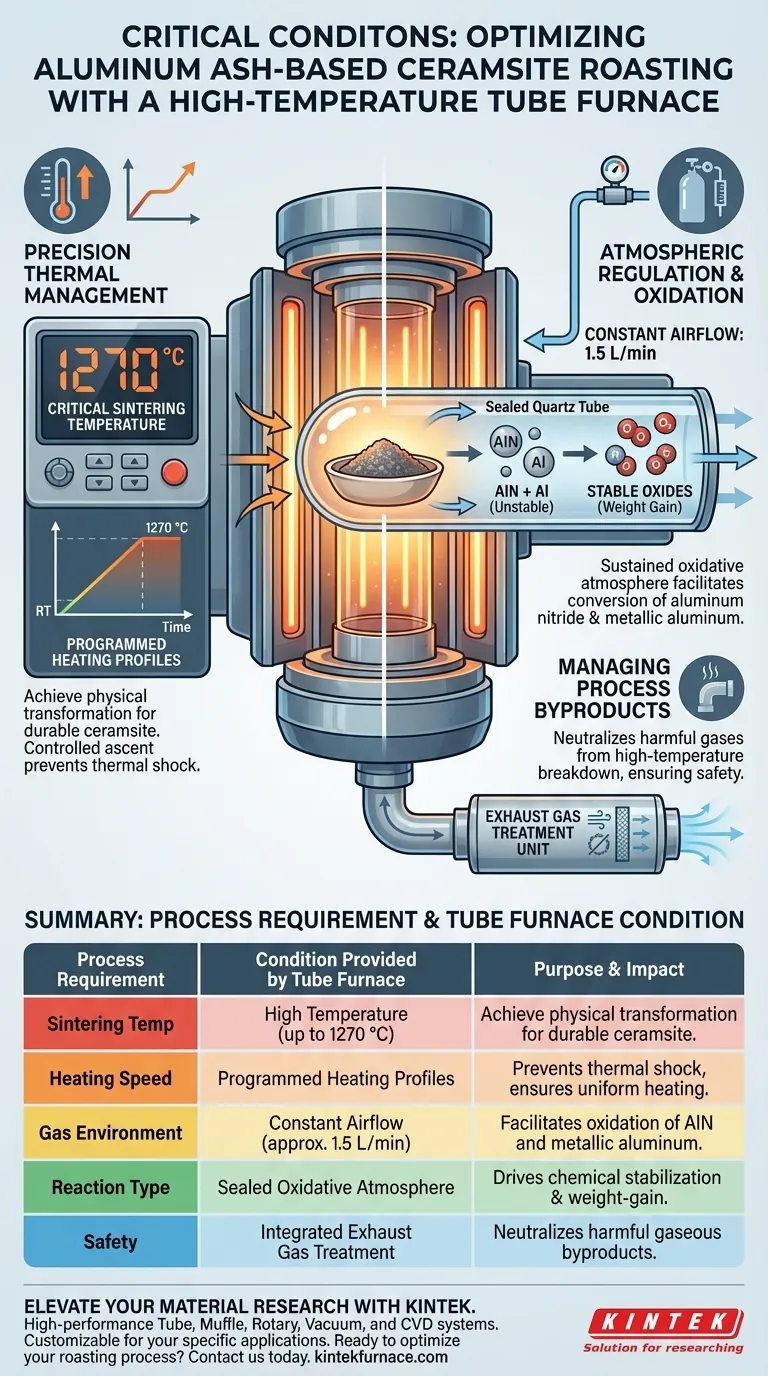
A high-temperature tube furnace provides the critical combination of precision thermal control and atmospheric regulation necessary for processing aluminum ash-based ceramsite. Specifically, it delivers a programmed heating environment capable of reaching 1270 °C while simultaneously maintaining a constant airflow, typically around 1.5 L/min, within a sealed chamber to drive essential chemical reactions.
By synchronizing high temperatures with a consistent oxygen supply, the tube furnace facilitates the conversion of unstable aluminum nitride and metallic aluminum into stable compounds. This process is not just about heating; it is about managing an oxidation reaction that results in specific weight-gain characteristics essential for the final product.
