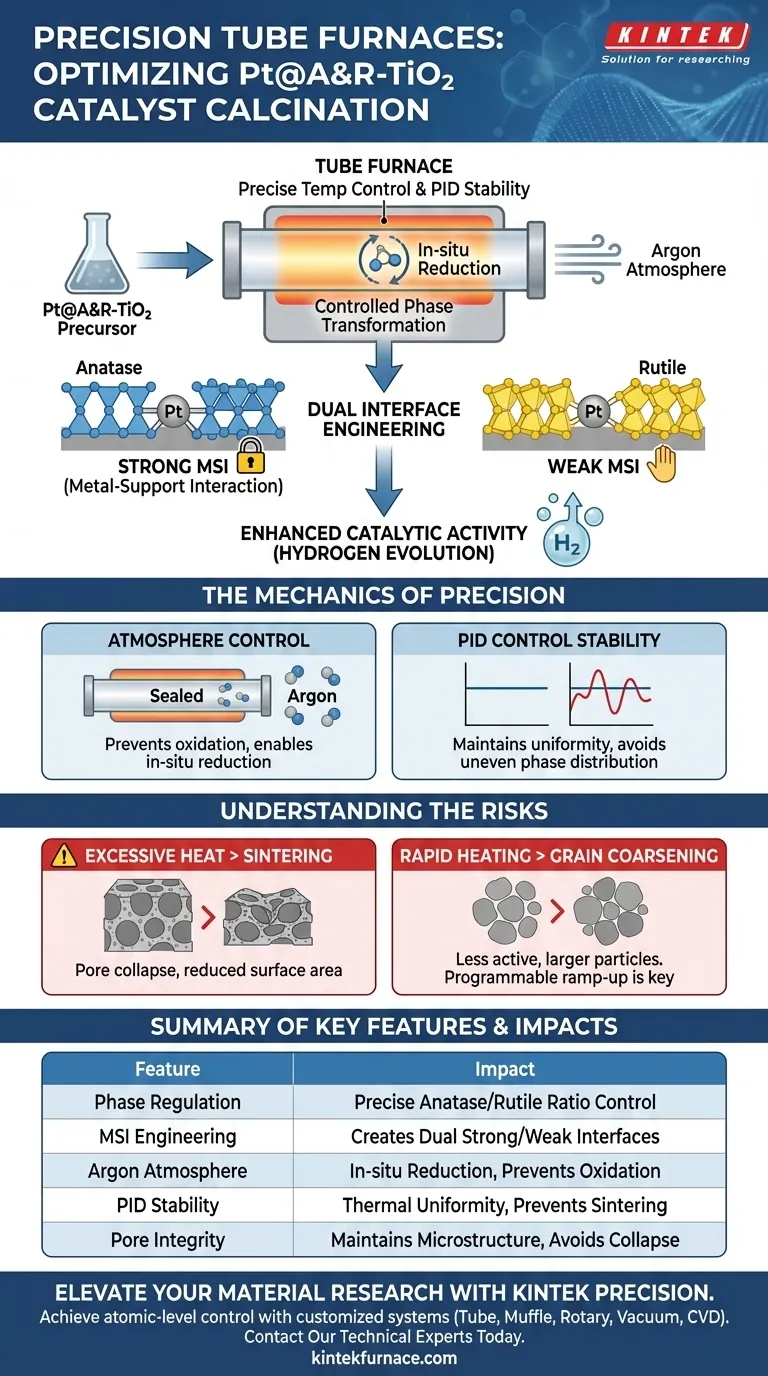
Precise temperature control in a tube furnace is essential for regulating the phase transformation of the titanium dioxide carrier during the calcination of Pt@A&R-TiO2 precursors. Specifically, it enables the in-situ reduction of the ball-milled precursor within a protected argon atmosphere. This strict thermal management allows for the accurate adjustment of the ratio between Anatase and Rutile phases, which is fundamental to the catalyst's final architecture.
The core objective of this thermal process is to engineer two distinct metal-support interaction (MSI) interfaces—one strong and one weak—on a single carrier. This specific dual-interface structure is critical for maximizing the catalyst's hydrogen evolution activity.

The Critical Role of Phase Manipulation
Tuning the Anatase-Rutile Ratio
The primary function of the tube furnace in this application is to dictate the crystallographic composition of the carrier. The precursor material requires a specific balance between the Anatase and Rutile phases of titanium dioxide.
