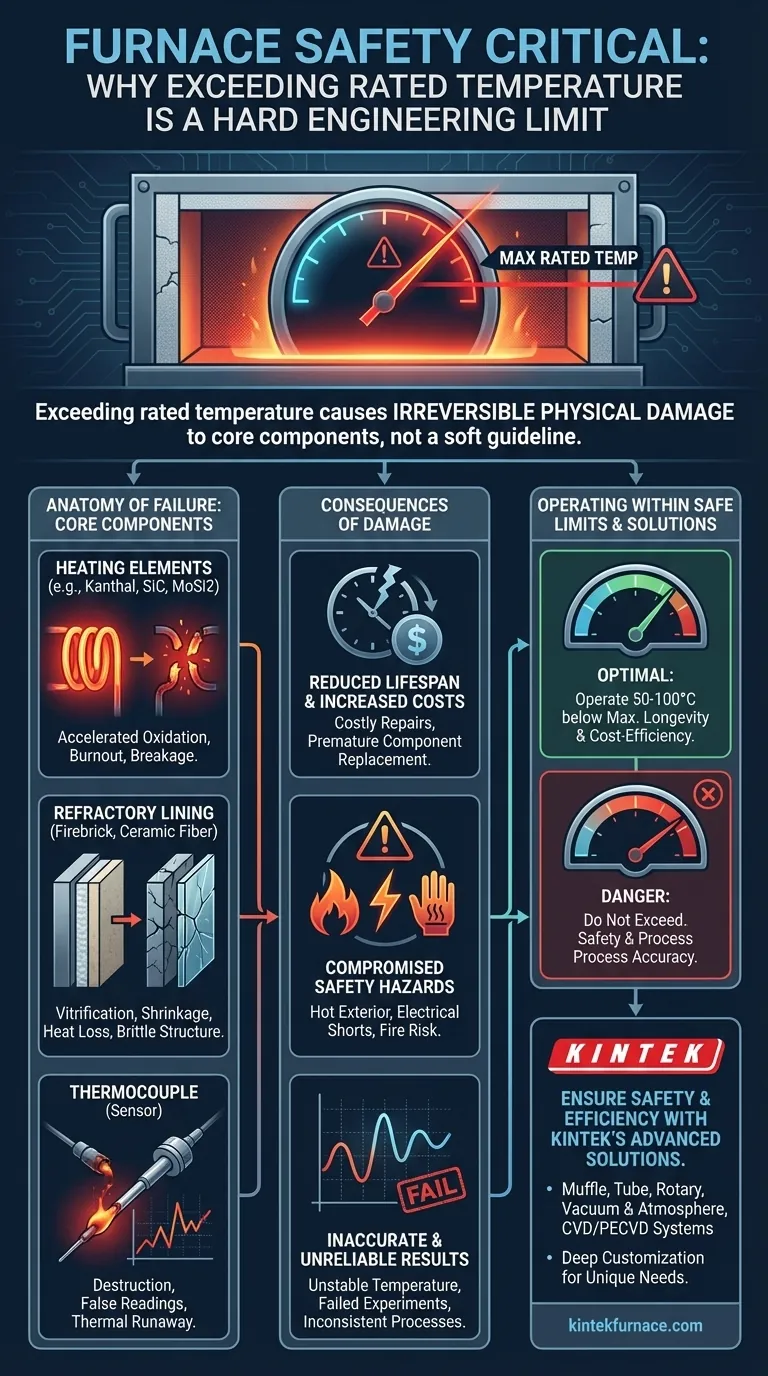
In short, exceeding a furnace's rated temperature causes irreversible physical damage to its core components. This is not a soft guideline but a hard engineering limit. Pushing past this temperature initiates a cascade of failures that will shorten the furnace's lifespan, compromise safety, and lead to expensive repairs.
The maximum rated temperature is the absolute limit at which the furnace's materials can operate without degrading. Exceeding it guarantees damage to the heating elements and internal insulation, fundamentally compromising the equipment's integrity and performance.

