In short, a three-zone furnace is a high-temperature tube furnace that uses three independently controlled heating sections instead of one. Its primary purpose is not to create three different temperatures, but to use the two outer "guard" zones to precisely counteract heat loss, thereby creating a significantly larger and more uniform temperature area in the central zone.
The core problem with any furnace is that heat escapes from the ends. A three-zone design solves this by adding programmable end heaters that act as thermal guards, forcing the central zone to maintain an exceptionally stable and uniform temperature profile required for sensitive applications.
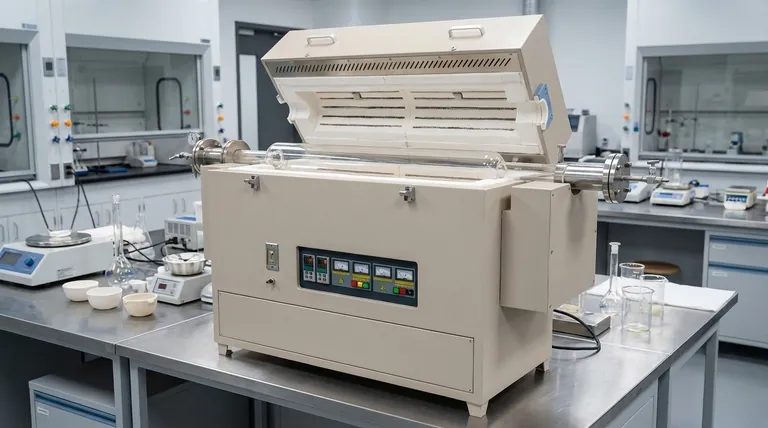

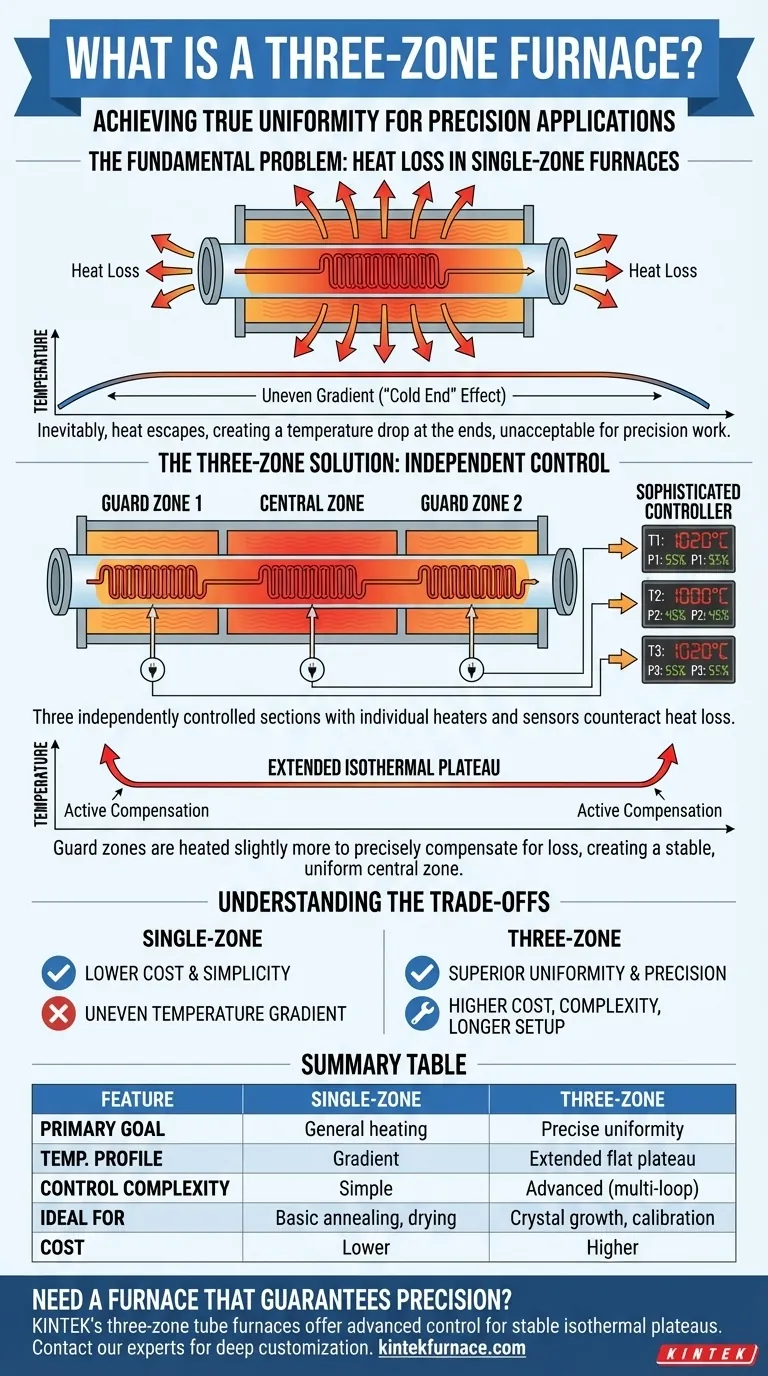
The Fundamental Problem: Heat Loss in Single-Zone Furnaces
To understand the value of a three-zone design, you must first understand the inherent limitation of a simpler, single-zone furnace.
