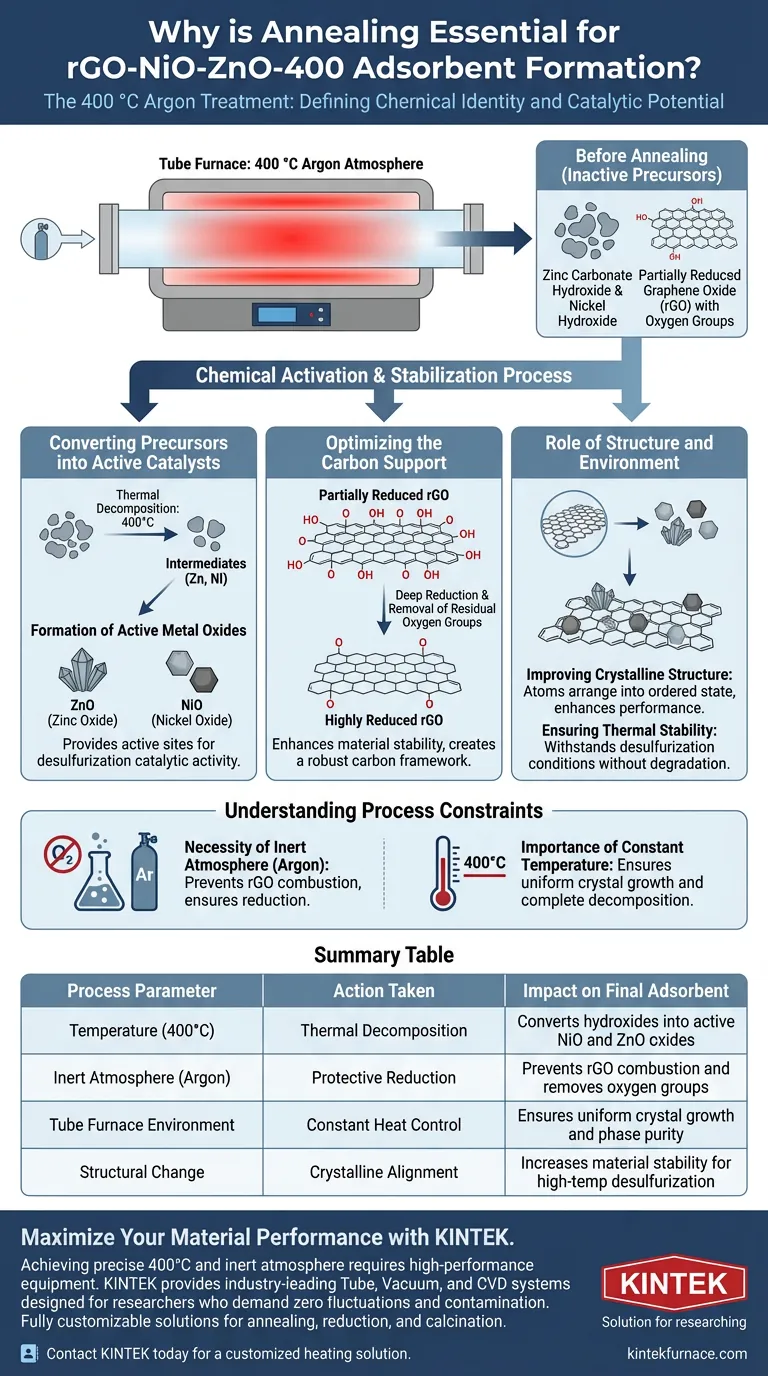
The annealing treatment defines the chemical identity and catalytic potential of the rGO-NiO-ZnO-400 adsorbent. This process, conducted at a precise 400 °C in an argon atmosphere, is the mechanism that chemically converts inactive precursors into functional metal oxides while simultaneously stabilizing the graphene backbone. Without this step, the material would lack the crystalline structure and reduction levels necessary to function as a desulfurization agent.
The annealing phase is not merely a drying step; it is a chemical activation process that transforms intermediate compounds into active catalysts and "locks in" the material’s thermal stability.

Converting Precursors into Active Catalysts
Thermal Decomposition of Intermediates
Before annealing, the material consists largely of intermediate compounds that are chemically inactive for the target application.
