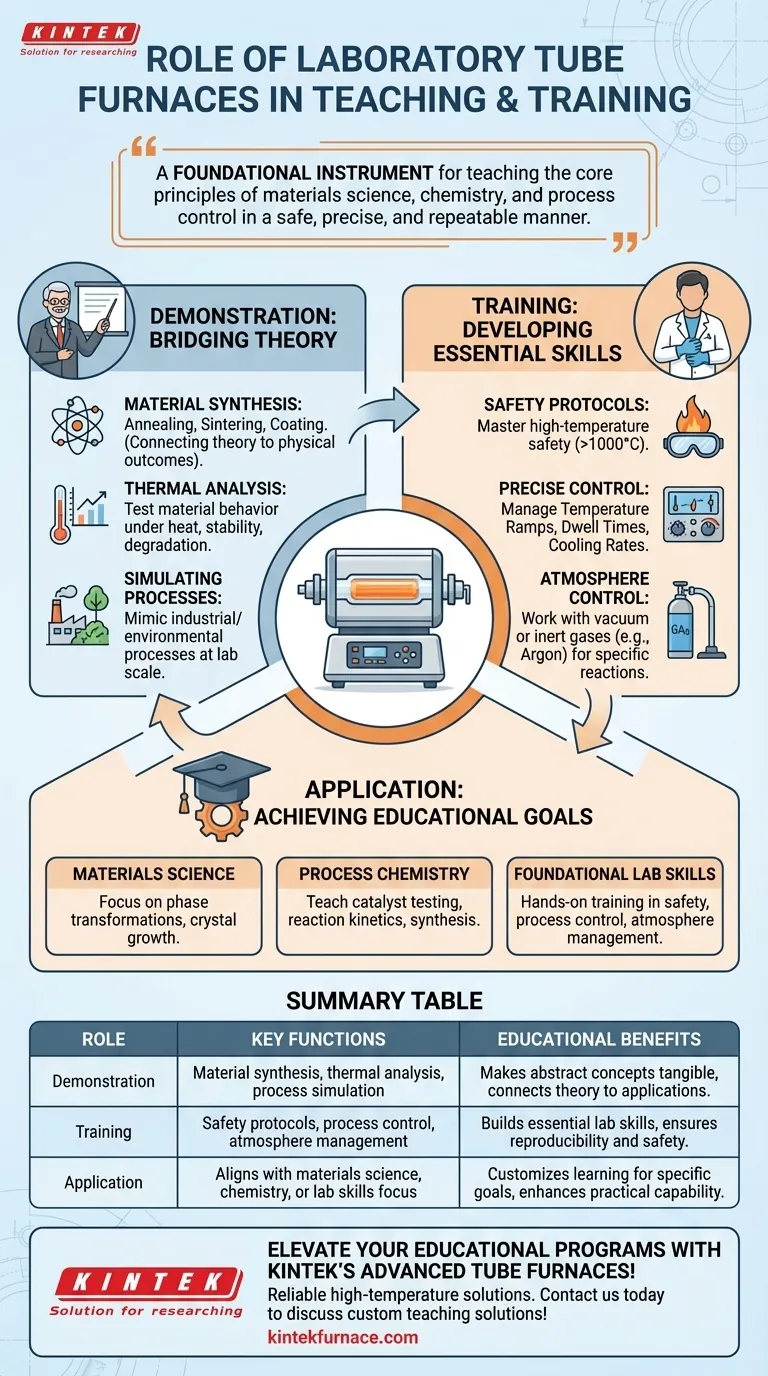
In a teaching and training environment, a laboratory tube furnace serves two primary functions. It is used for live experimental demonstrations of high-temperature processes and for providing students with critical, hands-on training in the safe operation of advanced thermal equipment and precise experimental procedures.
A tube furnace is more than just a heating device in an academic setting; it is a foundational instrument for teaching the core principles of materials science, chemistry, and process control in a safe, precise, and repeatable manner.

