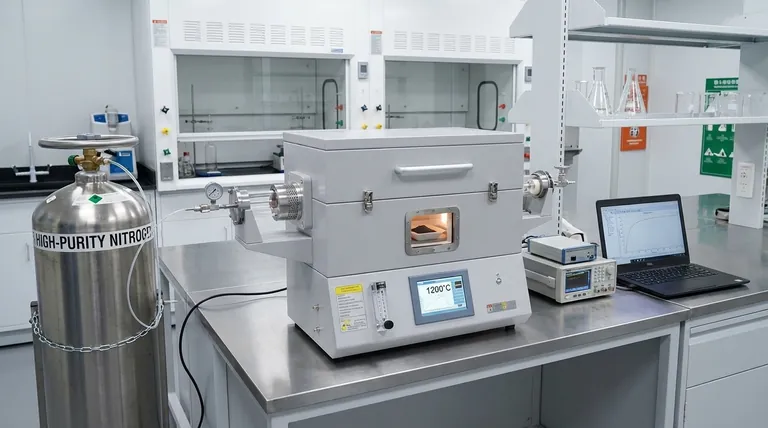
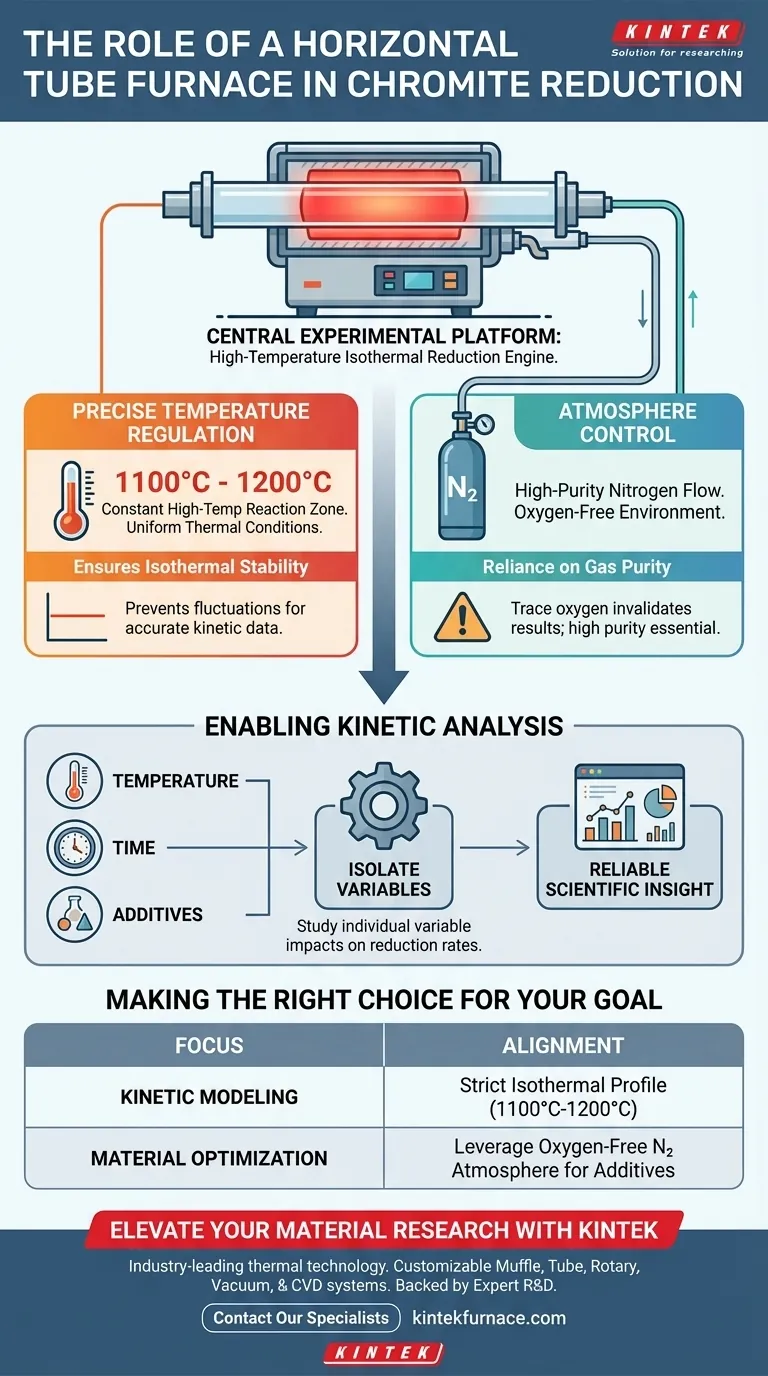
Acting as the central experimental platform, the horizontal tube furnace is the engine behind the high-temperature isothermal reduction of chromite. It provides a highly stable reaction zone—typically maintained between 1100°C and 1200°C—while utilizing high-purity nitrogen to prevent oxidation and ensure accurate data collection.
