylindrical heating chambers and high-quality, graded insulation are designed to create a highly uniform thermal zone, ensuring the entire sample experiences a consistent temperature. This uniformity is vital for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and annealing, where even minor temperature gradients can ruin outcomes.
High-Temperature Capabilities
These furnaces are available in models capable of reaching extremely high temperatures, often up to 1700°C or more. This makes them suitable for processing advanced materials, including ceramics, alloys, and composites that require significant thermal energy.
Controlled Atmospheres
The furnace's heating elements are isolated from the internal process tube. This allows you to maintain a precisely controlled atmosphere within the tube—whether it's a vacuum, an inert gas like argon, or a reactive gas—without risk of contamination or reaction with the heating elements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the split-tube design introduces considerations that differ from simpler, solid-core furnaces.
Split vs. Solid Tube Furnaces
The primary trade-off is mechanical complexity and cost. The hinge mechanism and the seam between the two halves make a split tube furnace inherently more complex and typically more expensive than a solid tube furnace of a similar size and temperature rating. While modern designs have excellent seals, the seam is a potential source of minor heat loss compared to a seamless solid tube.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation
Split tube furnaces are built with highly efficient, multi-layer insulation to minimize heat loss and reduce energy consumption during steady-state operation. However, the ability to open the furnace for rapid cooling is an intentional energy release. For processes requiring maximum thermal stability with no mid-process access, a solid tube furnace may offer marginally better thermal containment.
Mechanical Considerations
The hinge and clasp mechanisms are robust but represent additional mechanical components that require proper maintenance. Over many years of heavy use, they are potential points of wear that are absent in a simpler solid furnace design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your process requirements and priorities.
- If your primary focus is process development, in-situ analysis, or rapid quenching: The unparalleled sample access of a split tube furnace is a decisive advantage.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput, standardized processing of simple samples: A solid tube furnace may be a more cost-effective and mechanically simpler choice.
- If your primary focus is working with complex, pre-assembled reactors or delicate materials: The ability to place, rather than slide, your sample assembly makes the split tube design essential.
Ultimately, choosing a split tube furnace is an investment in operational flexibility, process visibility, and precise control.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Sample Accessibility | Hinged design allows direct top-down access for easy loading/unloading, ideal for complex or delicate setups and rapid quenching. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Offers stability of ±1°C with uniform heating, crucial for consistent results in processes like CVD and material annealing. |
| High-Temperature Capabilities | Can reach up to 1700°C or more, suitable for advanced materials processing such as ceramics and composites. |
| Controlled Atmospheres | Isolated heating elements enable use of vacuum, inert, or reactive gases without contamination, enhancing process flexibility. |
| Workflow and Safety | Reduces ergonomic strain and improves safety by simplifying handling of fragile tubes and complex assemblies. |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's efficiency with tailored high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced split tube furnaces and other products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, delivering reliable performance and process optimization. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















