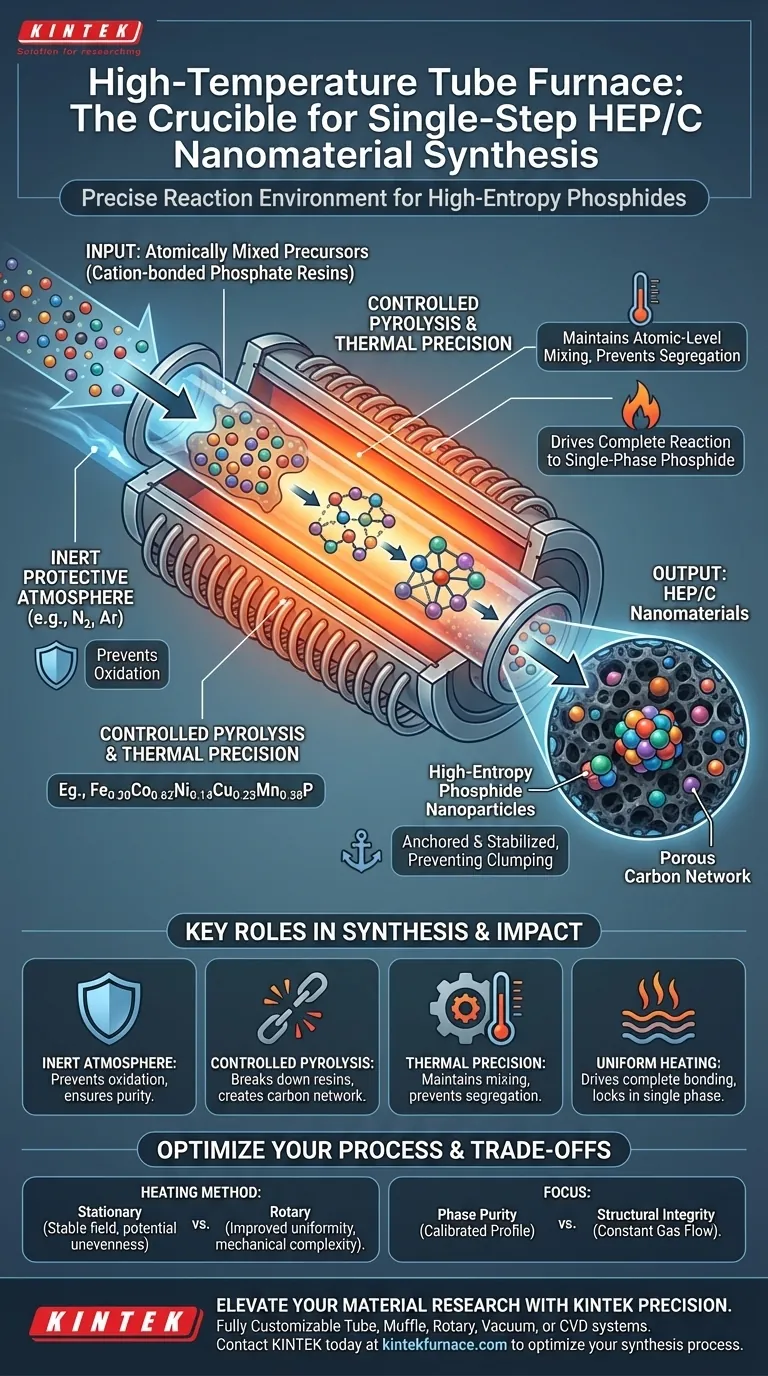
The high-temperature tube furnace serves as the precise reaction environment required to synthesize high-entropy metal phosphide (HEP/C) nanomaterials in a single step. Its primary function is to execute a controlled pyrolysis process under an inert protective atmosphere. This ensures that atomically mixed precursors transform into stable, single-phase phosphides without phase separation or oxidation.
Core Takeaway: By maintaining a strictly controlled thermal profile and an oxygen-free environment, the tube furnace facilitates the simultaneous formation of high-entropy phosphide nanoparticles and a supporting porous carbon network. This prevents the atomic segregation of complex metal mixtures during synthesis.

The Mechanism of Transformation
Controlled Pyrolysis of Precursors
The single-step preparation relies on the furnace's ability to induce controlled pyrolysis.
The process begins with cation-bonded phosphate resins. The furnace heats these resins to specific temperatures, breaking down the organic components while facilitating the chemical bonding of the remaining elements.