The 400 °C heat treatment drives the decomposition of these intermediates, specifically converting zinc carbonate hydroxide and nickel hydroxide.
Formation of Active Metal Oxides
The thermal energy facilitates the transformation of these precursors into their active forms: Zinc Oxide (ZnO) and Nickel Oxide (NiO).
These specific metal oxides provide the active sites required for the material's final desulfurization catalytic activity.
Optimizing the Carbon Support
Deep Reduction of rGO
The annealing process acts directly on the graphene component of the composite.
Subjecting the material to this environment increases the reduction degree of the reduced graphene oxide (rGO).
Enhancing Material Stability
This increased reduction removes residual oxygen-containing functional groups, resulting in a more stable carbon framework.
This ensures the rGO can effectively support the metal oxides during catalytic reactions.
The Role of Structure and Environment
Improving Crystalline Structure
The constant temperature provided by the tube furnace allows atoms to arrange themselves into a more ordered state.
This thermal treatment significantly enhances the crystalline structure of the final composite, which is directly correlated to improved performance.
Ensuring Thermal Stability
By annealing the material at 400 °C, the final product achieves a high level of thermal stability.
This prepares the adsorbent to withstand the operational conditions it will face during actual desulfurization processes without degrading.
Understanding the Process Constraints
The Necessity of an Inert Atmosphere
The reference highlights the specific use of an argon atmosphere within the tube furnace.
This is critical because heating carbon-based materials (like rGO) in the presence of oxygen would lead to combustion or degradation rather than reduction.
The Importance of Constant Temperature
The tube furnace is essential because it provides a constant temperature environment.
Fluctuations in heat during this conversion phase could lead to incomplete decomposition of precursors or inconsistent crystal growth, resulting in a heterogeneous and less effective adsorbent.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the successful synthesis of rGO-NiO-ZnO-400, consider how the annealing parameters align with your objectives:
- If your primary focus is Catalytic Activity: Ensure the temperature reaches a steady 400 °C to fully convert nickel and zinc intermediates into their active oxide forms.
- If your primary focus is Material Stability: Maintain a strict argon atmosphere to maximize the reduction of rGO without compromising the carbon structure through oxidation.
Ultimately, precision in the annealing environment is what bridges the gap between a mixture of raw chemicals and a high-performance desulfurization adsorbent.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Action Taken | Impact on Final Adsorbent |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (400°C) | Thermal Decomposition | Converts hydroxides into active NiO and ZnO oxides |
| Inert Atmosphere (Argon) | Protective Reduction | Prevents rGO combustion and removes oxygen groups |
| Tube Furnace Environment | Constant Heat Control | Ensures uniform crystal growth and phase purity |
| Structural Change | Crystalline Alignment | Increases material stability for high-temp desulfurization |
Maximize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Achieving the precise 400°C environment and inert atmosphere required for rGO-NiO-ZnO-400 synthesis demands high-performance equipment. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for researchers who cannot afford temperature fluctuations or atmospheric contamination.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our laboratory high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your specific annealing, reduction, and calcination needs. Whether you are developing advanced adsorbents or complex catalysts, KINTEK ensures your materials reach their full catalytic potential.
Ready to elevate your research? Contact KINTEK today for a customized heating solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Rodolfo Fernández-Martínez, J.M. Sánchez. Transformation of Graphite Recovered from Batteries into Functionalized Graphene-Based Sorbents and Application to Gas Desulfurization. DOI: 10.3390/molecules29153577
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a laboratory tube furnace in Ti-5Al-4W-2Fe alloy forging? Enhance Thermoplasticity & Purity
- What conditions does a tube furnace provide for aluminum ash-based ceramsite roasting? Master Precision Sintering
- Why should the furnace temperature not exceed the rated temperature? Avoid Damage and Ensure Safety
- What are some thermal processes that tube furnaces are used for? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment with Uniformity
- How does a two-zone tube furnace achieve stepwise control of precursors? Master CVD Heterostructure Growth
- What role does a Vacuum Tube Furnace play in NPCu annealing? Achieve Precise Structural Homogenization
- How does a tube furnace differ from HPHT methods for Fe2B-HS? Compare Diffusion and Structural Integrity
- What are the steps for insulation and cooling in a multi zone tube furnace? Master Precise Thermal Control



