Bridging Theory with Practical Demonstration
A key role of the tube furnace in education is to make abstract scientific concepts tangible. It allows instructors to demonstrate processes that are foundational to many scientific and industrial fields.
Material Synthesis and Transformation
Instructors use the furnace to show how raw materials can be transformed into new substances with different properties. This includes synthesizing novel compounds or purifying existing ones.
By controlling temperature and atmosphere, students can witness processes like annealing (softening metals), sintering (fusing powders into a solid), or coating surfaces, directly connecting classroom theory to physical outcomes.
Thermal Analysis and Property Testing
The furnace is ideal for experiments where a material's behavior under heat is studied. Students can test the limits of heat-resistant materials like aerospace ceramics or polymer composites.
This allows them to understand concepts like thermal stability, degradation points, and the effects of accelerated aging on different materials in a controlled environment.
Simulating Industrial and Environmental Processes
Tube furnaces can simulate large-scale industrial processes at a manageable lab scale. This is vital for teaching chemical engineering principles or environmental science.
For example, an experiment can mimic a high-temperature incineration process to analyze pollutants or test a material's corrosion resistance, providing insight into real-world applications.
Developing Essential Laboratory Skills
Beyond demonstrations, the tube furnace is an indispensable tool for training the next generation of scientists and technicians. It builds practical competencies that are critical for any research or industrial career.
Mastering High-Temperature Safety Protocols
Working with equipment that reaches over 1000°C requires rigorous training. The tube furnace provides a controlled context for students to learn and practice essential safety procedures for high-temperature work.
Achieving Precise Process Control
Modern tube furnaces feature advanced control systems. Training on this equipment teaches students how to precisely manage critical variables like temperature ramps, dwell times, and cooling rates, a skill essential for reproducible research.
Understanding Atmosphere Control
Many experiments require a specific atmosphere, such as a vacuum or an inert gas like argon, to prevent unwanted chemical reactions. The furnace is the primary tool for teaching the principles and techniques of atmospheric control in thermal processing.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, it's important to understand the context and limitations of using a tube furnace in a teaching lab.
Simplicity in Principle, Complexity in Practice
The basic concept of a tube furnace is simple: a heated tube. However, achieving precise, repeatable results requires a solid understanding of its control systems, heat distribution, and atmospheric seals.
Small Scale by Design
Tube furnaces are designed for small, research-scale samples. This is an advantage in a teaching setting, as it conserves materials and energy, but it's a limitation for any form of bulk production.
The Criticality of the "Uniform Zone"
The heat inside the tube is not perfectly even along its entire length. A key learning concept is identifying and using the central "uniform heat zone" where the temperature is stable, ensuring experimental results are valid and repeatable.
Applying the Tool to Your Educational Goal
To maximize its value, align the use of the tube furnace with your specific learning objectives.
- If your primary focus is materials science education: Use it to demonstrate phase transformations, crystal growth, and the effects of annealing and sintering on material properties.
- If your primary focus is process chemistry: It is the ideal tool for teaching catalyst testing, reaction kinetics, and the synthesis of compounds under controlled atmospheres.
- If your primary focus is foundational lab skills: It provides invaluable, hands-on training in high-temperature safety, precise process control, and handling experiments under vacuum or inert gas.
Ultimately, the laboratory tube furnace empowers students by transforming theoretical knowledge into practical capability.
Summary Table:
| Role | Key Functions | Educational Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Demonstration | Material synthesis, thermal analysis, process simulation | Makes abstract concepts tangible, connects theory to real-world applications |
| Training | Safety protocols, process control, atmosphere management | Builds essential lab skills, ensures reproducibility and safety in experiments |
| Application | Aligns with materials science, chemistry, or lab skills focus | Customizes learning for specific educational goals, enhances practical capability |
Elevate your educational programs with KINTEK's advanced tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable high-temperature solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization to precisely meet your unique teaching and training needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance hands-on learning and safety in your institution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