Preserving Atomic-Level Mixing
A critical challenge in high-entropy materials is maintaining the uniform distribution of multiple elements.
The precursor resins achieve atomic-level mixing before heating. The tube furnace must ramp up heat precisely to lock this mixture into a single crystalline phase, rather than allowing the different metals to separate into distinct compounds.
Ensuring Complete Reaction
The high-temperature environment drives the reaction to completion.
It ensures that the metal cations (such as Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, and Mn) react fully with phosphorus. This results in the formation of specific high-entropy nanoparticles, specifically identified in your reference as Fe0.20Co0.62Ni0.14Cu0.23Mn0.38P.
Creating the Structural Framework
The Inert Protective Atmosphere
The tube furnace allows for the introduction of inert gases, such as nitrogen or argon, during the heating process.
This inert atmosphere is non-negotiable. It prevents the metals from oxidizing (burning) and ensures that the phosphorus reacts with the metals rather than escaping or forming unwanted byproducts.
Anchoring in Porous Carbon
Simultaneous with the phosphide formation, the furnace converts the organic resin backbone into carbon.
This creates a porous carbon network. The furnace's thermal treatment ensures that the resulting phosphide nanoparticles are uniformly anchored within this network, preventing them from clumping together and enhancing their stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Stationary vs. Dynamic Heating
Standard tube furnaces often utilize a stationary reaction chamber.
While this provides a stable thermal field, it can sometimes lead to uneven heating or particle agglomeration in the sample bed. Rotary tube furnaces are an alternative that tumbles the material to improve uniformity, though they add mechanical complexity.
Throughput Limitations
Tube furnaces are generally batch-processing tools ideal for precision and research.
They are excellent for strictly controlling parameters for complex materials like HEP/C. However, their scalability is often limited compared to continuous flow industrial reactors, making large-scale production a challenge.
Profile Sensitivity
The success of the synthesis is highly dependent on the heating rate.
If the furnace creates a thermal gradient that is too steep or inconsistent, the complex high-entropy phase may fail to form correctly. The "single-phase" characteristic relies on the equipment's ability to maintain a uniform thermal field.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of the tube furnace in this process, focus on the following parameters:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure your heating profile is meticulously calibrated to prevent the segregation of the five distinct metal cations.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Verify that the inert gas flow is constant to protect the porous carbon network from degradation during the high-temperature dwell time.
The tube furnace is not just a heater; it is the stabilizing vessel that makes the complex chemistry of high-entropy phosphides possible.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in HEP/C Synthesis | Impact on Final Material |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation of metal cations | Ensures single-phase phosphide purity |
| Controlled Pyrolysis | Breaks down organic resins | Creates a supporting porous carbon network |
| Thermal Precision | Maintains atomic-level mixing | Prevents metal segregation and clumping |
| Uniform Heating | Drives complete chemical bonding | Locks multiple metals into a single crystal phase |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
High-entropy nanomaterial synthesis demands uncompromising thermal control and atmospheric purity. KINTEK provides state-of-the-art laboratory solutions tailored for complex chemical processes.
Why partner with us?
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Our systems are designed for the rigors of advanced materials science.
- Versatile Solutions: Whether you need Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, we have the technology to match your synthesis requirements.
- Fully Customizable: We adapt our high-temperature furnaces to meet the unique heating rates and gas flow needs of your specific HEP/C research.
Contact KINTEK today to optimize your synthesis process
Visual Guide
References
- Manchuan Guo, Jinliang Zhu. High-entropy metal phosphide nanoparticles for accelerated lithium polysulfide conversion. DOI: 10.1039/d5sc04604a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What Role Does a Tube Reactor Play in Food Waste Pyrolysis? Control Carbonization for High-Quality Biochar
- What function does a high-purity quartz tube serve during the vapor-phase synthesis of MoS2? Key Roles & Benefits
- What environmental conditions does a vacuum tube furnace provide for FTO(p)/ZnS(p) films? High-Purity Post-Treatment
- What are the main industrial applications of rotary tube furnaces? Boost Efficiency in Metallurgy and Materials Processing
- What role does a horizontal tube furnace play in chromite reduction? Master Precision Solid-State Processing
- How does a vacuum tube furnace contribute to the annealing of FePC amorphous alloys? Precision Microstructural Control
- What essential experimental conditions does a laboratory horizontal tube furnace provide for wood chip pyrolysis?
- What specific process environment does a tube furnace provide for PtTe2 tellurization? Achieve High Crystallinity



















