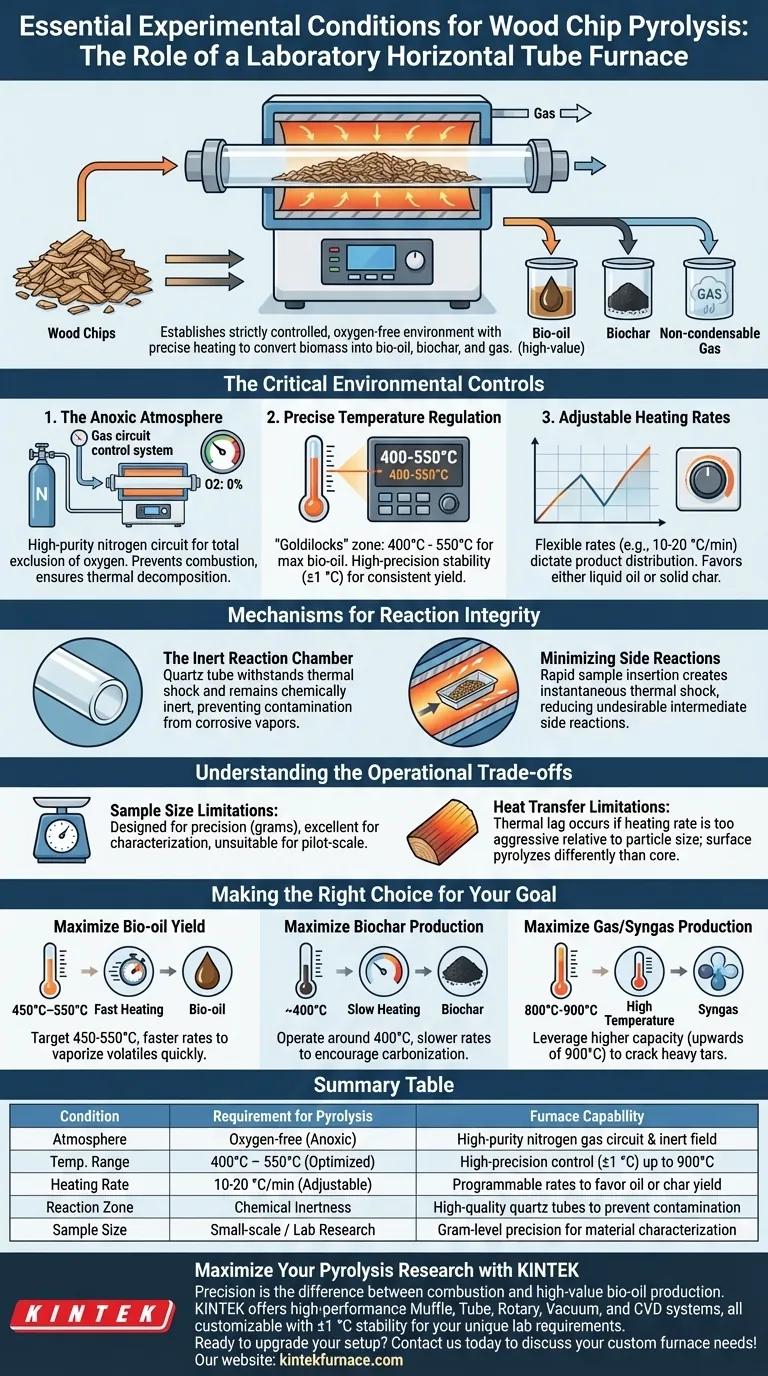
A laboratory horizontal tube furnace serves as the critical infrastructure for pyrolysis by establishing a strictly controlled, oxygen-free environment paired with a precise heating regimen. It provides the essential capability to heat wood chips to target temperatures—typically between 400°C and 550°C—at adjustable rates (e.g., 10-20 °C/min), ensuring the biomass undergoes deep thermal decomposition rather than combustion.
By maintaining a completely anoxic state and enabling high-precision thermal control (±1 °C), this equipment facilitates the conversion of solid biomass into high-value liquid bio-oil, solid biochar, and non-condensable gases.

The Critical Environmental Controls
The Anoxic Atmosphere
The most fundamental requirement for pyrolysis is the total exclusion of oxygen. If oxygen is present, the wood chips will simply burn (combust) rather than decompose chemically.