The Inevitable Temperature Drop
In any tube furnace, heat naturally radiates and convects away from the ends of the tube. This is a fundamental principle of thermodynamics.
The "Cold End" Effect
This heat loss causes the temperature at the ends of the furnace to be lower than the temperature at the very center. This creates an uneven temperature gradient along the length of the processing area.
Why This Matters for Precision Work
For many advanced material processes, research applications, or calibration procedures, this temperature variance is unacceptable. It means a sample is not being treated uniformly, which can ruin experiments in fields like crystal growth, semiconductor fabrication, or high-temperature sensor calibration.
The Three-Zone Solution: Achieving True Uniformity
A three-zone furnace is an elegant engineering solution designed specifically to overcome the "cold end" problem.
The "Center" and "Guard" Zones
The furnace is divided into three sections: a large central zone and two smaller end zones. Each has its own independent heating element and temperature sensor (thermocouple).
How Independent Control Works
A sophisticated controller reads the temperature from all three zones simultaneously. The user sets a single target temperature for the process.
Compensating for Heat Loss
The controller actively increases the power to the two end zones to be slightly hotter than the center. This extra heat output precisely compensates for the thermal energy that is naturally escaping from the ends of the furnace.
The Result: An Isothermal Plateau
This active compensation effectively builds a "thermal wall" at each end, preventing the central zone from losing heat. The result is a much longer, flatter, and more stable zone of uniform temperature—often called an isothermal plateau—than is possible with a single-zone design.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While superior for uniformity, a three-zone design is not always the best choice. It comes with clear trade-offs.
Increased Cost and Complexity
A three-zone furnace requires more heating elements, more thermocouples, and a more advanced multi-loop controller. This increases the initial purchase price, maintenance requirements, and potential points of failure.
Longer Setup and Profiling Time
Achieving the desired uniform temperature profile requires careful tuning, or "profiling," of the furnace. This process of adjusting the end zone offsets can be more time-consuming compared to the simple setup of a single-zone furnace.
Over-Engineered for Simple Tasks
For many basic applications, like simple annealing or drying where a few degrees of temperature variation are irrelevant, the precision of a three-zone furnace is unnecessary. A single-zone furnace is often more practical and cost-effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision between a single-zone and a three-zone furnace depends entirely on the temperature precision your application demands.
- If your primary focus is high-precision calibration or crystal growth: A three-zone furnace is essential to create the stable, uniform thermal environment required for melting and freezing fixed-point metals or growing homogenous crystals.
- If your primary focus is processing longer samples uniformly: The extended isothermal plateau of a three-zone design ensures the entire length of your sample experiences the same target temperature.
- If your primary focus is general heating with a limited budget: A single-zone furnace provides a robust and cost-effective solution for applications where absolute temperature uniformity is not the most critical parameter.
Ultimately, selecting a three-zone furnace is a strategic decision to invest in superior temperature uniformity for processes where precision is paramount.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Single-Zone Furnace | Three-Zone Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | General heating | Precise temperature uniformity |
| Temperature Profile | Gradient (hot center, cooler ends) | Extended flat isothermal plateau |
| Control Complexity | Simple | Advanced (multi-loop controller) |
| Ideal For | Basic annealing, drying | Crystal growth, calibration, semiconductor processing |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Need a furnace that guarantees precision? For sensitive applications like crystal growth or semiconductor fabrication, absolute temperature uniformity is non-negotiable. KINTEK's three-zone tube furnaces are engineered with advanced control systems to deliver the stable, extended isothermal plateau your research demands. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to perfectly match your unique experimental requirements. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of individually temperature-controlled zones in multi-zone furnaces? Unlock Precision Thermal Gradients
- How are multi zone tube furnaces applied in biomedical research? Unlock Advanced Biomaterial Engineering
- How does a multi-zone tube furnace achieve precise temperature gradient control? Master MoS2 Isotope Monolayer Synthesis
- What preparations are needed before starting a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safety and Accuracy in Your Lab
- How do multi zone tube furnaces improve laboratory efficiency? Boost Throughput with Parallel Processing



















