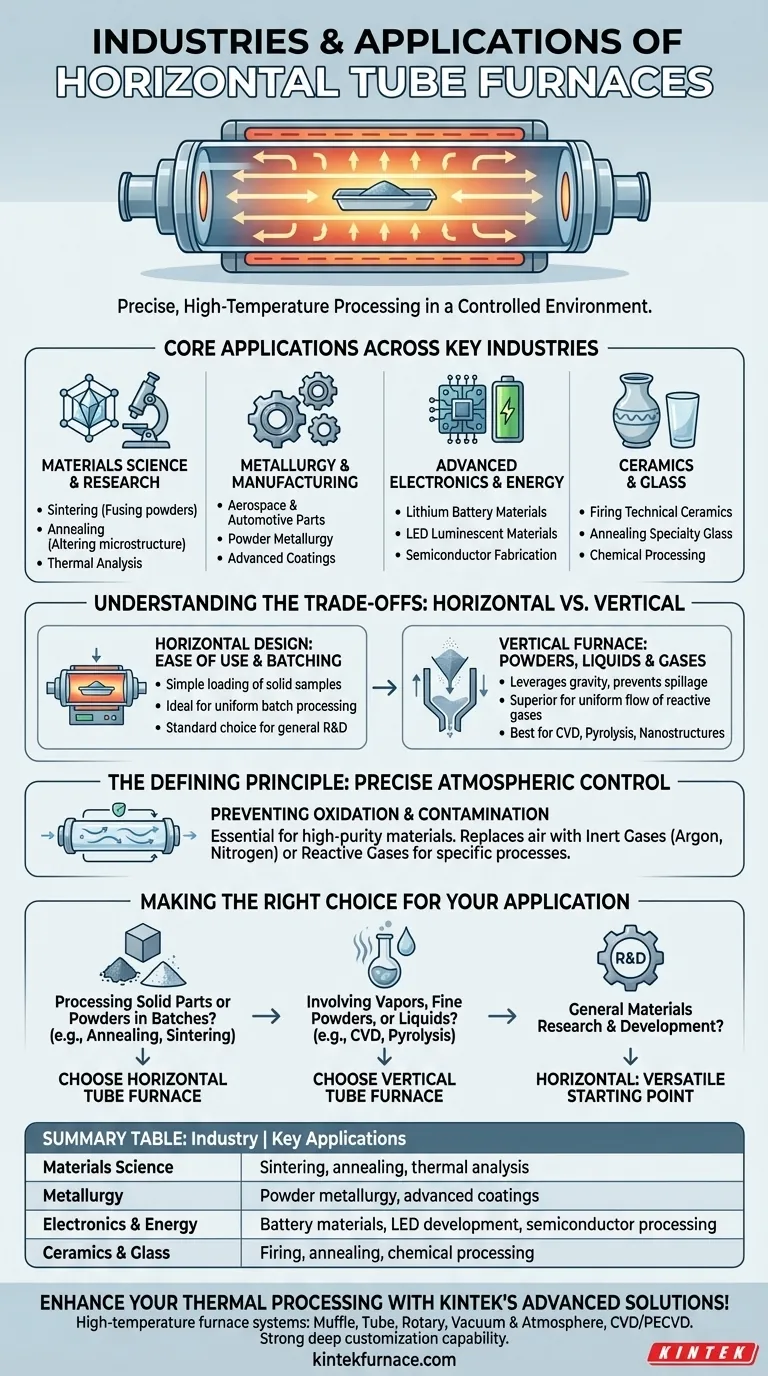
At their core, horizontal tube furnaces are workhorses in any industry that requires precise, high-temperature processing of materials in a controlled environment. They are most commonly used in materials science, metallurgy, advanced electronics, battery manufacturing, and ceramics. Their design is ideal for heat-treating solid samples, powders, and components in uniform batches.
The choice of a horizontal tube furnace is driven by the need for repeatable thermal processing of solid-state materials. Its primary advantage lies in ease of loading and its suitability for batch processes like annealing, sintering, and synthesis where precise atmospheric control is critical.