By maintaining exact temperature parameters, the furnace ensures that the phase transformation occurs to the precise degree required, rather than allowing a complete or uncontrolled conversion.
Constructing Dual Interaction Interfaces
The ultimate goal of adjusting the phase ratio is to manipulate the Metal-Support Interaction (MSI).
The distinct phases (Anatase and Rutile) interact differently with the platinum (Pt) component. This results in the formation of two types of interfaces: a strong interaction interface and a weak interaction interface.
Enhancing Catalytic Performance
The coexistence of these strong and weak interfaces is not accidental; it is a design feature.
This dual-interface structure significantly enhances the electronic properties and active site availability of the catalyst. Consequently, the material exhibits superior performance in hydrogen evolution reactions.
The Mechanics of Precision
Atmosphere Control
A tube furnace is required not just for heat, but for its ability to maintain a controlled atmosphere.
For this specific precursor, an argon-protected environment is necessary to facilitate in-situ reduction. The tube design ensures the inert gas effectively blankets the sample, preventing unwanted oxidation that might occur in an open air environment.
Stability via PID Control
To achieve the delicate balance of phases, the furnace utilizes advanced PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control systems.
This technology automatically adjusts heating power to maintain uniformity. It ensures the precursor is subjected to the exact target temperature without the fluctuations that could lead to uneven phase distribution or incomplete reduction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Sintering
While high temperatures are necessary for phase transition, exceeding the optimal range comes with significant risks.
Excessive heat can lead to severe sintering, where particles fuse together. This causes the pore structure to collapse and drastically reduces the specific surface area, limiting the catalyst's effectiveness.
Grain Coarsening
Rapid or uncontrolled heating can cause grain coarsening, leading to larger, less active particles.
A tube furnace with programmable heating rates allows for a slow, controlled ramp-up. This prevents the instantaneous high-temperature shock that degrades the material's microstructural integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the success of your Pt@A&R-TiO2 synthesis, consider the following parameters:
- If your primary focus is optimizing the MSI interfaces: Prioritize a furnace with high thermal uniformity to strictly maintain the specific temperature that yields the desired Anatase/Rutile ratio.
- If your primary focus is precursor reduction: Ensure the furnace system has a high-integrity sealing system for the Argon supply to prevent oxygen contamination during the in-situ reduction.
Precision in thermal processing is not just about heating; it is about architectural control at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Impact on Pt@A&R-TiO2 Catalyst |
|---|---|
| Phase Regulation | Precise control of Anatase to Rutile transformation ratio. |
| MSI Engineering | Creates dual (strong/weak) metal-support interaction interfaces. |
| Argon Atmosphere | Enables in-situ reduction while preventing unwanted oxidation. |
| PID Stability | Ensures thermal uniformity to prevent sintering and grain coarsening. |
| Pore Integrity | Avoids high-temperature collapse of the catalyst's microstructure. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving atomic-level architectural control in catalysts like Pt@A&R-TiO2 requires the highest standards of thermal stability. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to your specific calcination and reduction protocols.
Don't let temperature fluctuations compromise your Metal-Support Interaction (MSI) or catalytic activity. Partner with KINTEK to access lab high-temp furnaces designed for researchers who demand precision.
Contact Our Technical Experts Today to customize your furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Shaorou Ke, Minghao Fang. Strong-weak dual interface engineered electrocatalyst for large current density hydrogen evolution reaction. DOI: 10.1038/s43246-025-00735-0
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for the activation of nitro-functionalized catalysts? (ACN Mastery)
- What is the function of a high-temperature tube furnace? Master High-Entropy Metal Phosphide Synthesis
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in the carbonization of nitrogen-doped carbon? Optimize Your Material Synthesis
- What is the maximum sample size that the 3-Zone tube furnace can accommodate? Optimize for Uniform Heating and CVD
- Why is it important to calibrate the temperature profile of a tube furnace? Ensure Accurate and Repeatable Results
- What are the temperature capabilities of tube furnaces? Find the Perfect Heat for Your Process
- What are the key features of tube furnaces? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- Why is precise temperature control in a tubular furnace essential for SiO2/C microspheres? Master Carbonization Success



