The Anatomy of a Temperature Rating
A furnace's temperature rating is not an arbitrary number. It is a carefully calculated limit based on the material science of its most critical—and vulnerable—components. When you exceed this rating, you are pushing these materials past their physical breaking point.
The Heating Elements: The Engine of the Furnace
Heating elements are typically made of specialized resistance alloys like Kanthal (FeCrAl) or more advanced materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2).
These materials are chosen for their ability to withstand high heat while producing it efficiently. However, operating above their specified temperature drastically accelerates their degradation, primarily through oxidation.
The protective oxide layer that normally forms on the element's surface becomes unstable, leading to rapid corrosion, thinning of the element, and an increase in electrical resistance. This process culminates in a "burnout" or a complete break in the element.
The Refractory Lining: The Protective Shield
The interior of a furnace is lined with insulating materials, such as refractory firebrick or ceramic fiber insulation. Their purpose is to contain the extreme heat, ensure temperature stability, and protect the furnace's outer shell.
When exposed to temperatures beyond their rating, these materials begin to fail. Ceramic fibers can vitrify (turn to a glass-like state), shrink, and become brittle. This causes them to lose their insulating properties, allowing heat to escape and potentially damage the furnace's external structure and electronics.
The Thermocouple: The Critical Sensor
The thermocouple is the sensor that measures the internal temperature and reports it to the controller. It is the furnace's nervous system.
Exposing a thermocouple to temperatures far beyond its type rating (e.g., Type K, S, or B) will destroy it. A damaged thermocouple can provide false low readings, tricking the controller into sending even more power to the heating elements. This creates a dangerous thermal runaway condition, which can lead to catastrophic furnace failure.
Understanding the Consequences
Operating above the rated temperature is a trade-off where you gain nothing of value and risk significant loss. The consequences are not theoretical; they are a certainty.
Reduced Lifespan and Increased Costs
The most immediate consequence is financial. Each time the furnace exceeds its limit, you permanently reduce the lifespan of the heating elements and insulation.
Replacing heating elements is a significant expense, and a full relining of a furnace can cost a substantial fraction of a new unit. These are not maintenance items but costly repairs caused by improper use.
Compromised Safety
A furnace with a compromised refractory lining is a serious safety hazard. Heat can escape through the damaged insulation, making the outer shell of the furnace dangerously hot to the touch.
Furthermore, degradation of internal components can lead to electrical shorts, posing a significant fire risk in your lab or facility.
Inaccurate and Unreliable Results
For any scientific or industrial process, temperature stability is key. A damaged furnace can no longer maintain a stable or uniform temperature.
This degradation makes your results unreliable and your processes inconsistent. Experiments, heat treatments, or material processing will fail, costing time and resources.
Operating Within Safe and Effective Limits
Adhering to the manufacturer's temperature rating is the single most important rule of furnace operation. It is the foundation for safety, longevity, and reliable performance.
- If your primary focus is longevity and cost-efficiency: Never exceed the maximum rated temperature, and for general use, operate at least 50-100°C below this limit to minimize stress on the components.
- If your primary focus is safety: Treat the maximum temperature as a non-negotiable red line, as crossing it degrades the very systems designed to contain the heat and prevent electrical failure.
- If your primary focus is process accuracy: Understand that operating above the limit damages the components responsible for temperature control, destroying the furnace's ability to deliver a stable and uniform thermal environment.
Ultimately, respecting your equipment's engineering limits is the only way to ensure it performs safely and effectively for its entire intended service life.
Summary Table:
| Component | Effect of Exceeding Rated Temperature |
|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Accelerated oxidation, burnout, and increased resistance |
| Refractory Lining | Vitrification, shrinkage, loss of insulation |
| Thermocouple | Destruction, false readings, thermal runaway |
| Overall Furnace | Reduced lifespan, safety hazards, unreliable results |
Ensure your furnace operates safely and efficiently with KINTEK's advanced solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's performance and avoid costly downtime!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