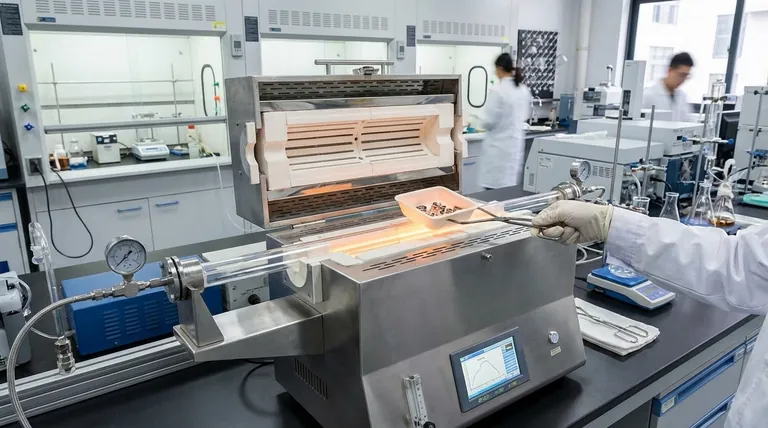

Core Applications Across Key Industries
The versatility of the horizontal tube furnace makes it a foundational tool across numerous research and manufacturing sectors. The specific process, rather than the industry itself, is what dictates its use.
Materials Science and Research
This is the foundational field for tube furnaces. Researchers rely on them for synthesizing and testing new materials under highly repeatable conditions.
Key processes include sintering (fusing powders into a solid mass), annealing (altering a material's microstructure with heat), and thermal analysis to study material properties at high temperatures.
Metallurgy and Manufacturing
Industries like aerospace, automotive, and tool manufacturing use horizontal furnaces for the critical heat treatment of metal parts and components.
This includes powder metallurgy, where metal powders are formed into complex parts, and the application of advanced coatings that require a specific thermal cycle to cure and bond correctly.
Advanced Electronics and Energy
The production of modern electronics and energy solutions depends on materials processed with extreme purity and precision.
Horizontal furnaces are essential for creating lithium battery positive and negative materials, developing LED luminescent materials, and conducting thermal processing steps in semiconductor fabrication.
Ceramics and Glass
The ceramics and glass industries use these furnaces for firing, annealing, and chemical processing. Their ability to achieve high temperatures uniformly is crucial for producing technical ceramics and specialty glass products.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Horizontal vs. Vertical
While versatile, the horizontal design is not universally optimal. Understanding its trade-offs compared to a vertical tube furnace is key to selecting the right tool.
The Advantage of Horizontal Design
The primary strength of a horizontal furnace is its simplicity and ease of use for solid samples. Loading and unloading boats or trays of components is straightforward.
This design is ideal for batch processing, where multiple discrete samples are treated simultaneously under the same conditions.
When a Vertical Furnace is a Better Fit
Vertical tube furnaces are superior for processes involving powders, liquids, or gases where gravity is beneficial. They prevent sample spillage and ensure a more uniform flow of reactive gases.
Processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), pyrolysis, and the synthesis of certain nanostructures are often better suited to a vertical orientation to achieve uniform coating and deposition.
The Defining Principle: Precise Atmospheric Control
The single most important feature of a tube furnace is its ability to maintain a controlled atmosphere, which is essential for high-technology materials.
What is a Controlled Atmosphere?
A controlled atmosphere involves sealing the process tube and purging the ambient air, replacing it with a specific gas or a vacuum.
This is typically an inert gas like argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation, or a reactive gas to participate in a chemical process.
Why It Matters for High-Tech Materials
For many advanced materials, reacting with oxygen at high temperatures can ruin their properties. A controlled atmosphere prevents oxidation and contamination.
This enables the creation of high-purity alloys, semiconductors, and ceramics that would be impossible to produce in open air.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the right furnace, focus on the material state and the process goal.
- If your primary focus is processing solid parts or powders in batches (e.g., annealing metal parts, sintering ceramics): A horizontal tube furnace is the standard choice for its ease of loading and operational simplicity.
- If your primary focus involves vapors, fine powders, or liquids (e.g., Chemical Vapor Deposition, pyrolysis): A vertical tube furnace is likely a better fit to leverage gravity and ensure process uniformity.
- If your primary focus is general materials research and development: A horizontal tube furnace is the most versatile starting point, covering the widest range of common thermal applications.
Ultimately, your choice is defined by the physics of your process and the form of your material.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Materials Science | Sintering, annealing, thermal analysis |
| Metallurgy | Powder metallurgy, advanced coatings |
| Electronics & Energy | Battery materials, LED development, semiconductor processing |
| Ceramics & Glass | Firing, annealing, chemical processing |
Enhance your thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your operations in materials science, metallurgy, electronics, or ceramics!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