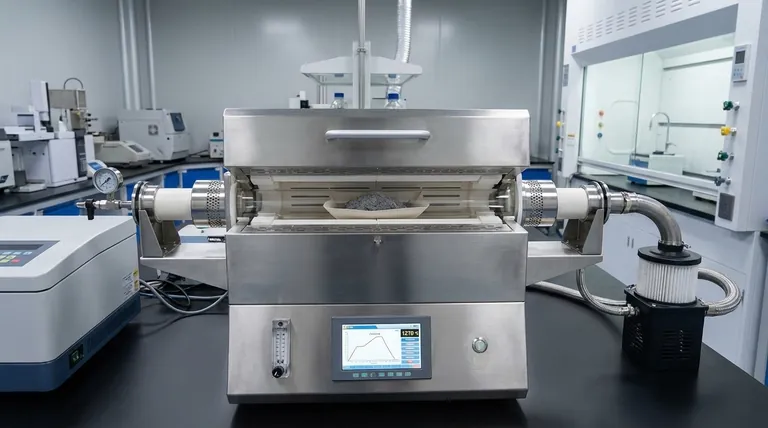

Precision Thermal Management
Reaching Critical Sintering Temperatures
The roasting process requires a thermal environment capable of achieving temperatures significantly higher than standard drying ovens. A high-temperature tube furnace is engineered to reach up to 1270 °C, a critical threshold for sintering aluminum ash. At this temperature, the material undergoes the physical changes necessary to form durable ceramsite.
Programmed Heating Profiles
Effective roasting is rarely about instantaneous heat; it requires a controlled rise in temperature. These furnaces support programmed heating, allowing operators to dictate the exact ramp rate from room temperature to the target sintering point. This controlled ascent ensures uniform heating and prevents thermal shock to the material.
Atmospheric Regulation and Oxidation
Maintaining an Oxidative Environment
The sealed structure of the tube furnace is vital for controlling the chemical atmosphere. Unlike an open kiln, the tube furnace allows for a precise, continuous flow of air—cited as 1.5 L/min in standard processing. This airflow ensures that fresh oxygen is constantly supplied to the sample surface throughout the heating cycle.
Facilitating Chemical Conversion
The primary "Deep Need" for this specific setup is the chemical stabilization of the ash. The constant airflow creates a sustained oxidative atmosphere. This environment promotes the oxidation of aluminum nitride (AlN) and metallic aluminum present in the raw ash. These reactions result in a "weight-gain" phenomenon, which indicates the successful transformation of unstable components into stable oxides.
Managing Process Byproducts
Handling Harmful Emissions
The sintering of aluminum ash generates gaseous byproducts that can be hazardous. A necessary condition provided by a proper tube furnace setup is the management of these emissions. These systems are typically equipped with exhaust gas treatment units. This ensures that the harmful gases released during the high-temperature breakdown of the ash are captured or neutralized rather than vented directly into the laboratory or production environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize the roasting of aluminum ash-based ceramsite, you must tune the furnace parameters to the specific chemical needs of the ash.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Stability: Prioritize the airflow rate (1.5 L/min) to ensure there is sufficient oxygen to fully oxidize the AlN and metallic aluminum.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Ensure the heating program is calibrated to reach and hold 1270 °C to achieve proper sintering density.
- If your primary focus is Operational Safety: Verify that the furnace's exhaust gas treatment unit is active and rated for the specific byproducts of aluminum ash sintering.
Success in this process relies on balancing thermal intensity with precise atmospheric flow to drive the required oxidation reactions.
Summary Table:
| Process Requirement | Condition Provided by Tube Furnace | Purpose & Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Sintering Temp | High Temperature (up to 1270 °C) | Achieve physical transformation for durable ceramsite formation. |
| Heating Speed | Programmed Heating Profiles | Prevents thermal shock and ensures uniform material heating. |
| Gas Environment | Constant Airflow (approx. 1.5 L/min) | Facilitates oxidation of aluminum nitride and metallic aluminum. |
| Reaction Type | Sealed Oxidative Atmosphere | Drives chemical stabilization and weight-gain characteristics. |
| Safety | Integrated Exhaust Gas Treatment | Neutralizes harmful gaseous byproducts during sintering. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between success and failure in aluminum ash processing. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the most demanding thermal profiles. Whether you need a controlled 1270 °C environment or custom atmospheric regulation for unique lab needs, our furnaces are fully customizable for your specific applications.
Ready to optimize your roasting process? Contact us today to discuss how our laboratory high-temp furnaces can deliver the structural integrity and chemical stability your projects require.
Visual Guide
References
- Weiwen He, Qifei Huang. Experimental research on mechanical and impact properties of ceramsite prepared from secondary aluminum dross and municipal solid waste incineration ash. DOI: 10.1186/s42834-024-00239-5
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is precise temperature control in a tubular furnace essential for SiO2/C microspheres? Master Carbonization Success
- What are some advanced features of more elaborate tube furnaces? Unlock Precision Control for High-Temp Processes
- What are the advantages of atmosphere control and high-temperature capabilities in a tube furnace? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What is the difference between a tube furnace and a box furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab
- What is a three zone furnace? The Key to Superior Temperature Uniformity
- What is the role of a laboratory tube furnace in teaching and training? Enhance Student Learning with Hands-On Thermal Experiments
- What are the main advantages of vacuum tube furnaces in the market? Achieve Purity and Precision in Material Processing
- How does the environmental control within a high-temperature tube furnace affect Ag-N-C catalyst pyrolysis?



