To achieve this, the tube furnace utilizes a gas circuit control system to introduce high-purity nitrogen. This creates an inert atmospheric field within the quartz reaction tube, forcing the biomass to break down thermally without oxidizing.
Precise Temperature Regulation
Wood chip pyrolysis requires a specific "Goldilocks" temperature zone to maximize bio-oil production, usually found between 400°C and 550°C.
The furnace provides the high-precision control necessary to hold these temperatures steady. While the equipment can handle broader ranges (350 °C to 900 °C), maintaining stability in the 400-550°C range is vital for consistent yield.
Adjustable Heating Rates
The speed at which the temperature rises significantly impacts the final product distribution.
The horizontal tube furnace allows for flexible adjustment of heating rates, such as 10-20 °C/min. This flexibility empowers researchers to manipulate the decomposition pathway, favoring either liquid oil generation or solid char formation.
Mechanisms for Reaction Integrity
The Inert Reaction Chamber
The core reactions occur within a quartz reaction tube. This material is essential because it withstands high thermal shock and remains chemically inert, ensuring that the container does not react with the corrosive vapors released during pyrolysis.
Minimizing Side Reactions
In advanced setups, the design of the central reaction zone allows for the rapid insertion of samples. This facilitates an instantaneous thermal shock, bringing the sample from a low pretreatment temperature to the target pyrolysis temperature immediately.
This rapid transition helps minimize undesirable intermediate side reactions that can degrade the quality of the resulting bio-oil.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Sample Size Limitations
Horizontal tube furnaces are designed for precision, not volume. They are strictly limited to small sample sizes (often grams), making them excellent for characterizing material properties but unsuitable for pilot-scale production simulation.
Heat Transfer Limitations
While the furnace controls the ambient temperature precisely, heat transfer into the center of a wood chip takes time.
If the heating rate is too aggressive relative to the particle size, you may experience a thermal lag where the surface pyrolyzes differently than the core, leading to inconsistent data.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a horizontal tube furnace for your specific pyrolysis objectives, consider the following parameters:
- If your primary focus is maximizing Bio-oil Yield: Target a temperature range of 450°C–550°C and utilize faster heating rates to vaporize volatiles quickly before they repolymerize into char.
- If your primary focus is Biochar Production: Operate at the lower end of the temperature spectrum (around 400°C) with slower heating rates to encourage carbonization.
- If your primary focus is Gas/Syngas Production: Leverage the furnace's higher capacity (upwards of 800°C-900°C) to crack heavy tars into non-condensable gases.
Success in pyrolysis relies not just on heating the wood, but on rigorously controlling the atmosphere and rate at which that heat is applied.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Requirement for Pyrolysis | Furnace Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Oxygen-free (Anoxic) | High-purity nitrogen gas circuit & inert field |
| Temp. Range | 400°C – 550°C (Optimized) | High-precision control (±1 °C) up to 900°C |
| Heating Rate | 10-20 °C/min (Adjustable) | Programmable rates to favor oil or char yield |
| Reaction Zone | Chemical Inertness | High-quality quartz tubes to prevent contamination |
| Sample Size | Small-scale / Lab Research | Gram-level precision for material characterization |
Maximize Your Pyrolysis Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between combustion and high-value bio-oil production. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique lab requirements. Whether you are targeting biochar, syngas, or liquid fuels, our horizontal tube furnaces provide the ±1 °C thermal stability and airtight seals your research demands.
Ready to upgrade your laboratory setup? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Vicky Kumar, Jia Huey Sim. Pyrolysis of sawdust in a horizontal tube furnace: Effects of temperature and heating rate on product composition. DOI: 10.1051/e3sconf/202560303001
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace equipped with an atmosphere control system required for synthesizing h-Zn-Co-O solid solutions?
- What are the key design features of a split tube furnace? Unlock Superior Access for Complex Experiments
- What conditions do tube furnaces provide for Au-Seeded TiO2 nanowires? Master Precision Thermal Synthesis
- What is the basic working principle of a tube furnace? Master Precise Heating for Material Processing
- What temperature range and applications is this tube furnace suitable for? Ideal for 500°C to 1800°C thermal processes
- What are the advantages of a one-zone tube furnace for MoS2 synthesis? Ensure Uniformity and Repeatability
- What is the function of a tube furnace in pRF preparation? Optimize Carbonization & Conductivity
- What is a tube furnace and its main characteristics? Discover Precision Heating for Your Lab



