By integrating precise thermal regulation with strict atmosphere control, the horizontal tube furnace allows researchers to isolate specific reaction variables. This ensures that observed changes in reduction rates are due to controlled factors like temperature or additives, rather than environmental inconsistencies.

Creating the Necessary Reaction Conditions
Precise Temperature Regulation
The reduction of chromite requires significant thermal energy to proceed. The horizontal tube furnace utilizes a specialized control system to generate a constant high-temperature reaction zone.
Researchers typically maintain this zone between 1100°C and 1200°C. This precision ensures that the thermal conditions remain uniform throughout the duration of the experiment.
Atmosphere Control
The presence of oxygen can interfere with the reduction process or degrade the sample. To counter this, the furnace is equipped with an atmosphere control system.
This system continuously introduces high-purity nitrogen into the tube. This creates a controlled, oxygen-free thermal environment essential for isolating the reduction mechanism.
Enabling Kinetic Analysis
Studying Variable Impacts
The primary scientific utility of this furnace is its ability to facilitate the study of specific variables. Because the environment is stable, researchers can alter one factor at a time.
This allows for the precise measurement of how temperature, time, and additives individually affect the reduction rates of chromite.
Ensuring Isothermal Stability
"Isothermal" reduction means the process occurs at a constant temperature. The horizontal tube furnace is designed specifically to maintain this stability.
By preventing temperature fluctuations, the equipment ensures that the data collected accurately reflects the material's behavior at a specific thermal set point.
Understanding the Operational Requirements
Reliance on Gas Purity
The accuracy of the results is heavily dependent on the quality of the inert atmosphere.
If the nitrogen introduced is not of high purity, trace oxygen can contaminate the reaction zone. This would compromise the oxygen-free environment and invalidate the study of the reduction rates.
Sensitivity to Control Systems
The furnace is not a passive heating element; it requires active management.
The effectiveness of the experiment relies entirely on the precise calibration of the temperature control system. Even minor deviations outside the 1100°C to 1200°C range can alter the kinetics of the solid-state reduction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When utilizing a horizontal tube furnace for chromite reduction, align your experimental design with the equipment's strengths.
- If your primary focus is Kinetic Modeling: Ensure the temperature control system is calibrated to maintain a strict isothermal profile between 1100°C and 1200°C.
- If your primary focus is Material Optimization: Leverage the oxygen-free nitrogen atmosphere to test various additives without the risk of oxidative interference.
Ultimately, the horizontal tube furnace provides the controlled isolation required to turn raw experimental data into reliable scientific insight.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Chromite Reduction | Benefit to Researcher |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 1100°C to 1200°C Isothermal Zone | Ensures consistent kinetic data |
| Atmosphere Control | High-purity Nitrogen flow | Prevents oxidation and ensures accuracy |
| Reaction Stability | Isolation of specific variables | Precise measurement of additive impacts |
| Platform Design | Horizontal Tube Configuration | Ideal for solid-state material optimization |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Unlock the full potential of your solid-state processes with industry-leading thermal technology. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you are optimizing chromite reduction or developing next-generation ceramics, our lab high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique experimental needs.
Ready to achieve superior thermal precision? Contact our specialists today to find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Xiaohong Jiang, Z. H. Lei. Mechanism of Iron Powder to Enhance Solid-State Reduction of Chromite Ore. DOI: 10.3390/min15060652
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some examples of applications for three-zone tube furnaces in advanced materials processing? Unlock Precision Thermal Control for Your Lab
- How does the size of tube and box furnaces affect their applications? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab Needs
- What is the specific role of a tube furnace in the synthesis and carbon-encapsulation of NiMo alloys? Explained
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature tube furnace for Ce-MOF to CeO2 conversion? Guide to Precision Nano-Engineering
- Why is annealing in a tube furnace essential for rGO-NiO-ZnO-400? Optimize Your Catalyst Synthesis
- How does a vacuum tube furnace serve as the core equipment in the consolidation of Ti-xCr-2Ge alloys?
- What are the primary applications of tube furnaces? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- Why is vacuum encapsulation in a quartz tube necessary for AFA alloys? Ensure Critical Elemental Integrity



















